Abstract
Objective
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in many biological processes and recent studies have provided growing evidences that miRNA dysregulation might play important roles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The aim of this study was to investigate the contribution of miRNAs to altered gene expressions in RA.
Methods
To investigate whether the differential expression of miRNA in RA could account for the altered expression of certain genes, we compared the different expressions of miRNAs and mRNAs in rheumatoid synovial fluid monocytes with that of normal peripheral blood (PB) monocytes by using a gene expression oligonucleotide microarray and a microRNA microarray.
Results
Comparative analysis of the mRNA profiles showed significant different expressions of 430 genes in RA synovial monocytes, of which 303 (70%) were upregulated and 127 (30%) were downregulated, as compared with that of normal PB monocytes. Out of differentially expressed 13 miRNAs, 9 miRNAs were upregulated and 4 miRNAs were downregulated in the RA synovial monocytes. A total of 62 genes were predicted as target genes of the 13 differentially expressed miRNAs in the RA synovial monocytes. Among the 62 miRNA-targeted genes, a few genes such as GSTM1, VIPR1, PADI4, CDA, IL21R, CCL5, IL7R, STAT4, HTRA1 and IL18BP have been reported to be associated with RA.
References
1. Sonkoly E, Pivarcsi A. Advances in microRNAs: implications for immunity and inflammatory diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13:24–38.

3. Brennan FM, McInnes IB. Evidence that cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118:3537–45.

4. Jing Q, Huang S, Guth S, Zarubin T, Motoyama A, Chen J, et al. Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich ele-ment-mediated mRNA instability. Cell. 2005; 120:623–34.

5. Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean S, Dumitru CD, Adair B, et al. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to en-dotoxin shock. J Immunol. 2007; 179:5082–9.
6. Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:12481–6.
7. Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Okubo A, Hashimoto M, Nishida K, Ochi M, et al. Expression of microRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:1284–92.

8. Stanczyk J, Pedrioli DM, Brentano F, Sanchez-Pernaute O, Kolling C, Gay RE, et al. Altered expression of MicroRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:1001–9.

9. Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL, Bubb MR, Reeves WH, Chan EK. Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008; 10:R101.

10. Berezikov E, Thuemmler F, van Laake LW, Kondova I, Bontrop R, Cuppen E, et al. Diversity of microRNAs in human and chimpanzee brain. Nat Genet. 2006; 38:1375–7.

11. Thomas PD, Campbell MJ, Kejariwal A, Mi H, Karlak B, Daverman R, et al. PANTHER: a library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res. 2003; 13:2129–41.

12. Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature. 2008; 455:64–71.

13. Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 2008; 455:58–63.

14. Mattey DL, Hassell AB, Plant M, Dawes PT, Ollier WR, Jones PW, et al. Association of polymorphism in glutathione S-transferase loci with susceptibility and outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with the shared epitope. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999; 58:164–8.

15. Yun BR, El-Sohemy A, Cornelis MC, Bae SC. Glutathione S-transferase M1, T1, and P1 genotypes and rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2005; 32:992–7.
16. Delgado M, Robledo G, Rueda B, Varela N, O'Valle F, Hernandez-Cortes P, et al. Genetic association of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor with rheumatoid arthritis: altered expression and signal in immune cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:1010–9.

17. Juarranz Y, Gutié rrez-Cañas I, Santiago B, Carrión M, Pablos JL, Gomariz RP. Differential expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide and its functional receptors in human osteoarthritic and rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:1086–95.

18. Anzilotti C, Pratesi F, Tommasi C, Migliorini P. Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 and citrullination in health and disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2010; 9:158–60.

19. Proost P, Loos T, Mortier A, Schutyser E, Gouwy M, Noppen S, et al. Citrullination of CXCL8 by peptidylarginine deiminase alters receptor usage, prevents proteolysis, and dampens tissue inflammation. J Exp Med. 2008; 205:2085–97.

20. Paira S, Roverano S, Rillo O, Barrionuevo A, Mahieu S, Millen N. Cytidine deaminase in polymyalgia rheumatica and elderly onset rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2005; 24:460–3.

21. Jüngel A, Distler JH, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Seemayer CA, Seibl R, Forster A, et al. Expression of interleukin-21 receptor, but not interleukin-21, in synovial fibroblasts and synovial macrophages of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:1468–76.

22. Li J, Shen W, Kong K, Liu Z. Interleukin-21 induces T-cell activation and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 2006; 64:515–22.

23. Stanczyk J, Kowalski ML, Grzegorczyk J, Szkudlinska B, Jarzebska M, Marciniak M, et al. RANTES and chemo-tactic activity in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2005; 2005; 343–8.

24. Hartgring SA, van Roon JA, Wenting-van Wijk M, Jacobs KM, Jahangier ZN, Willis CR, et al. Elevated expression of interleukin-7 receptor in inflamed joints mediates interleukin-7-induced immune activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:2595–605.

25. Walker JG, Ahern MJ, Coleman M, Weedon H, Papangelis V, Beroukas D, et al. Expression of Jak3, STAT1, STAT4, and STAT6 in inflammatory arthritis: unique Jak3 and STAT4 expression in dendritic cells in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:149–56.

26. Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW, et al. STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:977–86.
27. Grau S, Richards PJ, Kerr B, Hughes C, Caterson B, Williams AS, et al. The role of human HtrA1 in arthritic disease. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:6124–9.

28. Bresnihan B, Roux-Lombard P, Murphy E, Kane D, FitzGerald O, Dayer JM. Serum interleukin 18 and interleukin 18 binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:726–9.

29. Ji JD, Lee WJ, Kong KA, Woo JH, Choi SJ, Lee YH, et al. Association of STAT4 polymorphism with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 2010; 37:141–7.

30. Nakamachi Y, Kawano S, Takenokuchi M, Nishimura K, Sakai Y, Chin T, et al. MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:1294–304.

31. Alsaleh G, Suffert G, Semaan N, Juncker T, Frenzel L, Gottenberg JE, et al. Bruton's tyrosine kinase is involved in miR-346-related regulation of IL-18 release by lip-opolysaccharide-activated rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Immunol. 2009; 182:5088–97.

32. Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, et al. A mammalian microRNA expression at-las based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. 2007; 129:1401–14.

33. Ro S, Park C, Young D, Sanders KM, Yan W. Tissue-de-pendent paired expression of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:5944–53.

34. Chang X, Yamada R, Suzuki A, Sawada T, Yoshino S, Tokuhiro S, et al. Localization of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) and citrullinated protein in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:40–50.

35. Harney SM, Meisel C, Sims AM, Woon PY, Wordsworth BP, Brown MA. Genetic and genomic studies of PADI4 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:869–72.

36. Chang X, Zhao Y, Sun S, Zhang Y, Zhu Y. The expression of PADI4 in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2009; 29:1411–6.

37. Loos T, Mortier A, Gouwy M, Ronsse I, Put W, Lenaerts JP, et al. Citrullination of CXCL10 and CXCL11 by peptidylarginine deiminase: a naturally occurring posttranslational modification of chemokines and new dimension of immunoregulation. Blood. 2008; 112:2648–56.

38. Xu X, Hsu HC, Chen J, Grizzle WE, Chatham WW, Stockard CR, et al. Increased expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase is associated with anti-CCP and rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 2009; 70:309–16.

39. Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNAs and chromosomal ab-normalities in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2006; 25:6202–10.

Figure 1.
Hierarchical clustering of microRNA expression profile between RA synovial monocytes (RA1-RA6) and normal PB monocytes.
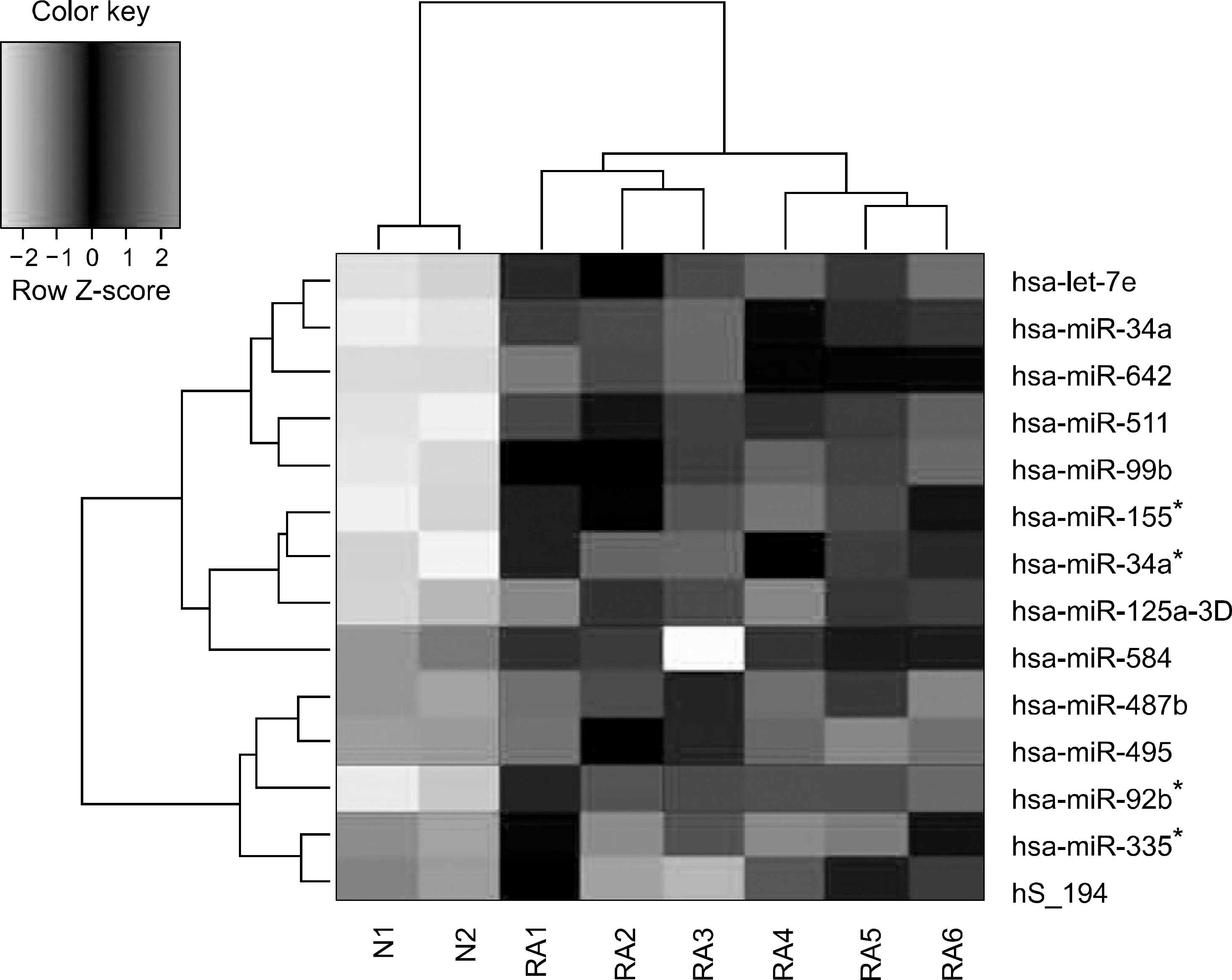
Figure 2.
Validation of the differentially expressed genes and miRNAs in the RA synovial monocytes. The array data for mRNAs (A) and miRNAs (B) was validated by performing quantitative real-time PCR on the normal peripheral blood monocytes from four healthy donors and the rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid monocytes from twelve patients (RA1-RA12). The data is shown as means± SD. ∗p<0.05.
Table 1.
Clinical and demographic features of the study patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Table 2.
Inverse relationship between microRNA and the target mRNA expression identified in the RA synovial monocytes (upregulated microRNAs)
Table 3.
Inverse relationship between microRNA and the target mRNA expression identified in RA synovial monocytes (downregulated microRNAs)
Table 4.
Roles of the differentially expressed mRNAs in the RA synovial monocytes




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download