Abstract
Purpose
Children and adolescent have high prevalences of allergic rhinitis (AR) and nonallergic rhinitis (NAR) as well as adult. The purpose of this study was to assess the symptomatic differences between AR and NAR in children.
Methods
This study included 138 patients with 2 or more of rhinitis symptoms, including rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction, nasal itching, and sneezing for over 1 hour on most days who visited Kyungpook National University Children's Hospital between March 2013 and June 2014. The levels of total IgE, specific IgE, eosinophil cationic protein, peripheral blood eosinophil count, and the skin prick test were carried out. All the patients or parents were asked to fill out a rhinitis symptom questionnaire and contents were rechecked by physician during the consultation. The symptoms of rhinorrhea, sneezing, nasal itching, nasal obstruction and eye itching were checked. Family history and comorbidity were also evaluated.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Symptomatic differences between allergic and nonallergic rhinitis in children. AR, allergic rhinitis; NAR, nonallergic rhinitis.
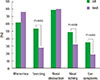
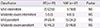
Table 1
Demographics of subjects

References
1. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2011: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-2) [Internet]. Cheongwon (KR): Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;c2013. cited 2013 Oct 30. Available from: http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/.
2. Huggins KG, Brostoff J. Letter: Local IgE antibodies in allergic rhinitis. Lancet. 1975; 2:618.
3. Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Casale TB, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:466–476.

4. Position paper: Allergen standardization and skin tests. The European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. Allergy. 1993; 48:14 Suppl. 48–82.
5. Di Lorenzo G, Pacor ML, Amodio E, Leto-Barone MS, La Piana S, D'Alcamo A, et al. Differences and similarities between allergic and nonallergic rhinitis in a large sample of adult patients with rhinitis symptoms. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 155:263–270.

6. Molgaard E, Thomsen SF, Lund T, Pedersen L, Nolte H, Backer V. Differences between allergic and nonallergic rhinitis in a large sample of adolescents and adults. Allergy. 2007; 62:1033–1037.

7. Bousquet J, Schunemann HJ, Samolinski B, Demoly P, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bachert C, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA): achievements in 10 years and future needs. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 130:1049–1062.
8. Sahay S, Bhargava SK, Shah A. Co-occurence of sinusitis in patients with asthma and/or allergic rhinitis in Delhi, India [abstract]. In : Proceedings of the Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology (KAAACI) and World Allergy Organisation (WAO) Joint Congress 2006 and the 9th West Pacific Allergy Organisation; 2006 Nov 3-5; Seoul, Korea. p. 263.
9. Sedaghat AR, Phipatanakul W, Cunningham MJ. Prevalence of and associations with allergic rhinitis in children with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 78:343–347.

10. Vichyanond P, Suratannon C, Lertbunnaphong P, Jirapongsananuruk O, Visitsunthorn N. Clinical characteristics of children with non-allergic rhinitis vs with allergic rhinitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2010; 28:270–274.
11. Sybilski AJ, Raciborski F, Lipiec A, Tomaszewska A, Lusawa A, Samel-Kowalik P, et al. Atopic dermatitis is a serious health problem in Poland. Epidemiology studies based on the ECAP study. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2015; 32:1–10.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download