Abstract
We report a case of vertebral osteomyelitis with epidural abscess caused by Streptococcus constellatus. The patient was present with fever, back pain, and dyspnea for 1 week. The patient was previously healthy and did not have any predisposing factor. After evaluation, the patient was diagnosed as Streptococcus constellatus vertebral osteomyelitis. He was successfully treated with surgical debridement and antibiotic therapy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of S. constellatus vertebral osteomyeltis with epidural abscess to be reported in Korea.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
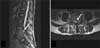
MR imaging of vertebral osteomyelitis with epidural abscess at diagnosis. (A) Sagittal T2 weighted image. (B) Transverse T2 weighed image. The images reveal disc space narrowing at L-4/5, with abscess on posterior aspect of L-4,L-5 spine (arrow) with marked compression on dural sac. Central and right paracentral bodies of L-4, L-5 spine are diffusely hyperintense on T2WI without significant contour deformity.
References
1. Whiley RA, Beighton D, Winstanley TG, Fraser HY, Hardie JM. Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus (the Streptococcus milleri group): association with different body sites and clinical infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1992. 30:243–244.

2. Gossling J. Occurrence and pathogenicity of the Streptococcus milleri group. Rev Infect Dis. 1988. 10:257–285.

3. Wang TD, Chen YC, Huang PJ. Recurrent vertebral osteomyelitis and psoas abscess caused by Streptococcus constellatus and Fusobacterium nucleatum in a patient with atrial septal defect and an occult dental infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1996. 28:309–310.

4. Molina JM, Leport C, Bure A, Wolff M, Michon C, Vilde JL. Clinical and bacterial features of infections caused by Streptococcus milleri. Scand J Infect Dis. 1991. 23:659–666.

5. Gelfand MS, Bakhtian BJ, Simmons BP. Spinal sepsis due to Streptococcus milleri: two cases and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1991. 13:559–563.

6. Schroeder TH, Krueger WA, Neeser E, Hahn U, Unertl K. Spinal epidural abscess-a rare complication after epidural analgesia for labour and delivery. Br J Anaesth. 2004. 92:896–898.

7. Claridge JE 3rd, Attorri S, Musher DM, Hebert J, Dunbar S. Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus ("Streptococcus milleri group") are of different clinical importance and are not equally associated with abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32:1511–1515.
8. Matsukawa Y, Kitamura N, Kaneko M, Yoshioka D, Miki T, Nishinarita S, Horie T, Hosokawa N, Iwasaki Y, Kumasaka K, Kawano K. Multibacterial sepsis in an alcohol abuser with hepatic cirrhosis. Intern Med. 2003. 42:208–210.

9. Morita E, Narikiyo M, Yokoyama A, Yano A, Kamoi K, Yoshikawa E, Yamaguchi T, Igaki H, Tachimori Y, Kato H, Saito D, Hanada N, Sasaki H. Predominant presence of Streptococcus anginosus in the saliva of alcoholics. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2005. 20:362–365.

11. Jaramillo-de la Terre JJ, Bohinski RJ, Kuntz C 4th. Vertebral osteomyelitis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2006. 17:339–351.

12. Roblot F, Besnier JM, Juhel L, Vidal C, Ragot S, Bastides F, Le Moal G, Godet C, Mulleman D, Azaïss I, Becq-Giraudon B, Choutet P. Optimal duration of antibiotic therapy in vertebral osteomyelitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007. 36:269–277.

13. Ferre BA, Stambough JL, Greiner AL. Spinal epidural abscess. A case report and literature review. Othorp Rev. 1989. 18:75–80.
14. Samuel W, Dryden M, Sampson M, Page A, Shepherd H. Spinal abscess of Haemophilus paraphrophilus. A case report. Spine. 1997. 22:2763–2765.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download