Abstract
Background
Hand eczema is one of the most common skin disorders and negatively affects quality of life. However, a large-scale multicenter study investigating the clinical features of patients with hand eczema has not yet been conducted in Korea.
Objective
To identify the prevalence of various hand diseases, which is defined as all cutaneous disease occurring in hands, and to investigate the clinical features of patients with hand eczema and the awareness about hand eczema in the general population and to compare the prevalence of hand eczema between health care providers and non-health care providers.
Methods
To estimate the prevalence of hand diseases, we analyzed the medical records of patients from 24 medical centers. Patients were assessed by online and offline questionnaires. A 1,000 from general population and 913 hand eczema patients answered the questionnaire, for a total of 1,913 subjects.
Results
The most common hand disease was irritant contact dermatitis. In an online survey, the lifetime prevalence of hand eczema was 31.2%. Hand eczema was more likely to occur in females (66.0%) and younger (20~39 years, 53.9%). Health care providers and housewives were the occupations most frequently associated with hand eczema. Winter (33.6%) was the most common season which people experienced aggravation. The 63.0% and 67.0% answered that hand eczema hinders their personal relationship and negatively affects daily living activities, respectively.
Hand eczema is an inflammation of the skin affecting hands1. It is one of the most common skin disorders encountered in clinical practice. Typical clinical signs and symptoms are redness, itching, pain, infiltration of the skin, scaling, edema, vesicles, hyperkeratosis, fissures, and erosions. According to a review of population-based studies, the point prevalence of hand eczema is estimated to be approximately 4%, the 1-year prevalence of approximately 10%, and a lifetime prevalence 15%2.
Hand eczema is caused by a combination of endogenous (individual susceptibility, atopic dermatitis, age, gender) and exogenous (allergens, irritants) factors3. The most common exogenous factors of hand eczema is contact with mild toxic agents or irritants (e.g., water and soaps)1.
There are several types of hand eczema that is classified based on etiology1. Irritant contact dermatitis is caused by repeated exposures to irritants over a prolonged period. Clinically, irritant contact dermatitis presents with xerosis, scaly erythematous plaques, fissuring, and lichenification. It commonly involves web spaces and can be extended to the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the hand and fingers. Vesicles do not typically form. Pruritus can be mild; however, stinging, burning and pain are possible symptoms. Allergic contact dermatitis usually occurs few days after the exposure of allergen. Clinically, allergic contact hand dermatitis can include itching, stinging, burning, and pain. Vesicles, bullae, erythematous papules, weeping, and crusting are also possible. Fingertips, nail folds, and dorsal hands are most commonly involved and may progress to forearm. Atopic dermatitis is one of the most common chronic inflammatory skin disorders. The prevalence of hand dermatitis in atopy is estimated to be around 60% among all ages. The most common distribution is over dorsal hands and dorsal fingers. The plaques are usually scaly, ill-defined, pink, thin, or lichenified. Papules or vesicles can be presented as well. Nail changes such as loss of the cuticle, thickening/inflammation of the nail folds, or irregular ridging can occur4.
Hand eczema can be treated with moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, and by avoiding irritants and allergens, however, some severe cases are refractory to treatments such as topical steroids, ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, oral immunosuprressives, retinoids, etc.56. Although severe chronic hand eczema may severely impair quality of life, increase anxiety and depression, and can be an economic burden5789, it is reported that only 44% or less patients with hand eczema visit dermatologists10.
Choi et al.11 reported on the various clinical characteristics of Korean patients with hand eczema. However, a large-scale multicenter study investigating the clinical features of patients with hand eczema has not yet been conducted in Korea.
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical features of hand eczema in Korean patients. In addition, we tried to increase awareness about hand eczema in the general population and compare the characteristics of hand eczema between health care providers and non-health care providers.
To estimate the prevalence of diseases affecting the hands, the present study analyzed medical records of department of dermatology at 24 university hospitals from January 2013 to December 2013. Chart review was performed retrospectively for the clinical evaluation of the enrolled patients. Cutaneous disease affecting the hands were investigated. The diseases investigated in this retrospective study included allergic contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, cutaneous autosensitization, erythema multiforme, hand-foot-mouth disease, irritant contact dermatitis, palmoplantar pustular psoriasis, pityriasis rubra pilaris, pompholyx, psoriasis, tinea manuum, and unspecified dermatitis. To gather information from the general population, an online survey asking questions about hand eczema was conducted in 1,000 people. Through a survey company (Macoll., Seoul, Korea), we randomly sent e-mails including the questionnaire to the general population of ages between 20 and 69, across the country.
In addition, clinical features of patients with hand eczema were evaluated by a paper-and-pencil questionnaire. The patients in the outpatient clinic were requested to fill up the questionnaires. A total of 913 patients were enrolled from 24 hospitals (Table 1) located in Korea from March 2014 to April 2014. Inclusion criteria were patients of any age who were diagnosed with hand eczema. To elucidate the difference in the rates of hand eczema between health care providers and those in other occupations, we reanalyzed data from the questionnaire survey after dividing into two groups (health care providers and non-health care providers). The Declaration of Helsinki principles was followed. We explained the object of the questionnaire to all patients and they verbally agreed to participate.
All of the subjects that were enrolled, which included people from the general population and patients, completed a questionnaire in which they could select multiple answers. The questionnaire for patients with hand eczema included age, gender, residential district, occupation, suspected substance, location of lesion, symptoms, disease duration, seasonal variation, economic burden, and the source of the irritation (Fig. 1).
The questionnaire of online survey for general population included questions to determine the subject's awareness of hand eczema and how to get information regarding hand eczema.
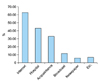
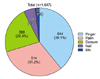
Among the 300,988 outpatients that were seen in department of dermatology at all 24 university hospitals, 7.52% (22,622/300,988) outpatients were diagnosed and treated with diseases affecting the hands. Our result showed that irritant contact dermatitis was the most common disease. The five most common diseases were irritant contact dermatitis 36.3% (8,218/22,622), palmoplantar pustular psoriasis 19.4% (4,396/22,622), atopic dermatitis 13.7% (3,108/22,622), allergic contact dermatitis 9.7% (2,187/22,622), and pompholyx 9.6% (2,167/22,622) (Fig. 2). The prevalence of these 5 diseases represented about 88.6% of all hand diseases (Fig. 2).
The online survey revealed that 31.2% (312/1,000) of general population had experienced or is currently experiencing hand eczema. The analysis on the perception of hand eczema shows that 37% (370/1,000) of general population does not know (5%) or not well known (32%) about hand eczema. In addition, 63.1% (631/1,000) of the general population responded that they searched the internet to obtain information regarding diagnosis and treatment of hand eczema (Fig. 3). It was observed that 51.3% (513/1,000) of the general population does not know that social phobias and depression can be caused by the morphology associated with chronic hand eczema (e.g., lichenification). But 82.5% (825/1,000) of general population responded that early treatment of hand eczema is needed.
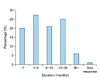
There were 603 females and 310 males making the gender ratio 1.95:1. Based on the survey of 913 patients, hand eczema predominantly affected individuals in their 20s and 30s (53.9%, 492/913) (Fig. 4). The 33.2% of patients with hand eczema answered that they suffered from hand eczema for more than a year (Fig. 5). As for the seasonal relationship of hand eczema, winter (33.6%) was the most common season of aggravation (Table 2). The highest prevalence of hand eczema was observed among health care providers (22.9%), followed by house wives (19.5%) (Table 3). For causative substance in doubt, 22.3% (156/700) chose disinfectant (Fig. 6). However, when comparing between health care providers and non-health care providers, disinfectant was the most frequent causative agent 49.8% (104/209) in health care providers, detergent 19.0% (134/704) was the most common cause in non-health care providers (Fig. 7). For the question 'Do you take steps to avoid the causative agent?', 71.8% (150/209) of health care providers and 62.9% (443/704) of non- health care providers answered that they did not know if they could avoid it.
Of the 958 replies (multiple selection), 55.9% (536/958) selected physical and psychological stress as aggravating factors (Table 4). The most frequent area affected in hand eczema was finger 39.1% (644/1,647), followed by palm 31.2% (514/1,647) (Fig. 8).
Regarding the question of managing and preventing hand eczema after diagnosis, 53.0% (484/913) of patients answered that they never (5%), rarely (20%), and sometimes (28%) did. For the question of economic burden, 47.0% (429/913) of patients answered that the costs of treatment is too expensive.
This survey included questions that asked about the quality of life in patients with hand eczema. In response to the question of whether hand eczema is an obstacle in personal relationships, 63.0% (575/913) of patients answered that hand eczema hinders personal relationships in occupational activity (Table 5). In addition, 67.0% (612/913) of patients answered that hand eczema negatively affects daily activities like work, exercise, and housekeeping. For the question as to whether hand eczema leads to depression and sleep disturbance, 47.0% (429/913) of patients answered that it does (Table 5).
Hand eczema is an inflammation of the skin affecting hands1. According to a review of population-based studies, the point prevalence of hand eczema is estimated to be approximately 4%, the 1-year prevalence of 10%, and a lifetime prevalence 15%2. Exposure to exogenous factors such as wetwork, food, gloves and oils cause irritant contact dermatitis. Allergic contact dermatitis is caused by exposure to allergens, such as chromate, nickel, biocides, and rubber chemicals. Endogenous factors such as atopic dermatitis also play a role cause hand eczema. Hand eczema can be managed with skin protection measures, including gloves and lifestyle modification, treatment education, topical treatments (e.g., moisturizers, corticosteroid, immunomodulator) and systemic treatments (e.g., azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclosporine, retinoids, corticosteroid)5.
Our results presented that irritant contact dermatitis was the most common disease among the Korean outpatients with hand disease. In addition, palmoplantar pustular psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, and pompholyx were particularly prevalent among patients with hand eczema. Irritant contact dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, and atopic dermatitis fall under etiological diagnosis of hand eczema. But, pompholyx is a type of eczma with unknown cause that is characterized by a pruritic vesicular eruption on fingers, palms, and soles1. This coincides with previous reports12,13. As Lantinga et al.12 reported irritant contact dermatitis was the most prevalent subtype (32%~48%) followed by irritant plus allergic dermatitis (14%~15%), allergic dermatitis (14%~22%), and irritant plus atopic dermatitis (6%~8%). And Meding and Swanbeck13 reported the prevalence of irritant contact dermatitis in 36%, allergic dermatitis in 16%, atopic dermatitis in 16%, pompholyx in 6%, hyperkeratotic dermatitis in 3%, nummular eczema in 2%, and unclassified eczema in 21%.
In this study, we conducted both the online survey from general population and questionnaire study from patients with hand eczema separately. The basis for this was to obtain the prevalence, knowledge and awareness of the general population regarding hand eczema and to know the clinical features and life quality of actual patients suffering from hand eczema in Korea. In this study in which an online survey of 1,000 people in the general population was conducted, the lifetime prevalence of hand eczema was 31.2%. This rate is higher compared to 15% in a previous report2. However, there might be bias, with people more interested in the topic of hand eczema being more likely to respond and since the responders are not doctors, they might be actually suffering from other diseases and not hand eczema. Analysis of the online survey regarding the perception of hand eczema showed that most of the gengeneral population was unaware of the disease and its treatment. Limited understanding of hand eczema is an obstacle to early diagnosis and treatment and in the end leads to chronic state of the disease. Over half of those who responded replied that internet is the main source of information, which is inadequate for the proper diagnosis and treatment of hand eczema. Without early diagnosis and prompt intervention, progression to chronic hand eczema may occur, in which resistance to topical treatment is common1. Approximately 80% of the general population is aware of the importance of early treatment for hand eczema. Therefore, dermatologists need to provide the correct information about hand eczema through the media, campaigns, and educational training, so people with hand eczema receive early and appropriate treatment. Age and gender distribution shows that hand eczema is most prevalent amongst people in their twenties and thirties, and females are twice more likely to be affected than males. This coincides with the previous reports214. The decade of 20~29 years is a period in life when many women, besides occupational exposure, also have skin irritant exposure to their hands from wetwork in home, including taking care of children. Also, many female-dominated occupations involve extensive wetwork (e.g., hairdressing, catering, cleaning and health-care work). This may be an important reason for the difference in occurrence of hand eczema between men and women. But, experimental studies of skin irritation have not confirmed differences between the sexes; thus, the higher prevalence of hand eczema among females is most likely due to exposure, occupational and non-occupational reasons1516.
The duration of the disease varies, but most hand eczema gets worse over time with symptoms fluctuating and persisting for several years17. In this study, the duration varied from less than a month to over three years, but 33.2% had hand eczema for over a year. Continuous exposure to allergens/irritants and the absence of adequate treatment may have a detrimental effect in hand eczema taking a chronic course. Patient's endogenous factors (e.g., atopic dermatitis) were also associated with long lasting hand eczema14.
In the search for common causative agents and aggravating factors, we first looked at the relationship between seasons and symptoms. Many patients (33.6%) answered that winter was the time when symptoms were the worst, while 30.4% answered that there was not one season when it was worse. Thyssen et al.2 suggested that hand eczema was more common in dry and cold weather. Climatic conditions may possibly affect the prevalence of hand eczema, although no studies have ever been sufficiently conducted.
In regards to occupation, health care providers are most commonly affected (22.9%) followed by house wives (19.5%). This may be due to the fact that health care providers are frequently exposed to water, disinfectant, chemicals, and dirt. This also coincides with the previous research results1819. Disinfectant and detergent are the most common self-considered causative agents of hand eczema in 22.3% and 20.7% of cases, respectively. Disinfectants are antimicrobial agents to destroy microorganisms that are living on the objects and work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with the metabolism. And detergents are surfactant or mixture of surfactants with cleaning properties in dilute solution. It is likely that these irritants aggravate the disease. However, there was a difference in the causative substance between health care providers and non- health care providers. As expected, health care providers answered that disinfectant was the most likely causative agent. Hand washing is now mandatory in most hospitals and other healthcare facilities for infection control. Because frequent hand washing with a disinfectant can induce hand eczema, further studies need to be conducted to elucidate the effect of hand washing policy on hand eczema in health care providers. It takes a lot of time and effort to avoid causative agents, however, avoidance alone can prevent the occurrence of hand eczema and improve symptoms. Therefore, health care providers should do whatever they can to avoid these causative agents to protect their skin. For example, skin care products in the form of thick creams, ointments, or petrolatum are important in helping to restore the skin's protective barrier. Frequent reapplication, especially after hand washing, is important. Use of protective gloves may be helpful as well. Also proper treatments such as topical steroids, UV irradiation and oral agents can improve lesions. In non- health care provider group, the largest proportion of patient with hand eczema were house wives, in which the hands were frequently exposed to detergents, may have been an important factor for this result. This result was similar to previous study7.
The regional distribution of hand eczema in this study shows that the lesions are more concentrated on the fingers and palms compared to lesions on the fingernails and dorsal side of the hand. These results were also observed in a previous study11, and it is likely that the fingers and palms are the areas of the hand most exposed to irritants.
The 53% of the patients did not properly manage after being diagnosed hand eczema. Lack of proper management and prevention leads to the chronic status of the disease which shows resistance to topical treatments1.
The economic impact of hand eczema is huge to both the individuals and society. In this study, 47% subjects responded that treatment and management of hand eczema was a financial burden. Hand eczema is chronic and requires consistent management with medication, topical agent, moisturizers, and emollients. Thus, treatment of hand eczema is costly and has been done over a long period of time. And painful fissures and blisters can prevent manual work, leading to significant disability and huge economic loss to both individuals and society. Hand eczema has been shown to be a major cause of morbidity and lost earnings20. Another survey, occupational HE leads to prolonged sick leave in 19.9% and job loss in 23% over the course of a year9. Socially, workers' compensation, disability payments, loss productivity, and costs of occupational retraining are all expenses 3.
In online survey from general population, more than half of the general population doesn't know that hand eczema affect psychological status. But, in questionnaire for patients with hand eczema, many patients answered that hand eczema hinders occupational activity and personal relationships. In addition, they replied that hand eczema negatively affects daily living activities like house work and exercise and leads to depression and sleep disturbance. Through these results, the psychological impact of hand eczema on the general population is thought to be minimal to none but many patients are actually suffering from the psychological impact of this disease. Hand eczema is localized on highly visible areas of the body, the hands. The hands are important organs of communication and expression. Therefore, any impairment in function and form may result in major psychosocial problems such as anxiety, low self-esteem, and social phobia5. Another study performed to investigate the associations between hand eczema and depressive mood7. In this study, positive associations between dermatology life quality index (DLQI) and hand eczema severity index (HECSI) scores. Beck's depression inventory (BDI-II) scores had also positive correlations with HECSI scores. And DLQI and BDI-II scores both increased with disease severity. These data revealed that emotional support might be helpful in treating patients with hand eczema. Psychiatric consultation should also be considered for treat patients with hand eczema.
The limitation of this study is in the online survey of the general population as it relies on the responders' self-diagnosis of hand eczema without the consultation of a doctor, which may lead to higher prevalence. Also, in the outpatient clinic investigation, the collection of data relied on the patients' memories and subjective interpretations. Therefore, the results from our survey could be affected by recall bias and subjective judgment. Also, the questionnaire was answered without the dermatologist cross checking which may lead to imprecise results. However, this was the first multicenter epidemiologic study of hand eczema in Korea, using data from a large number of patients, to identify the clinical feature and awareness of hand eczema.
In conclusion, this study presented the clinical characteristics of Korean patients with hand eczema. In addition, our data from the online survey suggested that dermatologists should take steps to educate the population about the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. This study will be useful as fundamental study when further studies in hand eczema take place.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 2
Prevalence of diseases affecting the hands. ICD: irritant contact dermatitis, PPP: palmoplantar pustular psoriasis, ACD: allergic contact dermatitis, H-F-M disease: hand foot mouth disease.
Table 1
Hospital list involved in patients survey

Table 2
Season in which patients with hand eczema experience the most aggravated symptoms

| Season | Patients* | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Spring | 152 | 12.2 |
| Summer | 208 | 16.8 |
| Fall | 87 | 7.0 |
| Winter | 417 | 33.6 |
| Unrelated | 377 | 30.4 |
| Total | 1,241 | 100.0 |
Table 3
Distribution of professions among patients with hand eczema

Table 4
Non-seasonal aggravating factors in patients with hand eczema
| Factor | Patients* (%) |
|---|---|
| Stress | 536 (55.9) |
| None | 255 (26.6) |
| Illness | 36 (3.8) |
| Etc. | 131 (13.7) |
| Total | 958 (100.0) |
Table 5
Questions about the quality of life in patients with hand eczema

References
2. Thyssen JP, Johansen JD, Linneberg A, Menné T. The epidemiology of hand eczema in the general population--prevalence and main findings. Contact Dermatitis. 2010; 62:75–87.

3. Diepgen TL, Coenraads PJ. The epidemiology of occupational contact dermatitis. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1999; 72:496–506.

4. Golden S, Shaw T. Hand dermatitis: review of clinical features and treatment options. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013; 32:147–157.

5. Diepgen TL, Agner T, Aberer W, Berth-Jones J, Cambazard F, Elsner P, et al. Management of chronic hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis. 2007; 57:203–210.

6. Scalone L, Cortesi PA, Mantovani LG, Belisari A, Ayala F, Fortina AB, et al. Clinical epidemiology of hand eczema in patients accessing dermatological reference centres: results from Italy. Br J Dermatol. 2015; 172:187–195.

7. Yu M, Han TY, Lee JH, Son SJ. The quality of life and depressive mood among Korean patients with hand eczema. Ann Dermatol. 2012; 24:430–437.

8. Cvetkovski RS, Zachariae R, Jensen H, Olsen J, Johansen JD, Agner T. Quality of life and depression in a population of occupational hand eczema patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2006; 54:106–111.

9. Cvetkovski RS, Rothman KJ, Olsen J, Mathiesen B, Iversen L, Johansen JD, et al. Relation between diagnoses on severity, sick leave and loss of job among patients with occupational hand eczema. Br J Dermatol. 2005; 152:93–98.

10. Hald M, Berg ND, Elberling J, Johansen JD. Medical consultations in relation to severity of hand eczema in the general population. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 158:773–777.

11. Choi JI, Pak HN, Park JS, Kwak JJ, Nagamoto Y, Lim HE, et al. Clinical significance of early recurrences of atrial tachycardia after atrial fibrillation ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010; 21:1331–1337.

12. Lantinga H, Nater JP, Coenraads PJ. Prevalence, incidence and course of eczema on the hands and forearms in a sample of the general population. Contact Dermatitis. 1984; 10:135–139.

13. Meding B, Swanbeck G. Epidemiology of different types of hand eczema in an industrial city. Acta Derm Venereol. 1989; 69:227–233.
14. Veien NK, Hattel T, Laurberg G. Hand eczema: causes, course, and prognosis I. Contact Dermatitis. 2008; 58:330–334.

15. Meding B. Differences between the sexes with regard to work-related skin disease. Contact Dermatitis. 2000; 43:65–71.
16. Darlenski R, Fluhr JW. Influence of skin type, race, sex, and anatomic location on epidermal barrier function. Clin Dermatol. 2012; 30:269–273.

17. Meding B, Wrangsjö K, Järvholm B. Fifteen-year follow-up of hand eczema: persistence and consequences. Br J Dermatol. 2005; 152:975–980.

18. Templet JT, Hall S, Belsito DV. Etiology of hand dermatitis among patients referred for patch testing. Dermatitis. 2004; 15:25–32.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download