INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Samples and patient information
2. Immunohistochemistry
3. Evaluation of specimens
RESULTS
Table 1
Patients' profile of this study

Table 2
Relationship of patients' age and serum E2 values

| Variables | <50 years old (n=14) | ≥50 years old (n=16) |
|---|---|---|
| E2<30 pg/mL | 8 | 2 |
| E2≥30 pg/mL | 4 | 7 |
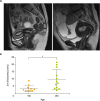 | Fig. 1Endometrial thickness. (A) Magnetic resonance imaging of representative cases (T2 weighted images, sagittal sections). Left: 34-year-old woman whose serum E2 level was 16.8 pg/mL with an endometrial thickness of 8.69 mm. Right: 71-year-old woman whose serum E2 level was 81.4 pg/mL with an endometrial thickness of 21.70 mm. (B) Differences in the endometrial thickness between patients under and over 50 years of age. Data are presented as mean±SD.
E2, 17β-estradiol; Em, endometrial; SD, standard deviation.
*p<0.05 (Mann-Whitney test).
|
 | Fig. 2Inhibin α and P450 aromatase expression. Representative images of inhibin α and P450 aromatase expression as determined immunohistochemically.
H&E, hematoxylin and eosin staining (original magnification: ×40).
|
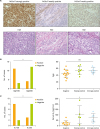 | Fig. 3Relationships between P450c17 expression and patient age and serum E2 levels. (A) Representative images of P450c17 expression. Samples are strongly positive (score 2) for P450c17 in luteinized cells (left upper), and weakly positive (score 1) for P450c17 in theca- or fibroblast-like cells (middle upper) and tumor cells (upper right), as determined by immunohistochemistry (original magnification: ×40). (B) Number of cases positive (score 1 or 2) or negative (score 0) for P450c17 among patients under and over 50 years of age (n=14 and 16, respectively). (C) Number of cases positive or negative for P450c17 among patients with serum E2 below or above 30 pg/mL (n=10 and 11, respectively).
E2, 17β-estradiol; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin staining; ns, not significant; P450c17, P450 17α-hydroxylase.
*p<0.05 (B, C: Fisher's exact test).
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download