Abstract
Materials and Methods:
This study involved nine ectopic thyroid cases (M: F=2: 7 å age range, 2 — 57 years) confirmed by RI thyroid scan between 1993 and 1997. We analyzed one neck ultrasonogram, five CT scans, three MR images, nine Tc-99m thyroid scans, and classified the ectopic thyroid by the basis of these findings. Hormonal abnormalities and symptoms were evaluated on the basis of medical records.
Results:
The status of nine patients was found to be euthyroid (n=6), hypothyroid (n二2) or hy- perthyroid (n=l). Among the nine, the ectopic thyroid was lingual (n=6), sublingual (n=3) or thyroglossal (n=l) å one patient had both the lingual and sublingual types. Ectopic thyroid was seen as a well-defined round mass, homogeneously enhanced on CT scan, homogeneously hypere- chogenic on ultrasonogram and of intermediate signal intense on MRI. All cases showed ectopic radioactivity uptake on Tc-99m thyroid scan. In eight patients, ectopic thyroid was the only hormone-producing thyroid tissue å one had both normal thyroia and ectopic thyroid tissue in a thyroglossal duct cyst. Among the six cases of euthyroidism, ectopic thyroid patients with the lingual type complained of throat discomfort. Those with the sublingual type complained of palpable neck mass, and preoperative evaluation of thyroglossal duct cyst showed that this was ectopic thyroia.
REFERENCES
1.Chanin LR., Greenberg LM. Pediatric upper airway obstruction due to ectopic thyroid. Laryngoscope. 1988. 98:422–427.

2.Hoyes AD., Kershaw DR. Anatomy and development of the thyroid gland. Ear Nose Throat J. 1985. 64:318–324.
3.Okstad S., Mair IWS., Sundsfjord JA., Eide TJ., Nordrum I. Ectopic thyroid tissue in the head and neck. J Otolaryngol. 1986. 15:52–55.
4.Zadvinskis DP., Benson MT., Som PM., Smoker WRK. Embryology and congenital cystic lesions. In:. Som PM, Curtin HD, editors. eds.Head and Neck Imaging. 3rd ed.St. Louis: Mosby;1996. p. 757–762.
6.Lim-Dunham JE., Feinstein KA., Yousefzadeh DK., Ben-Ami T. Sonographic demonstration of a normal thyroid gland excludes ectopic thyroid in patients with thyroglossal duct cyst. AJR. 1995. 164:1489–1491.

7.Wells RG., Sty JR., Duck SC. Technetium 99m pertechnetate thyroid scintigraphy: congenital hypothyroid screening. Pediatr Radiol. 1986. 16:368–373.

Fig. 1.
52-year-old man with neck mass Tc-99m thyroid scan shows smaller right thyroid in normal position with mild radioactivity uptake in above the isthmic portion of normal thyroid.
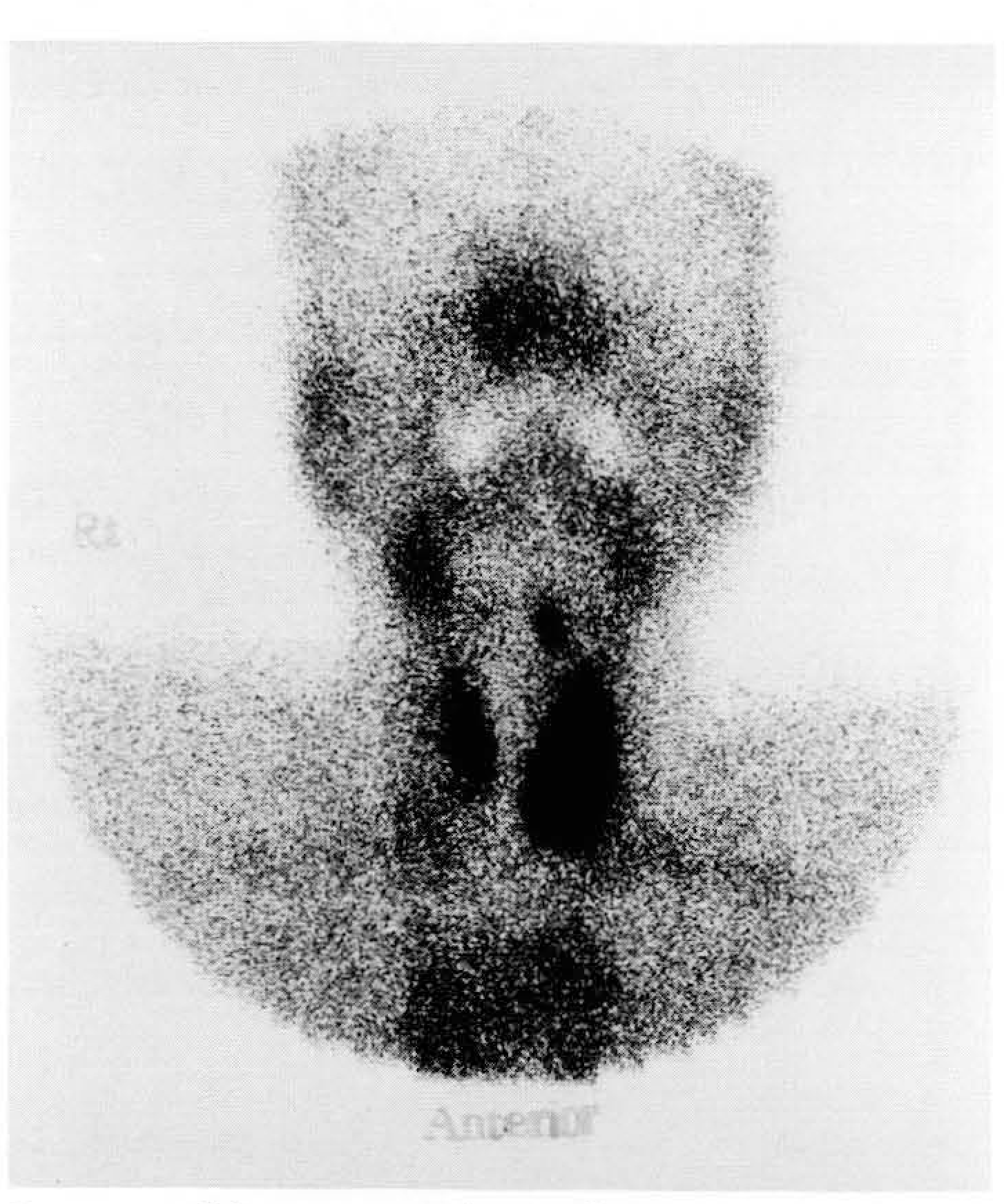
Fig. 2.
7-year-old girl with neck mass A. Ultrasonogram shows a well defined hyperechoic homogeneous mass (arrows) at sublingual site. B. Contrast enhanced CT scan shows a well defined oval shape mass in this site. C. Tc-99m thyroid scan shows radioactivity uptake at sublingual site and absence of uptake in normal thyroid position.
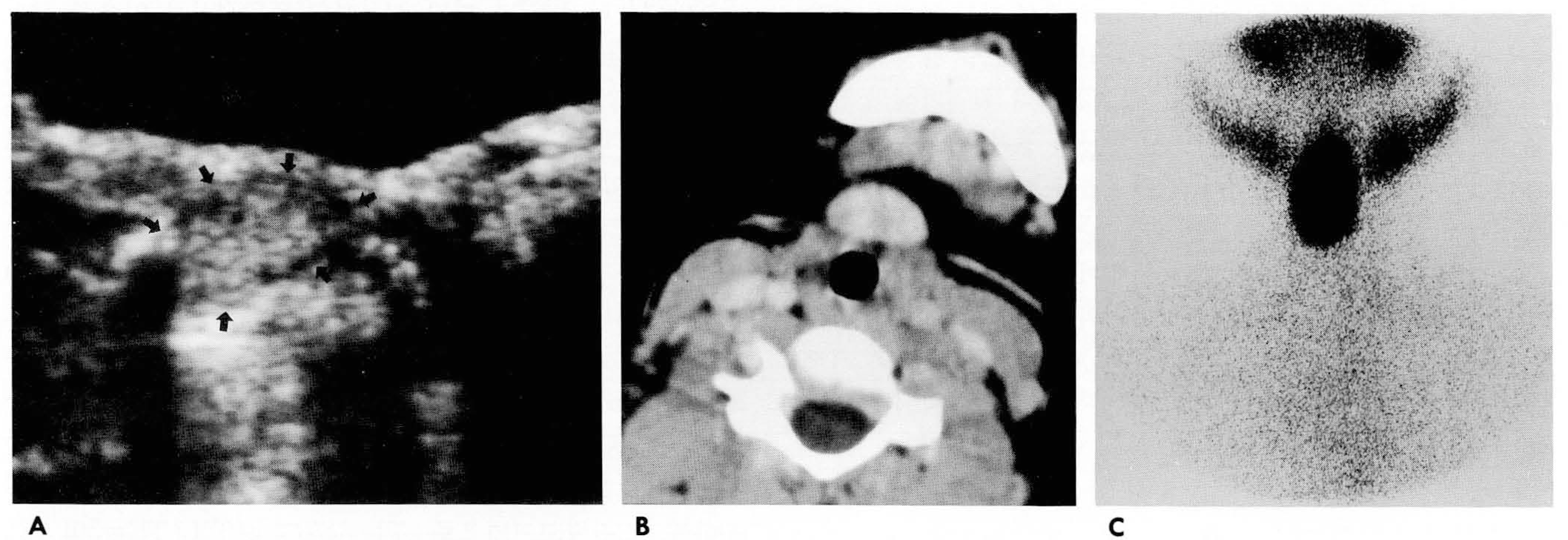
Fig. 3.
35-year-old woman with throat discomfort A. Contrast enhanced CT scan shows a well enhanced round mass at tongue base. B. The signal intensity of the mass is slightly higher than that of tongue muscle on Tl weighted MR image. C. The signal intensity of the mass is slightly higher than that of tongue muscle on T2 weighted MR image. D. Gadolinium-enhanced Tl weighted MR image shows mild peripheral enhancement of the mass.

Fig. 4.
12-year-old girl with neck mass A and B. Contrast enhanced CT scans show a well enhanced mass at tongue base (A) and another well enhanced mass at left submental area(B). C. Tc-99m thyroid scan shows two separate foci of radioactivity. Note absence of uptake in lower neck.

Table 1.
Summary of Nine Patients with Ectopic Thyroid Gland




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download