Abstract
Purpose
We wanted to describe the CT findings of small bowel anisakiasis with the pathologic correlation.
Materials and Methods
Four patients with surgically and pathologically proven small bowel anisakiasis were included in this retrospective study. They were three men and one woman and their ages ranged from 28 to 43 years (mean age: 38 years). We evalu-ated their clinical, CT and histological findings.
Results
All the patients had a history of ingesting raw fish within 24 hours from the time of symptom onset. They complained of abdominal pain (n=4), nausea (n=4), vomiting (n=2) and diarrhea (n=1). Physical examination revealed tenderness (n=4), rebound tenderness (n=4) and increased bowel sounds (n=3). Leukocytosis was noted in all the patients on the laboratory examination. None of the patients showed eosinophilia. The CT findings were segmental small bowel wall thickening with preserved layering (n=4), focal segmental luminal narrowing with proximal dilatation (n=4), peritoneal thickening (n=3), mesenteric or omental infiltration (n=4) and vary-ing degrees of ascites (n=4). On the histopathologic examination, they revealed an infiltration of eosinophils (n=4) in all layers of the bowel wall with severe edema. The larvae were found on surgico-pathologic examination in all the cases.
Index words
Anisakiasis Tomography, X-Ray Computed Intestinal Diseases, Parasitic infectionREFERENCES
1. Shirahama M, Koga T, Ishibashi H, Uchida S, Ohta Y, Shimoda Y. Intestinal anisakiasis: US in diagnosis. Radiology. 1992; 185:789–793.

2. Takei H, Powell SZ. Intenstinal anisakidosis (anisakiosis). Ann Diagn Pathol. 2007; 11:350–352.
3. Ishikura H, Kikuchi K, Nagasawa K, Ooiwa T, Takamiya H, Sato N, et al. Anisakidae and anisakidosis. Prog Clin Paraisitol. 1993; 3:43–102.

4. Ido K, Yuasa H, Ide M, Kimura K, Toshimitsu K, Suzuki T. Sonographic diagnosis of small intestinal anisakiasis. J Clin Ultrasound. 1998; 26:125–130.

5. Matsuo S, Azuma T, Susumu S, Yamaguchi S, Obata S, Hayashi T. Small bowel anisakiosis: a report of two cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:4106–4108.

6. Kim LS, Lee YH, Kim S, Park HR, Cho SY. A case of anisakiasis causing intestinal obstruction. Korean J Parasitol. 1991; 29:93–96.

7. Sasaki T, Fukumori D, Matsumoto H, Ohmori H, Yamamoto F. Small bowel obstruction caused by anisakiasis of the small intens-tine: report of a case. Surg Today. 2003; 33:123–125.
8. Yoon SW, Yu JS, Park MS, Shim JY, Kim HJ, Kim KW. CT findings of surgically verified acute invasive small bowel anisakiasis resulting in small bowel obstruction. Yonsei Med J. 2004; 45:739–742.

9. Ishida M, Harada A, Egawa S, Watabe S, Ebina N, Unno M. Three successive cases of enteric anisakiasis. Dig Surg. 2007; 24:228–231.

10. Masui N, Fujima N, Hasegawa T, Kigawa S, Kagei N, Nagashima K, et al. Small bowel strangulation caused by parasitic peritoneal strand. Pathol Int. 2006; 56:345–349.

11. Hong SS, Kim JH, Park ST, Chan YW, Kim HJ, Kwon KH, et al. Duodenal anisakiasis presenting as bowel obstruction and fistula formation: a case report. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2009; 60:419–422.

12. Chung TW, Kang HK, Jeong YY, Jeong GW, Seo JJ, Kim YH, et al. Radiographic findings of gastrointestinal anisakiasis: clinical and pathologic correlation. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2000; 43:209–213.

13. Montalto M, Miele L, Marcheggiano A, Santoro L, Curigliano V, Vastola M, et al. Anisakis infestation: a case of acute abdomen mimicking Crohn's disease and eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Dig Liver Dis. 2005; 37:62–64.

14. Nakata H, Takeda K, Nakayama T. Radiological diagnosis of acute gastric anisakiasis. Radiology. 1980; 135:49–53.

15. Pellegrini M, Occhini R, Tordini G, Vindigni C, Russo S, Marzocca G. Acute abdomen due to small bowel anisakiasis. Dig Liver Dis. 2005; 37:65–67.

16. Asaishi K, Nishino C, Ebata T, Totsuka M, Hayasaka H, Suzuki T. Studies on the etiologic mechanism of anisakiasis. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1980; 15:120–127.

Fig. 1.
A 43-year-old male patient with small bowel anisakiasis (Case 2). The CT findings (A and B): The axial scan of abdominal CT at the level of the iliac crest (A) shows circumferential wall thickening or edema of a long segment of the jejunum with peritoneal thickening and mesenteric infiltration. Proximal luminal dilatation from the transition zone is also noted (arrow). There is ascites at the right gutter. The axial scan at the level of the kidney (B) shows dilated proximal bowel loops that mimic obstructive ileus (arrows). The pathologic features (C and D): Photomicroscopy (C) show a helminthic larva (arrows) penetrating the bowel mucosa (H & E, ×40). There is a dense infiltration of eosinophils with other inflammatory cells in all the layers of the small bowel (H & E, ×20) (D).
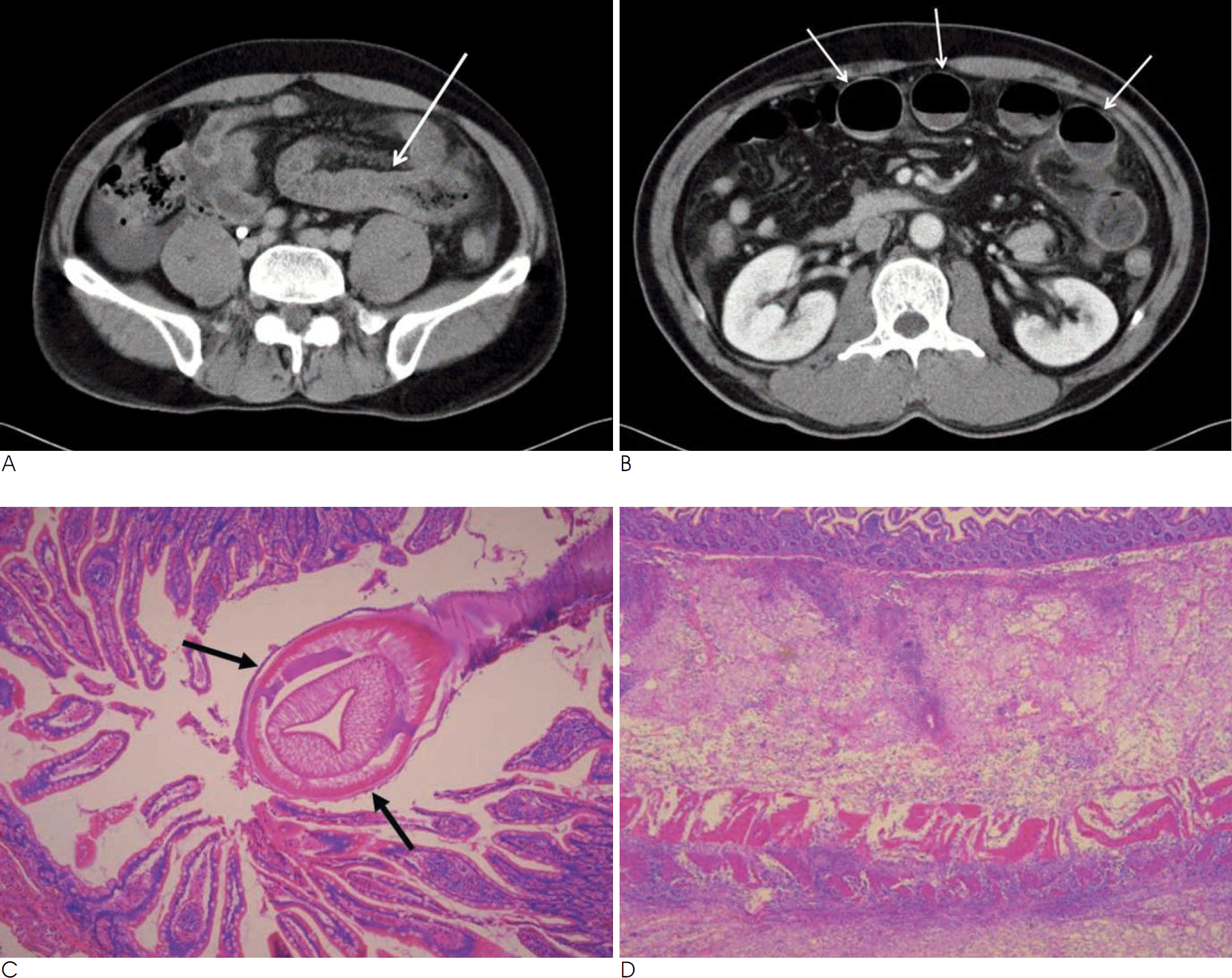
Table 1.
Clinical Features of the Small Bowel Anisakiasis Patients
Table 2.
CT Findings of the Small Bowel Anisakiasis Patients




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download