Abstract
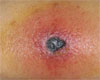
Invasive aspergillosis (IA) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with hematological malignancies. While the development of new effective antifungals and advancement of diagnostic techniques have lead to improved outcomes, relapse of IA in patients with subsequent immunosuppression is emerging as a major issue. The primary IA site is the most common relapse site, but disseminated infection from the lung to multiple organs, including the brain, thyroid, liver, spleen, kidney, bone, heart valve, and skin, can often occur in patients with severe immunosuppression. Furthermore, relapsing or disseminated IA have very poor outcomes. We report a case of disseminated IA presenting as multiple cutaneous lesions without involvement of any other organs in an acute leukemia patient. The patient had suffered from prior invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, which was treated successfully. The multiple skin lesions were fully resolved after antifungal therapy for 6 weeks.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 2005. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;3495.
2. Maschmeyer G, Haas A, Cornely OA. Invasive aspergillosis: epidemiology, diagnosis and management in immunocompromised patients. Drugs. 2007. 67:1567–1601.
3. Lass-Flörl C. The changing face of epidemiology of invasive fungal diseases in Europe. Mycoses. 2009. 52:197–205.
4. Yoo JH, Choi JH, Lee DG, Choi S, Shin WS, Kim CC. Analysis of invasive fungal infection after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or chemotherapy in patients with hematologic diseases. Infect Chemother. 2004. 36:40–45.
5. Lin SJ, Schranz J, Teutsch SM. Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32:358–366.

6. Park SH, Choi SM, Lee DG, Choi JH, Yoo JH, Lee JW, Min WS, Shin WS, Kim CC. Current trends of infectious complications following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a single center. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:199–207.

8. Seo JK, Chun JS, Seol JE, Choi JH, Hwang SW, Sung HS, Lee D. A case of invasive aspergillosis with skin involvement in a renal transplant recipient. Korean J Dermatol. 2009. 47:1190–1192.
9. Park JH, Lee YJ, Park SH, Choi SY, Lee MS, Kim JH, Park SK. Disseminated aspergillosis with cutaneous aspergillosis and aspergergillus thyroiditis in a renal allograft recipient. Korean J Med. 2001. 60:85–91.
10. Kim YS, Kim SM, Peck KR, Cho SU, Shin HS, Bae HJ, Woo JH, Song YW, Choe GW. Clinical study on invasive aspergillosis. Korean J Intern Med. 1990. 38:526–538.
11. D'Antonio D, Pagano L, Girmenia C, Parruti G, Mele L, Candoni A, Ricci P, Martino P. Cutaneous aspergillosis in patients with haematological malignancies. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000. 19:362–365.
12. Hope WW, Walsh TJ, Denning DW. The invasive and saprophytic syndromes due to Aspergillus spp. Med Mycol. 2005. 43:Suppl 1. 207–238.

13. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, Pappas PG, Maertens J, Lortholary O, Kauffman CA, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Maschmeyer G, Bille J, Dismukes WE, Herbrecht R, Hope WW, Kibbler CC, Kullberg BJ, Marr KA, Muñoz P, Odds FC, Perfect JR, Restrepo A, Ruhnke M, Segal BH, Sobel JD, Sorrell TC, Viscoli C, Wingard JR, Zaoutis T, Bennett JE. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infect ions Cooperative Group. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for research and treatment of cancer/invasive fungal infections cooperative group and the national institute of allergy and infectious diseases mycoses study group (EORTC/MSG) consensus group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:1813–1821.

14. Cornely OA, Böhme A, Reichert D, Reuter S, Maschmeyer G, Maertens J, Buchheidt D, Paluszewska M, Arenz D, Bethe U, Effelsberg J, Lövenich H, Sieniawski M, Haas A, Einsele H, Eimermacher H, Martino R, Silling G, Hahn M, Wacker S, Ullmann AJ, Karthaus M; Multinational Case Registry of the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the German Society for Hematology and Oncology. Risk factors for breakthrough invasive fungal infection during secondary prophylaxis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008. 61:939–946.

15. Sipsas NV, Kontoyiannis DP. Clinical issues regarding relapsing aspergillosis and the eff icacy of secondary antifungal prophylaxis in patients with hematological malignancies. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42:1584–1591.

16. Upton A, Kirby KA, Carpenter P, Boeckh M, Marr KA. Invasive aspergillosis following hematopoietic cell transplantation: outcomes and prognostic factors associated with mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:531–540.

17. Fukuda T, Boeckh M, Guthrie KA, Mattson DK, Owens S, Wald A, Sandmaier BM, Corey L, Storb RF, Marr KA. Invasive aspergillosis before allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: 10-year experience at a single transplant center. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004. 10:494–503.

18. Offner F, Cordonnier C, Ljungman P, Prentice HG, Engelhard D, De Bacquer D, Meunier F, De Pauw B. Impact of previous aspergillosis on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 1998. 26:1098–1103.

19. Bae KS, Park JY, Shin SY, Mun YC, Choi HJ, Cho MS, Seong CM. Disseminated aspergillosis following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in an acute leukemic patient who was previously treated for invasive aspergillosis. Infect Chemother. 2003. 35:221–225.
20. Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, Morrison VA, Segal BH, Steinbach WJ, Stevens DA, van Burik JA, Wingard JR, Patterson TF. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Treatment of aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:327–360.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download