Dear Editor:
Fixed drug eruption (FDE) is a distinctive variant of drug-induced cutaneous reactions. It is characterized by recurrent erythematous or dusky red patches at the same sites each time the causative drug is administered.
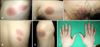
A 38-year-old Korean male presented with recurrent erythematous patches on the trunk and extremities. Multiple erythematous to dusky red, round to oval-shaped patches had appeared on the left chest, right back, suprapubic area, left knee, left upper inner arm, and fingers (Fig. 1). The subjective symptom was mild pruritus. Headache presented one day before the skin lesions appeared. Two years prior, the patient had been taking sildenafil citrate 50 mg once or twice a month. He recalled about 20 similar episodes of skin lesions, located on the same sites over the two years. The patient also recalled that all episodes of skin eruptions were correlated with intake of sildenafil citrate. The lesions were revealed in two days to a week after taking the medicine.
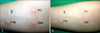
An intradermal test with sildenafil citrate at concentrations of 25 mg/ml, 2.5 mg/ml and 1.25 mg/ml showed positive results at 10 minutes and 1 hour (Fig. 2). We did biopsy the lesion site on the back (Fig. 1B). The histopathological findings showed superficial perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrations and melanin deposits in the upper dermis, consistent with FDE (Supplementary Fig. 1). Based on the patient's history, clinical findings and histological findings, we diagnosed FDE caused by sildenafil citrate. The patient was advised to avoid sildenafil citrate and successfully relieved of skin lesions through systemic and topical corticosteroids.
Sildenafil is one of the inhibitors of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5). Oral inhibitors of PDE5 including sildenafil and tadalafil are considered the first-line therapies for erectile dysfunction. The common adverse events of sildenafil are headache, vasodilation, rhinitis, flushing, and dizziness. Dermatitis are uncommon adverse events of sildenafil. FDE induced by PDE5 inhibitors has been rarely documented. Only one case of non-pigmenting mucosal FDE due to sildenafil and four cases of FDE, which symptoms include multiple mucocutaneous erythema fixum, blister on the glans penis and erosion on the tongue, due to tadalafil have been reported in the English literature1234.
We report the present case as the second case of FDE induced by sildenafil citrate. Skin tests including prick and intradermal tests, patch test, and oral challenge test with suspected drugs may be useful in confirming the diagnosis of FDE. In the present case, there was obvious clinical correlation between sildenafil intake and typical recurrent cutaneous lesions, and the intradermal test with sildenafil produced positive results. And lesional patch test results confirmed the clinical suspicion of culprit drug, but the lack of sensitivity is a major limitation5. Therefore, we did not perform a patch test and oral challenge or provocation test with sildenafil citrate. We recommend that physicians assessing a patient presenting with drug eruptions, especially healthy men, should consider a thorough personal history of lifestyle drugs including PDE5 inhibitors.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Ghosh SK, Bandyopadhyay D. Nonpigmenting mucosal fixed drug eruption due to sildenafil citrate. J Sex Med. 2009; 6:3500–3501.
2. Beach RA, Murphy F, Vender RB. Cutaneous reaction to drugs used for erectile dysfunction: case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Med Surg. 2006; 10:128–130.

3. Bjekic M, Markovic M, Sipetic S. Fixed drug eruption caused by tadalafil--case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013; 88:617–619.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary data can be found via http://anndermatol.org/src/sm/ad-29-247-s001.pdf.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download