Abstract
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is a potentially life-threatening clinical reaction in which anaphylaxis develops when physical activity occurs within a few hours after ingesting a specific food. An 18-year-old girl experienced generalized urticaria, periorbital swelling, and dyspnea repeatedly by exercise after intake of a red ginseng health supplement. A confirmed diagnosis was established in this case by using an exercise challenge test after ingesting mixed-plant extract containing red ginseng health supplement. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of FDEIA caused by components in a red ginseng health supplement.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Specific IgE was not detected in the patient and normal control by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Fig. 2
Different sized protein bands were shown in fresh ginseng by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. On the other hand, protein bands were not identified in red ginseng powder and health product. M, marker: 1, fresh ginseng powder; 2, red ginseng powder: 3, red ginseng product.
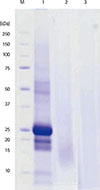
Table 1
Results of skin prick test
Table 2
Results of exercise challenge test after ingestion of red ginseng product

Table 3
Results of exercise challenge test after ingestion of mixed plants extract

References
1. Sharma R, Sinha R, Menon PS, Sirohi D. Management protocol for anaphylaxis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:855–862.

2. Radlińska A, Barg W, Wolanczyk-Medrala A, Medrala W. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: current concepts in pathogenesis, diagnostics and treatment. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2011; 30:49–51.
3. Du Toit G. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007; 18:455–463.

4. Kiefer D, Pantuso T. Panax ginseng. Am Fam Physician. 2003; 68:1539–1542.
5. Kim YK, Oh SY, Jung JW, Min KU, Kim YY, Cho SH. IgE binding components in Tetranychus urticae and Panonychus ulmi-derived crude extracts and their cross-reactivity with domestic mites. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:1457–1463.

6. Lee JY, Jin HJ, Park JW, Jung SK, Jang JY, Park HS. A case of korean ginseng-induced anaphylaxis confirmed by open oral challenge and basophil activation test. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:110–111.

7. Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:433–434.

8. Sheffer AL, Tong AK, Murphy GF, Lewis RA, McFadden ER Jr, Austen KF. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a serious form of physical allergy associated with mast cell degranulation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985; 75:479–484.

9. Matsuo H, Morimoto K, Akaki T, Kaneko S, Kusatake K, Kuroda T, et al. Exercise and aspirin increase levels of circulating gliadin peptides in patients with wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:461–466.

11. Cheng CX, Li YN, Ohno H, Sawanobori K, Li YC, Shimada O, et al. Mast cells appearing in long-term skeletal muscle cell cultures of rat. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2007; 290:1424–1430.

12. Wolanczyk-Medrala A, Barg W, Gogolewski G, Panaszek B, Liebhart J, Litwa M, et al. Influence of hyperosmotic conditions on basophil CD203c upregulation in patients with food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2009; 16:301–304.
13. Katsunuma T, Iikura Y, Akasawa A, Iwasaki A, Hashimoto K, Akimoto K. Wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: inhibition by sodium bicarbonate. Ann Allergy. 1992; 68:184–188.
14. Palosuo K, Varjonen E, Nurkkala J, Kalkkinen N, Harvima R, Reunala T, et al. Transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking of a peptic fraction of omega-5 gliadin enhances IgE reactivity in wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:1386–1392.

15. Pedersen BK, Steensberg A, Schjerling P. Exercise and interleukin-6. Curr Opin Hematol. 2001; 8:137–141.

16. Morita E, Kunie K, Matsuo H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2007; 47:109–117.

17. Kleiman J, Ben-Shoshan M. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis with negative allergy testing. BMJ Case Rep. 2014; 02. 06. [E-pub] http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-202057.

19. Hawkes C. Nutrition labels and health claims: the global regulatory environment. Geneva: World Health Organization;2004.
20. Sanz ML, Gamboa PM, De Weck AL. In vitro tests: basophil activation tests. In : Pichler WJ, editor. Drug hypersensitivity. Basel: Karger;2007. p. 391–402.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download