Abstract
Objective
Chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) is one of the most common types of intracranial hemorrhage, especially in the elderly. Burr hole drainage has been widely used to treat CSDH. However, the incidence of recurrent CSDH varies from 3.7 to 30% after surgery. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the risk factors associated with the recurrence of CSDH in burr hole drainage technique.
Methods
A total of 260 consecutive cases who underwent burr hole drainage for CSDH were included in this study. Thirty patients (11.5%) underwent a repeated operation because of the recurrence of CSDH. We analyzed retrospectively the demographic, clinical, radiologic factors and surgical treatments associated with the recurrence of CSDH.
Results
In our study, two risk factors were found to be independently related to the recurrence of CSDH. The incidence of CSDH recurrence in the high- or mixed-density groups was significantly higher than those in the low- or iso-density groups (p<0.001). The duration of drainage was also significantly related to the recurrence rate (p=0.007). Prolonged duration of drainage did not increase the frequency of infection in our series.
Conclusion
These results suggest that high- and mixed-density shown on computed tomographic (CT) scan was closely related with a high incidence of recurrence. Therefore, the operation could be delayed in those cases unless severe symptoms or signs are present. Also, we found in this study that the duration of drainage play an important role in the treatment of CSDH and 3 full days of drainage seems to be necessary.
Figures and Tables
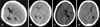
FIGURE 1
Chronic subdural hematoma is classified according to its density on brain CT scans. A: High-type. B: Iso-type. C: Low-type. D: Mixed-type.
References
1. Apfelbaum RI, Guthkelch AN, Shulman K. Experimental production of subdural hematomas. J Neurosurg. 1974; 40:336–346.

2. Arbit E, Patterson RH Jr, Fraser RA. An implantable subdural drain for treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 1981; 15:175–177.

3. El-Kadi H, Miele VJ, Kaufman HH. Prognosis of chronic subdural hematomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:553–567.

4. Frati A, Salvati M, Mainiero F, Ippoliti F, Rocchi G, Raco A, et al. Inflammation markers and risk factors for recurrence in 35 patients with a posttraumatic chronic subdural hematoma: a prospective study. J Neurosurg. 2004; 100:24–32.

5. Kang HL, Shin HS, Kim TH, Hwang YS, Park SK. Clinical analysis of recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2006; 40:262–266.
6. Kang MS, Koh HS, Kwon HJ, Choi SW, Kim SH, Youm JY. Factors influencing recurrent chronic subdural hematoma after surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2007; 41:11–15.
7. Kiymaz N, Yilmaz N, Mumcu C. Controversies in chronic subdural hematoma: continuous drainage versus one-time drainage. Med Sci Monit. 2007; 13:CR240–CR243.
8. Ko BS, Lee JK, Seo BR, Moon SJ, Kim JH, Kim SH. Clinical analysis of risk factors related to recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:11–15.

9. Kostanian V, Choi JC, Liker MA, Go JL, Zee CS. Computed tomographic characteristics of chronic subdural hematomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:479–489.

10. Kotwica Z, Brzeziński J. Chronic subdural haematoma treated by burr holes and closed system drainage: personal experience in 131 patients. Br J Neurosurg. 1991; 5:461–465.

11. Kuroki T, Katsume M, Harada N, Yamazaki T, Aoki K, Takasu N. Strict closed-system drainage for treating chronic subdural haematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001; 143:1041–1044.

13. Markwalder TM, Steinsiepe KF, Rohner M, Reichenbach W, Markwalder H. The course of chronic subdural hematomas after burr-hole craniostomy and closed-system drainage. J Neurosurg. 1981; 55:390–396.

14. Matsumoto K, Akagi K, Abekura M, Ryujin H, Ohkawa M, Iwasa N, et al. Recurrence factors for chronic subdural hematomas after burr-hole craniostomy and closed system drainage. Neurol Res. 1999; 21:277–280.

15. Murakami H, Hirose Y, Sagoh M, Shimizu K, Kojima M, Gotoh K, et al. Why do chronic subdural hematomas continue to grow slowly and not coagulate? Role of thrombomodulin in the mechanism. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:877–884.

16. Muzii VF, Bistazzoni S, Zalaffi A, Carangelo B, Mariottini A, Palma L. Chronic subdural hematoma: comparison of two surgical techniques. Preliminary results of a prospective randomized study. J Neurosurg Sci. 2005; 49:41–46. discussion 46-47.
17. Nakaguchi H, Tanishima T, Yoshimasu N. Factors in the natural history of chronic subdural hematomas that influence their postoperative recurrence. J Neurosurg. 2001; 95:256–262.

18. Nakaguchi H, Tanishima T, Yoshimasu N. Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:791–795.

19. Nomura S, Kashiwagi S, Fujisawa H, Ito H, Nakamura K. Characterization of local hyperfibrinolysis in chronic subdural hematomas by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot. J Neurosurg. 1994; 81:910–913.

20. Oishi M, Toyama M, Tamatani S, Kitazawa T, Saito M. Clinical factors of recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2001; 41:382–386.

21. Okada Y, Akai T, Okamoto K, Iida T, Takata H, Iizuka H. A comparative study of the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma--burr hole drainage versus burr hole irrigation. Surg Neurol. 2002; 57:405–409. discussion 410.

22. Probst C. Peritoneal drainage of chronic subdural hematomas in older patients. J Neurosurg. 1988; 68:908–911.

23. Sharp AA. Diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Br Med Bull. 1977; 33:265–272.

24. Voelker JL. Nonoperative treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:507–513.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download