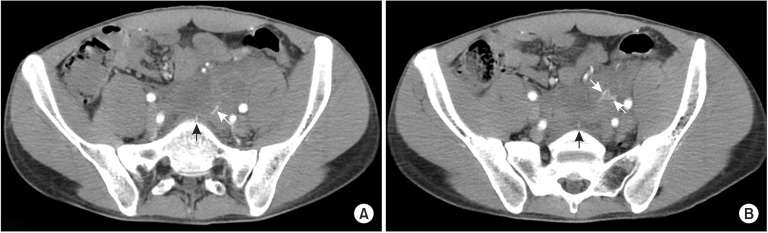
Disc decompression using the Dekompressor® (Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA) is an effective procedure for treating patients with contained disc herniation [1,2,3,4,5]. Iatrogenic vascular injuries during lumbar disc decompression, although rare, are serious complications, that can be fatal without prompt diagnosis and management [5]. In this paper we present the case of a 23-year-old man with median sacral artery injury during lumbar disc decompression using the Dekompressor®. After the procedure, blood pressure decreased, and dizziness, and abdominal pain occurred in the recovery room. Abdomino-pelvic computed tomography (CT) without contrast medium showed a 7.5 cm sized hematoma in the left prevertebral space of the L5-S1 level. Leakage of contrast medium from the median sacral artery was noted by a contrast-enhanced CT scan (Fig. 1). Fortunately, the patient's vital signs were generally maintained by rapid transfusion. The next day, the patient underwent a repeat contrast-enhanced CT scan. There was no definite contrast extravasation, and the size of the retroperitoneal hematoma had decreased from 7.5 to 6 cm. The patient was treated by conservative management and recovered uneventfully.
References
1. Han SS, Sim SE, Kim YH, Lee EH, Joh JY, Kim JY, et al. Clinical outcomes of percutaneous lumbar discectomy using Dekompressor. Korean J Pain. 2005; 18:187–191.

2. Kim YH, Gu MS, Lee EH, Joh JY, Han SS, Lee CJ, et al. Percutaneous cervical discectomy using Dekompressor. Korean J Pain. 2005; 18:271–274.
3. Cho OG, Kim C, Han KR, Lee HH, Cho HW. Percutaneous discectomy of herniated intervertebral disc with a Dekompressor. Korean J Pain. 2005; 18:192–197.

4. Lemcke J, Al-Zain F, Mutze S, Meier U. Minimally invasive spinal surgery using nucleoplasty and the Dekompressor tool: a comparison of two methods in a one year follow-up. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2010; 53:236–242. PMID: 21302191.

5. Singh V, Benyamin RM, Datta S, Falco FJ, Helm S 2nd, Manchikanti L. Systematic review of percutaneous lumbar mechanical disc decompression utilizing Dekompressor. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:589–599. PMID: 19461825.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download