Abstract
Olmesartan is an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and is widely used in clinical practice to treat hypertension. To compare the pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters and tolerability of two oral formulations of olmesartan (test drug: OMETAN® 20 mg tablet, reference drug: OLMETEC® 20 mg tablet) and assess their bioequivalence, a randomized, single dose, two-treatment crossover clinical study was conducted. At each period, 40 subjects received the test drug or the reference drug. Blood samples were collected at pre-dose and up to 48 h after study drug administration of each period. Plasma concentrations of olmesartan were measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. To evaluate PK profiles, maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve from zero to last measurable time (AUClast) were estimated using a non-compartmental method. Tolerability was evaluated based on the incidence of adverse events, vital signs, electrocardiograms, and laboratory tests. A total of 39 subjects completed the study. The geometric mean ratio and 90% confidence intervals (CI) of test drug to reference drug were 1.027 (0.969–1.088) for Cmax and 1.014 (0.957–1.074) for AUClast, respectively. There were no serious adverse events and both formulations of olmesartan were well tolerated. The OMETAN 20 mg tablet was judged to be bioequivalent to the OLMETEC 20 mg tablet.
Go to : 
References
1. von Bergmann K, Laeis P, Puchler K, Sudhop T, Schwocho LR, Gonzalez L. Olmesartan medoxomil: influence of age, renal and hepatic function on the pharmacokinetics of olmesartan medoxomil. J Hypertens Suppl. 2001; 19:S33–S40.

3. Jaques H. NICE guideline on hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2013; 34:406–408.
4. Greathouse M. A review of olmesartan medoxomil monotherapy: antihypertensive efficacy similar to that of other angiotensin II receptor blocker/hydrochlorothiazide combinations? Congest Heart Fail. 2002; 8:313–320.

5. Jiang J, Liu D, Hu P. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of olmesartan medoxomil in healthy Chinese subjects after single and multiple administrations. Pharmazie. 2009; 64:323–326.
6. Rozza F, Trimarco V, Izzo R, Santoro M, Manzi MV, Marino M, et al. Antihypertensive response to combination of olmesartan and amlodipine does not depend on method and time of drug administration. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2013; 20:25–32.

7. Domjan A, Kakuk P, Sandor J. The Helsinki Declaration at 50 years: comments on the 2013 modifications. Lege Artis Med. 2014; 24:152–158.
8. Jemal M. High-throughput quantitative bioanalysis by LC/MS/MS. Biomed Chromatogr. 2000; 14:422–429.

11. Yoshihara K, Gao Y, Shiga H, Wada DR, Hisaoka M. Population pharmacokinetics of olmesartan following oral administration of its prodrug, olmesartan medoxomil: in healthy volunteers and hypertensive patients. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005; 44:1329–1342.
12. Johns EJ. The neural regulation of the kidney in hypertension and renal failure. Exp Physiol. 2014; 99:289–294.

13. Monhart V. Hypertension and chronic renal insufficiency-chronic kidney failure. Vnitr Lek. 2003; 49:388–394.
Go to : 
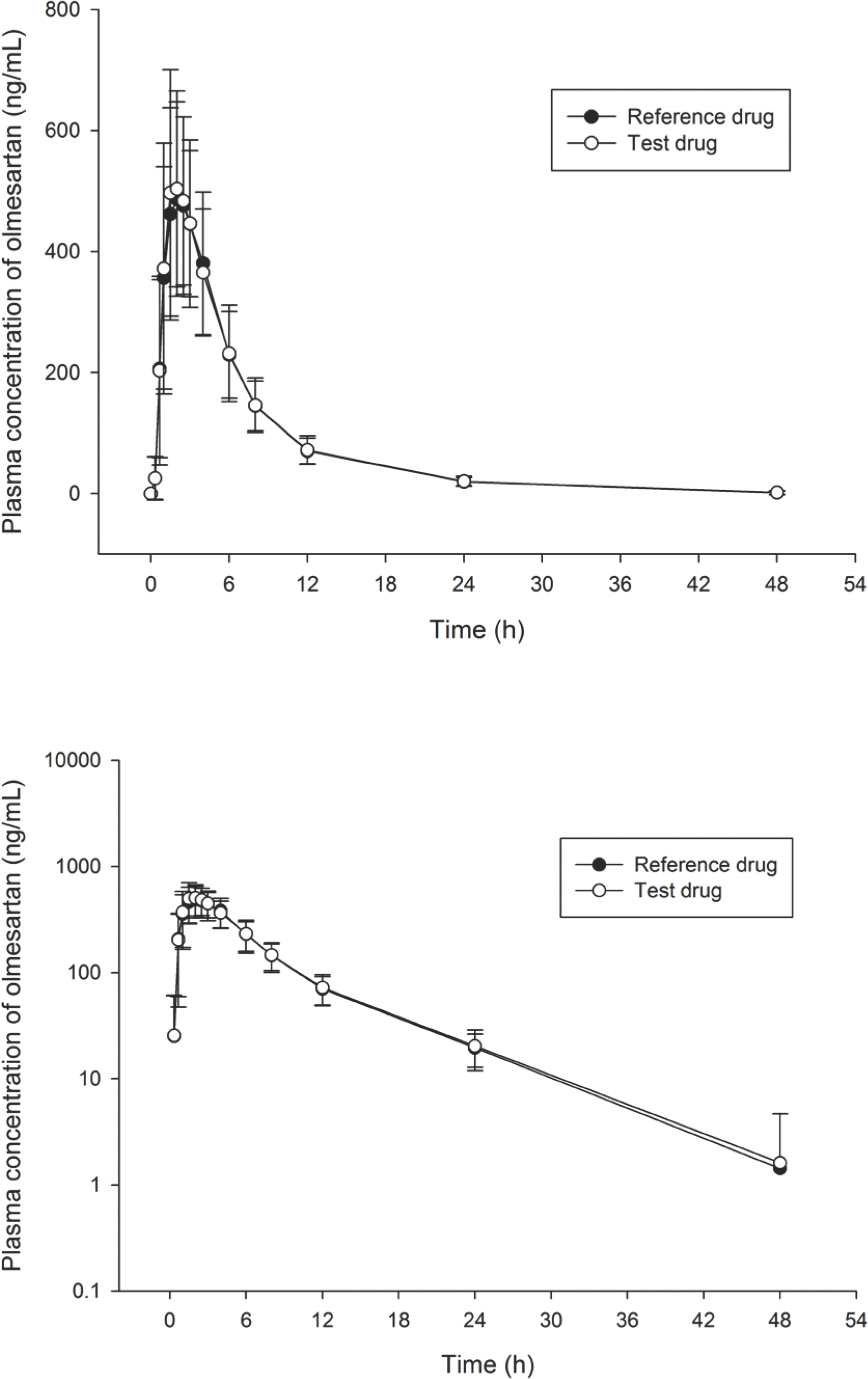 | Figure 1.Mean plasma concentration versus time curves of olmesartan after oral administration of a single dose 20 mg olmesartan in healthy Korean subjects (n=39). The error bars represent the standard deviation of olmesartan plasma concentrations (Upper: linear scale, Lower: log scale). |
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of the study subjects
| Characteristics | Mean | Median [min–max] | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 24.9 | 25.0 [19.0–37.0] | 3.5 | 14.0 |
| Height (cm) | 176.2 | 177.0 [166.0–186.0] | 4.8 | 2.7 |
| Weight (kg) | 70.6 | 70.0 [56.2–95.0] | 8.0 | 11.3 |
Table 2.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of olmesartan after a single administration of 20 mg test and reference drug in Korean healthy subjects (n = 39)
| Parameters | Test drug (n = 39) | Reference drug (n = 39) | Intrasubject CV (%) | Intersubject CV % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | CV (%) | Mean | SD | CV (%) | |||
| Tmax(h)+ | 2.0 [1.5 – 6.0] | 2.0 [1.0 – 4.0] | – | – | ||||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 561.56 | 155.19 | 27.64 | 541.31 | 138.00 | 25.49 | 15.24 | 21.33 |
| AUClast (ng·h/mL) | 3560.70 | 938.58 | 26.36 | 3490.45 | 848.44 | 24.31 | 14.88 | 20.00 |
| AUCinf (ng·h/mL) | 3670.40 | 930.79 | 25.36 | 3628.67 | 882.33 | 24.32 | 14.19 | 20.40 |
| CL/F (L/h) | 5.80 | 1.45 | 25.09 | 5.83 | 1.41 | 24.20 | – | – |
Table 3.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of olmesartan for the bioequivalence study with geometric mean ratios (test/reference) and 90% confidence intervals after a single dose of reference or test formulation in healthy Korean subjects




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download