Abstract
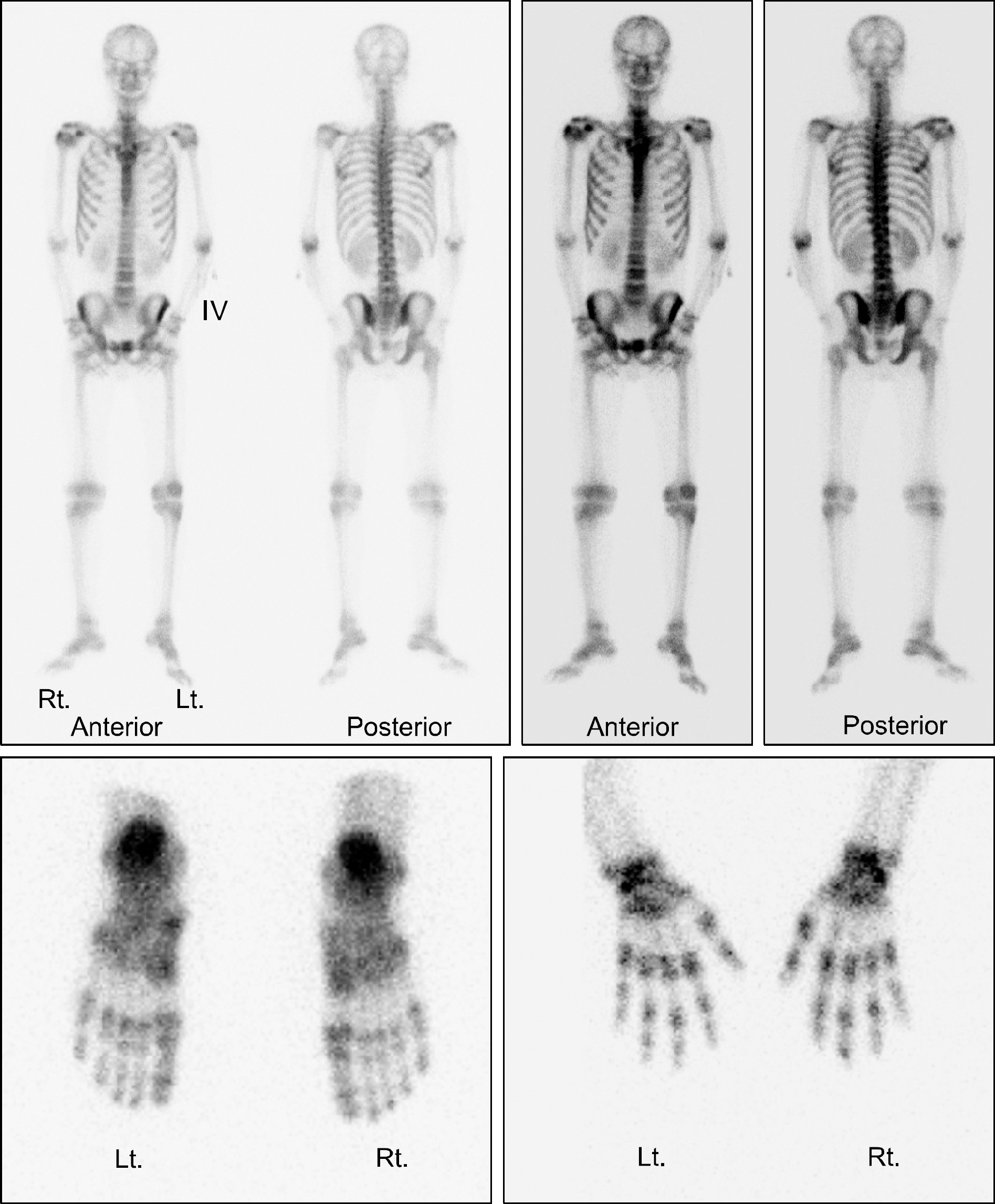
Hepatitis viruses (hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus) have been associated with development of inflammatory arthritis. Approximately 400 million people worldwide have chronic HBV infection. HBV infection is the one of the most common causes of liver disease, and the prevalence of HBV infection in Korea is almost 6%. Arthritis in patients with HBV can be encountered in two settings: as a rheumatoid arthritis (RA)-like, acute, self-limited polyarthritis during the pre-symptomatic phase of acute hepatitis B, or, more rarely, as arthritis oc-curring in the context of HBV-associated polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). In both cases, the pathogenesis of arthritis is attributed to the deposition of immune complexes containing viral antigens (HBsAg or HBeAg) and their respective antibodies (anti-HBs and anti-HBe) in synovial tissues. Here we report on a case of polyarthritis associated with reactivation of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with a review of the literature.
References
1. Vassilopoulos D, Calabrese LH. Virally associated arthritis 2008: clinical, epidemiologic, and pathophysiologic considerations. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008; 10:215.

2. Kwon SY, Lee CH. Epidemiology and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection. Korean J Hepatol. 2011; 17:87–95.

4. Vassilopoulos D, Manolakopoulos S. Rheumatic manifestations of hepatitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010; 22:91–6.

6. Aydeniz A, Namiduru M, Karaoglan I, Altindag O, Yagiz E, Gursoy S. Rheumatic manifestations of hepatitis B and C and their association with viral load and fibrosis of the liver. Rheumatol Int. 2010; 30:515–7.

7. Siegel LB, Gall EP. Viral infection as a cause of arthritis. Am Fam Physician. 1996; 54:2009–15.
8. Inman RD. Rheumatic manifestations of hepatitis B virus infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1982; 11:406–20.

9. Willson RA. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic viral hepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:4–16.
10. Bae SK, Song JS, Park W. Musculoskeletal manifestations and factors elevating hepatic enzyme in patients with hepatitis B and C viral infection. Korean Journal of Medicine. 2001; 60:32–9.
11. Wands JR, Mann E, Alpert E, Isselbacher KJ. The pathogenesis of arthritis associated with acute hepatitis-B sur-face antigen-positive hepatitis. Complement activation and characterization of circulating immune complexes. J Clin Invest. 1975; 55:930–6.

12. Csepregi A, Nemesanszky E, Rojkovich B, Poor G. Rheumatoid arthritis and hepatitis B virus: evaluating the pathogenic link. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28:474–7.
13. Csepregi A, Rojkovich B, Nemesánszky E, Poór G, Héjjas M, Horányi M. Chronic seropositive polyarthritis associated with hepatitis B virus-induced chronic liver disease: a sequel of virus persistence. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:232–3.

14. Lee JH, Kim M, Lee JS, Chang SH, Yoon BY, Lee YW. A case of rheumatoid arthritis and cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa in chronic hepatitis B with acute exacerbation. Inje Medical Journal. 2009; 30:69–76.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download