In the scholarly publishing industry, editorial articles are written by or under the concerted supervision of the key editors of journals. The first principle is that a worthy editorial article is an opinion maker.1 Editorials should stretch views on topmost topics of the day and try to invite scholars' attention and exertion headed for the topic. Generally, it should ground more research and publication on its highlighted themes. By this, the journal editors are leading sciences to solve our world's problems.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a crisis that has produced huge losses for the world thus far. Therefore, it is expected that world-class journals use their leading means, editorial articles, to relieve the crisis. Scopus, as one of the chief databases of journals, attest that until June 30, 2020 near 1,800 editorials in relation to the COVID-19 are published from different fields. Majority of these editorials were in the field of medicine, though journals from other fields were not beyond the trend.
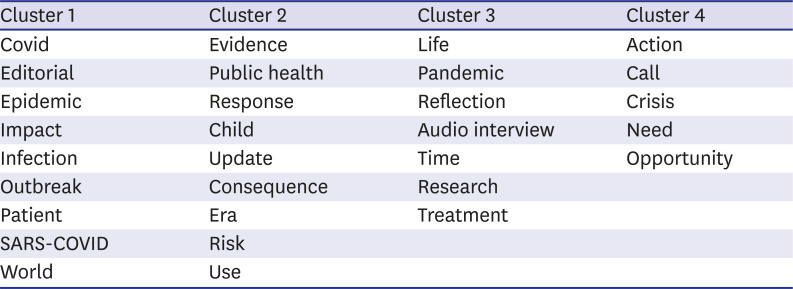
Many editorials do not have abstract, keywords, or sub-sections, but their title and the core body are the concern. Considering the fact that the chosen title is the most important part to attract readers' attentiveness and affect the readerships and the editorial's encouragement power2, title exploration of the recorded editorials, per VOSviewer software (Leiden University, Rapenburg, Netherland), performed. The result reveals four clusters of the titles' coders, as shown in Table 1.
Because of the role of the editorials in solving the current world problem, from a holistic view, it is expected, at least by the author of this paper, that the common crisis management coders, such as those related to the crisis grounds and effects, cure and management, and future alterations due to the crisis, were more highlighted. Hence, future editorials are invited to pay more attention to the formulation of the document title.
Table 1
VOSviewer output




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download