Abstract
Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test employing whole virus antigen is a prescribed serological test for serotyping, diagnosis and surveillance for avian paramyxoviruses (APMVs). For use as alternative to the virus antigen, hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) protein gene of the wild duck isolate APMV-6/WB12-163FS of APMV serotype 6 (APMV-6) was amplified, cloned and expressed in Spodoptera frugiperda insect cells. The HN gene of 1,842 bps in length showed nucleotide and amino acid homology of 93.4% and 97.1%, respectively with that of APMV-6 prototype strain. Putative sialic acid binding motif and potential N-linked glycosylation sites were conserved. In Western blot analysis, the expressed protein had a molecular mass of 66 kDa and reacted specifically with antiserum to APMV-6. In addition, the recombinant HN protein showed biological properties such as hemagglutination (HA) and elution. The recombinant HN protein produced from infected cells showed high HA titers (approximately 213 HA unit/ml). The HA activity of the recombinant HN protein was inhibited by antisera to APMV-6. In cross HA inhibition test, the recombinant HN protein had the highest titers with antisera to homologous APMV serotype, although there was weak cross reaction with some of antisera to other APMV serotypes. Our results indicated that recombinant APMV-6 HN protein would have the potential as alternative to the APMV-6 antigen in HI assays.
REFERENCES
1). Alexander DJ. Newcastle disease and other avian paramyxoviridae infections. Calnek BW, editor. Diseases of Poultry. 10th ed.IOWA: Iowa state university press;1997. p. 541–69.
2). Miller PJ, Afonso CL, Spackman E, Scott MA, Pedersen JC, Senne DA, et al. Evidence for a new avian paramyxovirus serotype 10 detected in rockhopper penguins from the Falkland Islands. J Virol. 2010; 84:11496–504.

3). Briand FX, Henry A, Massin P, Jestin V. Complete genome sequence of a novel avian paramyxovirus. J Virol. 2012; 86:7710.

4). Terregino C, Aldous EW, Heidari A, Fuller CM, De Nardi R, Manvell RJ, et al. Antigenic and genetic analyses of isolate APMV/wigeon/Italy/3920-1/2005 indicate that it represents a new avian paramyxovirus (APMV-12). Arch Virol. 2013; 158:2233–43.

5). Warke A, Stallknecht D, Williams SM, Pritchard N, Mundt E. Comparative study on the pathogenicity and immunogenicity of wild bird isolates of avian paramyxovirus 2, 4, and 6 in chickens. Avian Pathol. 2008; 37:429–34.

6). Warke A, Appleby L, Mundt E. Prevalence of antibodies to different avian paramyxoviruses in commercial poultry in the United States. Avian Dis. 2008; 52:694–7.

7). Zhang GZ, Zhao JX, Wang M. Serological survey on prevalence of antibodies to avian paramyxovirus serotype 2 in China. Avian Dis. 2007; 51:137–9.

8). Chang PC, Hsieh ML, Shien JH, Graham DA, Lee MS, Shieh HK. Complete nucleotide sequence of avian paramyxovirus type 6 isolated from ducks. J Gen Virol. 2001; 82:2157–68.

9). Xiao S, Subbiah M, Kumar S, De Nardi R, Terregino C, Collins PL, et al. Complete genome sequences of avian paramyxovirus serotype 6 prototype strain Hong Kong and a recent novel strain from Italy: evidence for the existence of subgroups within the serotype. Virus Res. 2010; 150:61–72.

10). Schaper UM, Fuller FJ, Ward MD, Mehrotra Y, Stone HO, Stripp BR, et al. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope protein genes of a highly virulent, neurotropic strain of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1988; 165:291–5.

11). Nagy E, Derbyshire JB, Dobos P, Krell PJ. Cloning and expression of NDV hemagglutinin-neuraminidase cDNA in a baculovirus expression vector system. Virology. 1990; 176:426–38.

12). Lee YJ, Sung HW, Choi JG, Lee EK, Yoon H, Kim JH, et al. Protection of chickens from Newcastle disease with a recombinant baculovirus subunit vaccine expressing the fusion and hemagglutininneuraminidase proteins. J Vet Sci. 2008; 9:301–8.

13). Choi KS, Kye SJ, Jeon WJ, Park MJ, Kim S, Seul HJ, et al. Preparation and diagnostic utility of a hemagglutination inhibition test antigen derived from the baculovirus-expressed hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein gene of Newcastle disease virus. J Vet Sci. 2013; 14:291–7.

14). Spalatin J, Hanson RP, Beard PD. The hemagglutination-elution pattern as a marker in characterizing Newcastle disease virus. Avian Dis. 1970; 14:542–9.

15). Lee EK, Jeon WJ, Kwon JH, Yang CB, Choi KS. Molecular epidemiological investigation of Newcastle disease virus from domestic ducks in Korea. Vet Microbiol. 2009; 134:241–8.

16). Choi KS, Kye SJ, Kim JY, Seul HJ, Lee HS, Kwon HM, et al. Baculovirus expression of the avian paramyxovirus 2 HN gene for diagnostic applications. J Virol Methods. 2014; 198:12–7.

17). OIE (World Organisation for Animal Health). Newcastle disease. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals (Mammals, Birds and Bees), standards for diagnostic tests and vaccines. 7th ed.Paris: OIE;2012. p. 555–73.
18). Park MJ, Kye SJ, Kim JY, Kim S, Seul HJ, Park CK, et al. Generation and biological characterization of a neutralization-resistant mutant of Newcastle disease virus. J Bacteriol Virol. 2012; 42:330–8.

19). Saif YM, Mohan R, Ward L, Senne DA, Panigrahy B, Dearth RN. Natural and experimental infection of turkeys with avian paramyxovirus-7. Avian Dis. 1997; 41:326–9.

20). Shortridge KF, Alexander DJ, Collins MS. Isolation and properties of viruses from poultry in Hong Kong which represent a new (sixth) distinct group of avian paramyxoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1980; 49:255–62.

Figure 1.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of recombinant plasmids digested with restriction enzymes of EcoR I and Hind III. M, DNA marker; Lane 1, pCR/APMV6HN; lane 2, pFB/APMV6HN.
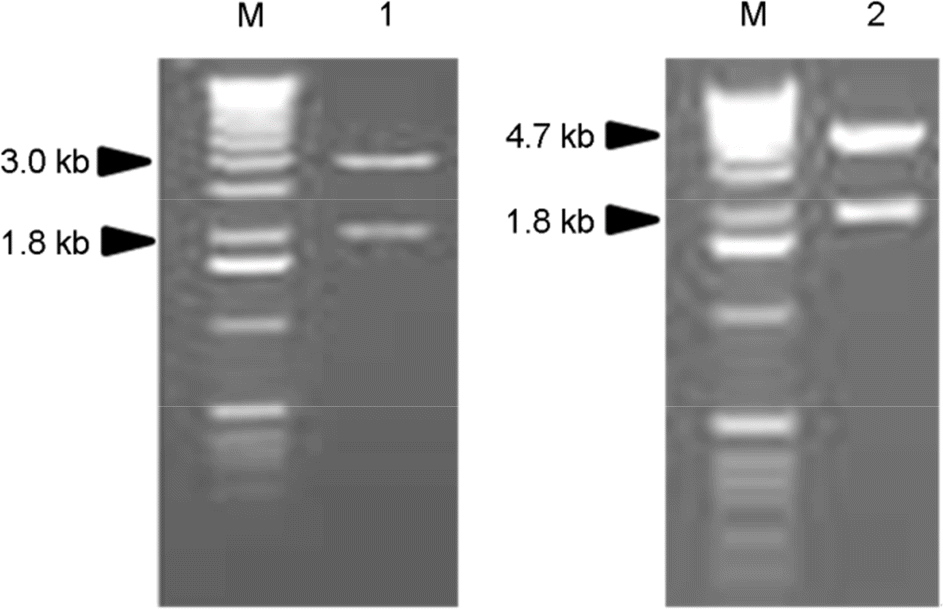
Figure 2.
Predicted amino acid sequence of HN protein gene of APMV-6/WB12-163FS and comparison with APMV-6 prototype strain (APMV-6/duck/Hong Kong/199/77). Black dot (●) represents putative N-linked glycosylation site. Putative sialic acid binding motif was expressed in a box.

Figure 3.
Western blot analisis of recombinant APMV-6 HN protein using APMV-6 reference antiserum. P. protein markar; lane 1, SPF ECE fluid; lane 2, normal Sf9 cell lysate; lane 3, APMV-6/WB12-163Fs; lane 4, rAPMV-6 HN. Allow represents HN protein of APMV-6.
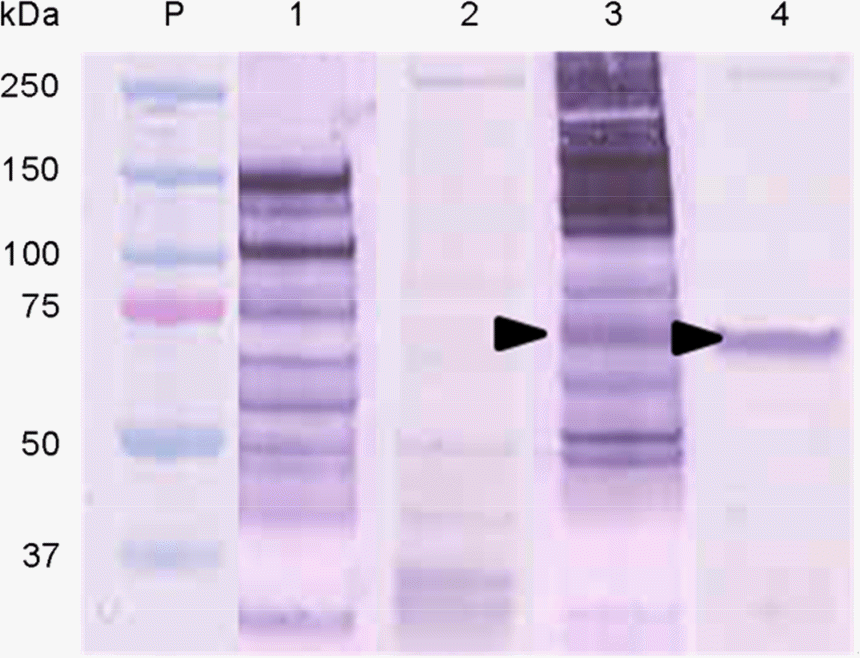
Table 1.
Heat stability and hemagglutination elution pattern of th rAPMV-6 HN protein
| HA titeer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat treatmenta | Incubation at 4°C | |||
| Before | After | 1 h | 24h | |
| APMV-6b | 256 | 128 | 256 | 256 |
| rAPMV6 HN | 256 | 4 | 256 | 256 |
Table 2.
Results of cross HI test using recombinant APMV-6 HN protein and representative APMV serotypes
| Antiserum | Antigen | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rAPMV-6HN | APMV-1 | APMV-2 | APMV-3 | APMV-4 | APMV-6 | 163FSc | APMV-7 | APMV-8 | APMV-9 | |
| rAPMV-6 HN | 256a | 2 | 8 | <2 | 2 | 256 | 256 | 2 | 4 | <2 |
| APMV-1 | <2 | 128 | NTb | NT | NT | <2 | <2 | NT | NT | NT |
| APMV-2 | <2 | NT | 512 | NT | NT | 8 | 32 | NT | NT | NT |
| APMV-3 | <2 | NT | NT | 512 | NT | 16 | <2 | NT | NT | NT |
| APMV-4 | <2 | NT | NT | NT | 32 | <2 | <2 | NT | NT | NT |
| APMV-6 | 128 | <2 | 16 | <2 | <2 | 512 | 64 | 4 | 2 | <2 |
| 163FS | 512 | 8 | 32 | 16 | 2 | 1024 | 256 | 8 | 16 | 2 |
| APMV-7 | 16 | NT | NT | NT | NT | <2 | 16 | 256 | NT | NT |
| APMV-8 | <2 | NT | NT | NT | NT | 2 | 4 | NT | 256 | NT |
| APMV-9 | <2 | NT | NT | NT | NT | 8 | 8 | NT | NT | 256 |
| Negative serum | <2 | <2 | <2 | <2 | <2 | <2 | <2 | <2 | <2 | <2 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download