Abstract
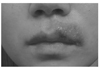
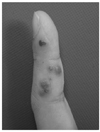
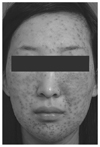
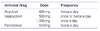
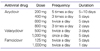
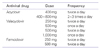
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is one of Herpesviridae family viruses which belong to DNA viruses. HSV-associated diseases are among the most widespread infections, affecting nearly 60% to 95% of human adults. Labial herpes typically results from infection with HSV type 1 (HSV-1), whereas most genital herpes is caused by HSV type 2 (HSV-2). They are incurable and persist during the lifetime of the host, often in latent form. Antiviral agents do not cure HSV infections, but rather modify the clinical course of the disease. Topical, oral, or intravenous antiviral agents may be used in the management of HSV infections. Acyclovir, valacyclovir hydrochloride, and famciclovir are the 3 antiviral drugs commonly used to treat symptomatic HSV infections. However, it is very difficult to choose an appropriate drug and dosing regimen.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Fatahzadeh M, Schwartz RA. Human herpes simplex virus infections: epidemiology, pathogenesis, symptomatology, diagnosis, and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007. 57:737–763. quiz 64-66.

2. Cernik C, Gallina K, Brodell RT. The treatment of herpes simplex infections: an evidence-based review. Arch Intern Med. 2008. 168:1137–1144.

3. KDA. Textbook Editing Board. Dermatology. 2008. 5th ed. Seoul: Ryo Moon Gak;386–389.
4. Marques AR, Strauss SE. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller A, Leffell DJ, editors. Herpes simplex. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2007. 7th ed. Columbus: McGraw-Hill;1873–1885.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download