Abstract
Spinal meningiomas typically adhere to the dura matter. Non-dural based spinal meningiomas are rare and most are clear cell meningiomas. We report here the first case of a fibrous meningioma with non-dural attachment. The patient was a 49-year-old female, who complained of numbness in the legs and a gait disturbance. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a 1.7×1.4-cm mass in the C7-T1 intra-dural extramedullary space, showing peripheral gadolinium enhancement without a "dural tail sign". A complete microsurgical resection was performed. The mass was covered with a white membrane but was not adhered to the dura, and its appearance was consistent with a neurilemmoma. The histopathological diagnosis was fibrous-type meningioma. The recovery of the patient was uneventful. No surgical complications and no recurrence of the tumor had occurred at the 6-month follow-up.
Spinal meningiomas are common, comprising 25-46% of primary intra-spinal tumors7). They affect mostly female patients, and the average age of patients is about 50 years7,15,23,24). Spinal meningiomas are located in the intra-dural and extramedullary spaces, and typically adhere to the dura matter7,15). To date, few cases of non-dural-based meningiomas have been reported2,3,4,6,8,9,11,13,14,16,17,18,19,20,21,22), as most are reports of clear cell meningiomas2,3,4,6,8,11,13,14,16,18,20,21,22). This case report describes the first case of a non-dural based fibrous meningioma in the cervico-thoracic region in a 49-year-old female patient.
A 49-year-old female patient was admitted complaining of persistent pain and numbness in both legs for 4 months and a recently developed gait disturbance. These symptoms had intensified recently, and she was unable to walk without assistance. No remarkable disease or trauma history was noted. A neurological examination revealed bilateral numbness of the lower extremities that was particularly right-side dominant with an unclear dermatome. Hip flexion and extension motor grade was grade IV bilaterally. The pathological Babinski and ankle clonus reflexes were positive. Bladder and anal sphincter functions were preserved and motor and sensory functions of the upper extremities were normal. A laboratory examination and plain radiography of the cervical and thoracic spine were unremarkable. Magnetic resonance image (MRI) demonstrated a 1.7×1.4-cm lobulated mass in the C7-T1 dorsal space, probably the intra-dural extramedullary space (Fig. 1). T2-weighted MRI showed a low-signal-intensity elliptical lesion, which was enhanced peripherally on a gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted image. The spinal cord was severely compressed and displaced anteriorly by the mass lesion.
A C7-T1 cervical laminectomy and vertical incision in the dura were performed. No dural attached or adherent point was observed around the mass lesion when the intra-dural space was explored. The mass was covered with a white membrane, which was dissected and opened, revealing a 1.6×1.4-cm yellowish round mass (Fig. 2). Debulking and careful resection was performed using a microsurgical technique. A complete resection was achieved.
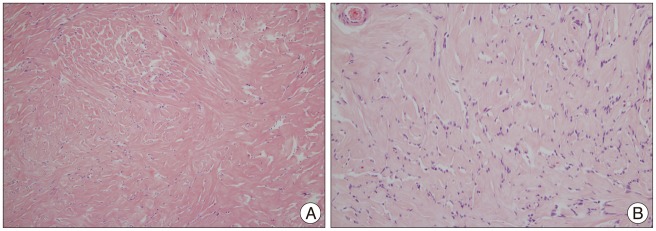
Spindle-shaped cells in a collagen-rich matrix were observed microscopically. The spindle tumor cells showed moderate nuclear polymorphism and formed parallel fascicles. Immunohistochemical staining revealed vimentin-positive, epithelial membrane antigen-negative, and S-100-protein-negative tissues (Fig. 3). These findings were consistent with a fibrous-type meningioma.
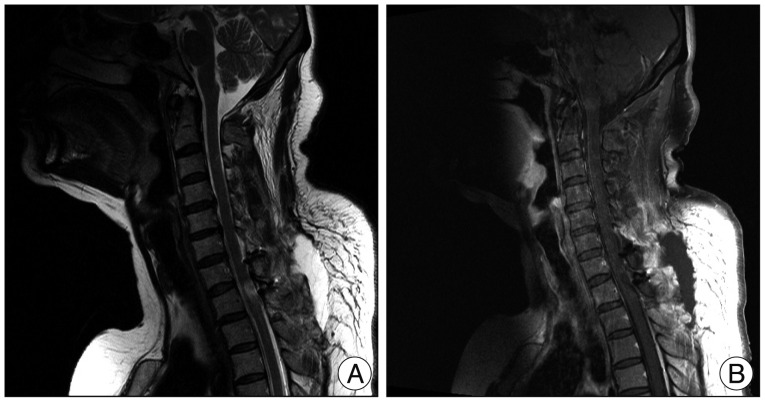
The leg numbness and gait disturbance showed gradual improvement postoperatively. The 1 week postoperative MRI revealed no residual tumor and no complications (Fig. 4). The patient was discharged without any complications. At the 1-month follow-up, the gait disturbance had improved, and she was able to walk without assistance.
Spinal meningiomas typically affect females at a female-to-male ratio of 4-5 : 1 and usually occur in patients >50 years7,15,24). The most frequent site of a spinal meningioma is the thoracic spine, followed in frequency by the cervical and lumbo-sacral spinal levels7,15,24). Meningothelial and psammomatous meningiomas are the most common histopathological subtypes of spinal menin-giomas15,24). A fibrous meningioma is an uncommon subtype, representing about 1% of all spinal meningiomas15,24) and has benign features.
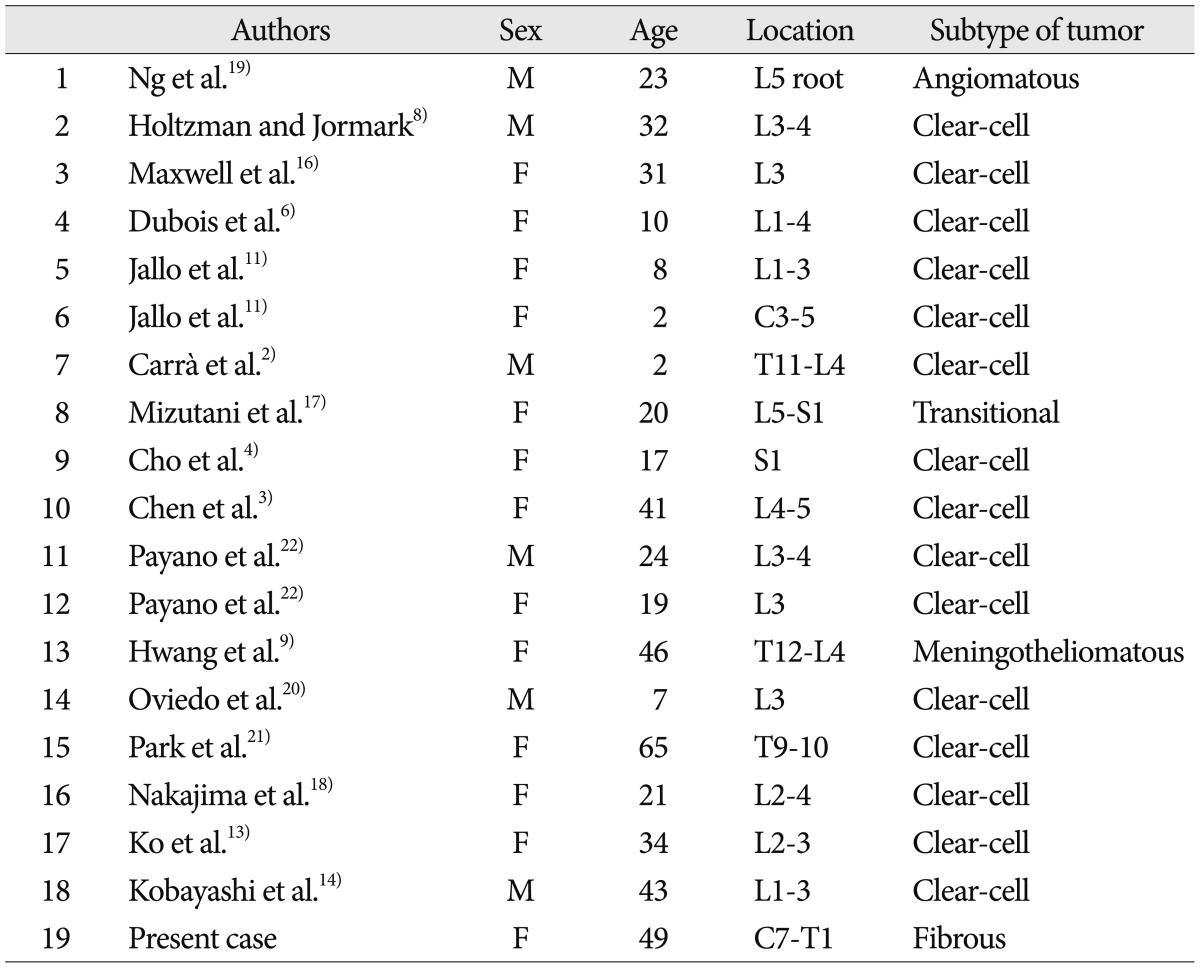
Spinal meningiomas typically attach to the dura, and non-dural spinal meningiomas are rare1,7,10,12). Eighteen cases of non-dural based spinal meningiomas have been reported to date (Table 1)2,3,4,6,8,9,11,13,14,16,17,18,19,20,21,22). Most tumors in these cases occur in the lumbo-sacral region (16 cases), including the thoraco-lumbar junction (two cases)2,3,4,6,8,9,11,13,14,16,17,18,19,20,22). The other two cases were cervical (C3-5) and thoracic (T9-10) meningiomas11,21). Our case is the third case that involvesd cervico-thoracic spine (C7-T1). The average age of these cases was about 25 years, which is less than the average age of patients with general spinal meningiomas, except one case (a 65-year-old female with a thoracic clear cell meningioma)21).
Most of histopathologic subtype of non-dural-based spinal meningiomas was clear cell meningioma (15 cases)2,3,4,6,8,11,13,14,16,18,20,21,22), whereas the remaining three cases were angiomatous, transitional, and meningotheliomatous meningiomas9,17,19). The clear cell meningiomas were quite predominant, as high as approximately 83.3%. In several cases of clear cell meningioma, complete total resection with postoperative radiotherapy was considered because of high recurrence rate4,13,22). Therefore, in cases of non-dural based spinal mengiomas, the possibility of total resection and/or radiotherapy should be taken into consideration. However, it is remarkable that subtype of present case was benign as fibrous subtype, and there were other three cases of benign subtypes.
MRI of a spinal meningioma typically shows homogenous enhancement and the "dural tail sign", which is dural enhancement or thickening near the tumor on enhanced T1-weighted images5). However, the meningioma in the present case showed only peripheral enhancement of the tumor on a gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted image and no "dural tail sign". Therefore, even if no typical sign of a meningioma on MRI such as the "dural tail sign" is present, the possibility of a meningioma should not be ruled out.
References
1. Abraham J, Chandy J. Meningiomas of the posterior fossa without dural attachment : a case report. J Neurosurg. 1963; 20:177–179. PMID: 14192092.
2. Carrà S, Drigo P, Gardiman M, Perilongo G, Rigobello L. Clear-cell meningioma in a 22-month-old male : a case report and literature review. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2001; 34:264–267. PMID: 11423779.
3. Chen MH, Chen SJ, Lin SM, Chen MH. A lumbar clear cell meningioma with foraminal extension in a renal transplant recipient. J Clin Neurosci. 2004; 11:665–667. PMID: 15261248.

4. Cho CB, Kim JK, Cho KS, Kim DS. Clear cell meningioma of cauda equina without dural attachment. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003; 34:584–585.
5. De Verdelhan O, Haegelen C, Carsin-Nicol B, Riffaud L, Amlashi SF, Brassier G, et al. MR imaging features of spinal schwannomas and meningiomas. J Neuroradiol. 2005; 32:42–49. PMID: 15798613.

6. Dubois A, Sévely A, Boetto S, Delisle MB, Manelfe C. Clear-cell meningioma of the cauda equina. Neuroradiology. 1998; 40:743–747. PMID: 9860126.

7. Gottfried ON, Gluf W, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Kan P, Schmidt MH. Spinal meningiomas : surgical management and outcome. Neurosurg Focus. 2003; 14:e2. PMID: 15669787.
8. Holtzman RN, Jormark SC. Nondural-based lumbar clear cell meningioma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1996; 84:264–266. PMID: 8592230.
9. Hwang SL, Liu CS, Su YF, Shen WJ, Chuo CY, Liu GC, et al. Giant nondural-based cauda equina meningioma with multiple cysts. J Neurooncol. 2005; 74:173–177. PMID: 16132526.

10. Ishigaki D, Arai H, Sasoh M, Ogasawara K, Uesugi N, Sugai T, et al. Meningioma in the posterior fossa without dural attachment. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2007; 47:364–366. PMID: 17721053.
11. Jallo GI, Kothbauer KF, Silvera VM, Epstein FJ. Intraspinal clear cell meningioma : diagnosis and management : report of two cases. Neurosurgery. 2001; 48:218–221. discussion 221-222. PMID: 11152351.

12. Kim SM, Jung SS, Park MS, Park KS. Meningioma in the lateral cerebellomedullary Cistern without dural attachment. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 47:464–466. PMID: 20617095.

13. Ko JK, Choi BK, Cho WH, Choi CH. Non-dura based intaspinal clear cell meningioma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 49:71–74. PMID: 21494369.

14. Kobayashi Y, Nakamura M, Tsuji O, Iwanami A, Ishii K, Watanabe K, et al. Nondura-based clear cell meningioma of the cauda equina in an adult. J Orthop Sci. 2013; 18:861–865. PMID: 22437332.

15. Levy WJ Jr, Bay J, Dohn D. Spinal cord meningioma. J Neurosurg. 1982; 57:804–812. PMID: 7143063.

16. Maxwell M, Shih SD, Galanopoulos T, Hedley-Whyte ET, Cosgrove GR. Familial meningioma : analysis of expression of neurofibromatosis 2 protein Merlin. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1998; 88:562–569. PMID: 9488313.

17. Mizutani J, Fukuoka M, Tsubouchi S, Otsuka T, Tono Y, Shimizu S, et al. A rare case of lumbosacral meningioma : nondural attachment and possible enlargement by orally administered sex steroid. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:E377–E381. PMID: 12195080.
18. Nakajima H, Uchida K, Kobayashi S, Takamura T, Yayama T, Baba H. Microsurgical excision of multiple clear cell meningiomas of the cauda equina : a case report. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2009; 52:32–35. PMID: 19247902.

19. Ng TH, Chan KH, Mann KS, Fung CF. Spinal meningioma arising from a lumbar nerve root. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1989; 70:646–648. PMID: 2926506.
20. Oviedo A, Pang D, Zovickian J, Smith M. Clear cell meningioma : case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2005; 8:386–390. PMID: 16010490.

21. Park SH, Hwang SK, Park YM. Intramedullary clear cell meningioma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006; 148:463–466. PMID: 16341630.

22. Payano M, Kondo Y, Kashima K, Daa T, Yatsuka T, Kida H, et al. Two cases of nondura-based clear cell meningioma of the cauda equina. APMIS. 2004; 112:141–147. PMID: 15056231.

23. Scheithauer BW. Tumors of the meninges : proposed modifications of the World Health Organization classification. Acta Neuropathol. 1990; 80:343–354. PMID: 2239146.

24. Solero CL, Fornari M, Giombini S, Lasio G, Oliveri G, Cimino C, et al. Spinal meningiomas : review of 174 operated cases. Neurosurgery. 1989; 25:153–160. PMID: 2671779.
Fig. 1
Preoperative magnetic resonance image of the cervical spine. A 1.7×1.4-cm lobulated mass in the C7-T1 dorsal space. A low-signal-intensity elliptical lesion on a T2-weighted image (A). Peripherally enhanced lesion on a gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted image (B).
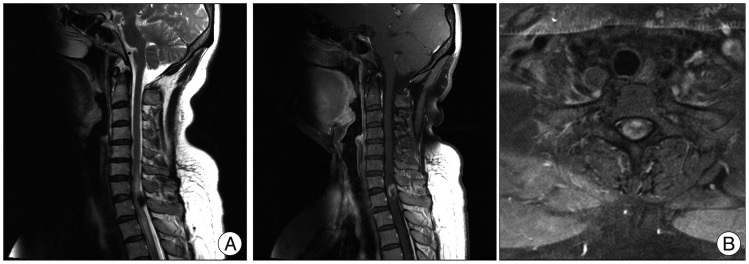
Fig. 2
Operative microscopic view. The tumor is covered with a white membrane, and there is no attachment to the dura mater.
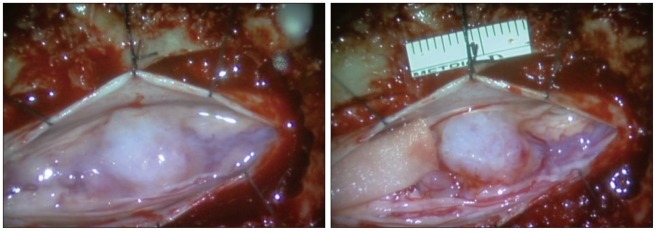
Fig. 3
Pathologic findings of the tumor. Spindle-shaped cells in a collagen-rich matrix, showing moderate nuclear polymorphism, and forming parallel fascicles. H&E stain, ×100 (A), ×200 (B).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download