Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the association between retinal vascular caliber and cardiovascular risk factors including smoking, blood pressure, diabetes and age.
Methods
This study included 60 Korean male participants 40-69 years of age. The retinal vessel caliber was measured using computer-assisted fundus photography. Four vessels coursing through the area of one half disc diameter from the optic disc margin were measured. Additionally, we analyzed the association between the retinal vessel caliber and risk factors including smoking, diabetes, hypertension and age.
Results
Smoking was not significantly associated with retinal vessel calibers. The diabetes group showed larger average retinal vessel calibers than normal group, but veins were significantly wider (p < 0.05). The average retinal vessel caliber was wider and inferior vein and artery were significantly larger in the hypertension group (p < 0.05). Although the retinal vessel caliber increased with age, significance was observed only in the superior artery (p < 0.05).
References
1. Lombardo M, Parravano M, Serrao S, et al. Analysis of retinal ca-pillaries in patients with type 1 diabetes and nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy using adaptive optics imaging. Retina. 2013; 33:1630–9.

2. Muraoka Y, Tsujikawa A, Kumaqai K, et al. Age- and hypertension-dependent changes in retinal vessel diameter and wall thickness: an optical coherence tomography study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 156:706–14.

3. von Hanno T, Bertelsen G, Sjølie AK, Mathiesen EB. Retinal vascular calibres are significantly associated with cardiovascular risk factors: the Tromsø Eye Study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014; 92:40–6.

4. Yanagi M, Misumi M, Kawasaki R, et al. Is the association between smoking and the retinal venular diameter reversible following smoking cessation? Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014; 55:405–11.

5. Cheung CY, Lamoureux E, Ikram MK, et al. Retinal vascular geometry in Asian persons with diabetes and retinopathy. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012; 6:595–605.

6. Nguyen TT, Wang JJ, Sharrett AR, et al. Relationship of retinal vascular caliber with diabetes and retinopathy: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:544–9.
7. Avery CL, Kucharska-Newton A, Monda KL, et al. Impact of long-term measures of glucose and blood pressure on the retinal microvasculature. Atherosclerosis. 2012; 225:412–7.

8. Hubbard LD, Brothers RJ, King WN, et al. Methods for evaluation of retinal microvascular abnormalities associated with hypertension/sclerosis in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:2269–80.
9. Knudtson MD, Lee KE, Hubbard LD, et al. Revised formulas for summarizing retinal vessel diameters. Curr Eye Res. 2003; 27:143–9.

10. Ikram MK, de Jong FJ, Vingerling JR, et al. Are retinal arteriolar or venular diameters associated with markers for cardiovascular dis-orders? The Rotterdam Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:2129–34.

11. Wong TY, Islam FM, Klein R, et al. Retinal vascular caliber, cardiovascular risk factors, and inflammation: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:2341–50.

12. Jeganathan VS. Smokers’ veins: a useful clinical sign-comment. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2005; 33:675–6. author reply 676.
13. Wimpissinger B, Resch H, Berisha F, et al. Response of retinal blood flow to systemic hyperoxia in smokers and nonsmokers. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005; 243:646–52.

14. Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, et al. Retinal vascular caliber in persons with type 2 diabetes: the Wisconsin Epidemiological Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: XX. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1488–98.
15. Tikellis G, Wang JJ, Tapp R, et al. The relationship of retinal vascular calibre to diabetes and retinopathy: the Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle (AusDiab) study. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:2263–71.

16. Curtis TM, Gardiner TA, Stitt AW. Microvascular lesions of diabetic retinopathy: clues towards understanding pathogenesis? Eye (Lond). 2009; 23:1496–508.

17. Ikram MK, Ong YT, Cheung CY, Wong TY. Retinal vascular caliber measurements: clinical significance, current knowledge and future perspectives. Ophthalmologica. 2013; 229:125–36.

18. Liew G, Sharrett AR, Wang JJ, et al. Relative importance of systemic determinants of retinal arteriolar and venular caliber: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008; 126:1404–10.
19. Kawasaki R, Cheung N, Wang JJ, et al. Retinal vessel diameters and risk of hypertension: the Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J Hypertens. 2009; 27:2386–93.

20. Cheung N, Sharrett AR, Klein R, et al. Aortic distensibility and retinal arteriolar narrowing: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Hypertension. 2007; 50:617–22.
21. Smith W, Wang JJ, Wong TY, et al. Retinal arteriolar narrowing is associated with 5-year incident severe hypertension: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Hypertension. 2004; 44:442–7.
22. Hughes AD, Stanton AV, Jabbar AS, et al. Effect of antihypertensive treatment on retinal microvascular changes in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2008; 26:1703–7.

23. Leung H, Wang JJ, Rochtchina E, et al. Relationships between age, blood pressure, and retinal vessel diameters in an older population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:2900–4.

24. Sun C, Liew G, Wang JJ, et al. Retinal vascular caliber, blood pressure, and cardiovascular risk factors in an Asian population: the Singapore Malay Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:1784–90.

25. Lim LS, Cheung CY, Lin X, et al. Influence of refractive error and axial length on retinal vessel geometric characteristics. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:669–78.

26. Wong TY, Knudtson MD, Klein R, et al. Computer-assisted measurement of retinal vessel diameters in the Beaver Dam Eye Study: methodology, correlation between eyes, and effect of refractive errors. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:1183–90.
Figure 1.
The masurement of the retinal vessel caliber using computer-assisted method on fundus photography. Inferior and superior temporal veins and arteries coursing through the area of one half disc diameter from the optic disc margin were measured.
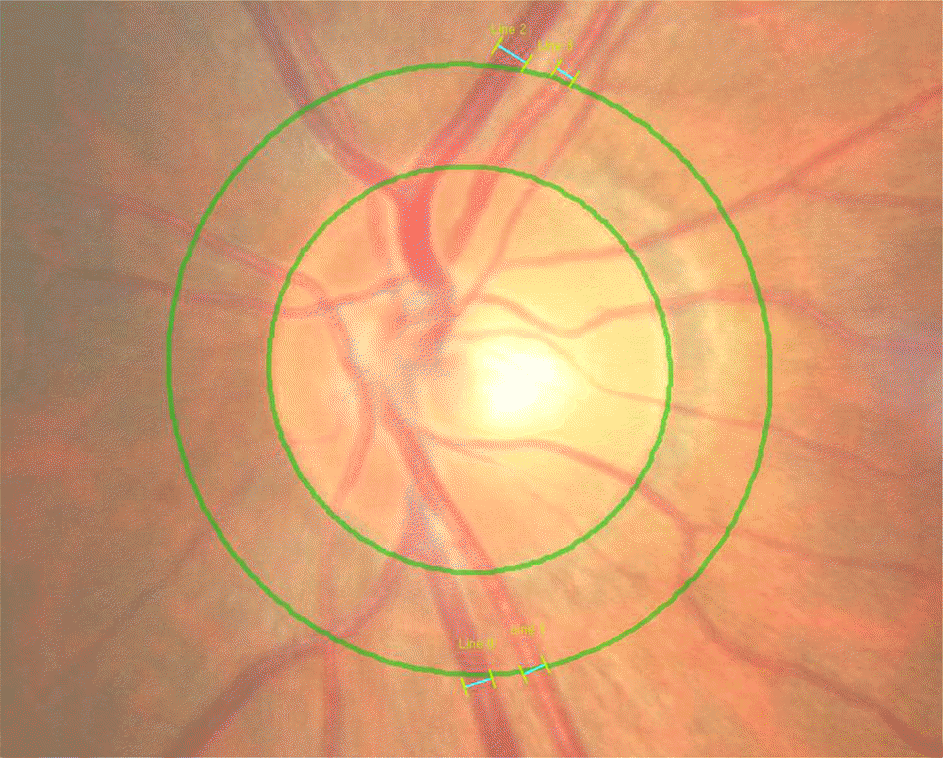
Table 1.
Patients demographics
Table 2.
The average data of the retinal vessel caliber by diseases (μ m)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download