Abstract
Cardiac rhythm management device (CRMD) infection is rare, but potentially life-threatening complication. Despite technical evolution of cardiac device, the cases of CRMD infection have increased remarkably over the past decades. In this review, several important key points were discussed with regards to the epidemiology, pathogenesis, risk factors, microbiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of CRMD infection.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Management of cardiac rhythm management device infection (adapted from Sohail et al. [19]). *The duration of antibiotics should be counted from the day of device explantation.
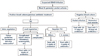
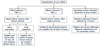
Figure 2
Implantation of a new device in patients with cardiac rhythm management device infection (adapted from Sohail et al.[19]).
References
1. Bluhm G. Pacemaker infections. A clinical study with special reference to prophylactic use of some isoxazolyl penicillins. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1985. 699:1–62.
2. Conklin EF, Giannelli S Jr, Nealon TF Jr. Four hundred consecutive patients with permanent transvenous pacemakers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1975. 69:1–7.

3. Mela T, McGovern BA, Garan H, Vlahakes GJ, Torchiana DF, Ruskin J, Galvin JM. Long-term infection rates associated with the pectoral versus abdominal approach to cardioverter-defibrillator implants. Am J Cardiol. 2001. 88:750–753.

4. Mirowski M, Reid PR, Mower MM, Watkins L, Gott VL, Schauble JF, Langer A, Heilman MS, Kolenik SA, Fischell RE, Weisfeldt ML. Termination of malignant ventricular arrhythmias with an implanted automatic defibrillator in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980. 303:322–324.

5. Zhan C, Baine WB, Sedrakyan A, Steiner C. Cardiac device implantation in the United States from 1997 through 2004: a population-based analysis. J Gen Intern Med. 2008. 23:Suppl 1. 13–19.

6. Baddour LM, Epstein AE, Erickson CC, Knight BP, Levison ME, Lockhart PB, Masoudi FA, Okum EJ, Wilson WR, Beerman LB, Bolger AF, Estes NA 3rd, Gewitz M, Newburger JW, Schron EB, Taubert KA. American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee. Council on Cardiovascular Disease in Young. Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia. Council on Cardiovascular Nursing. Council on Clinical Cardiology. Interdisciplinary Council on Quality of Care. American Heart Association. Update on cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections and their management: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010. 121:458–477.

7. Cox JN. Pathology of cardiac pacemakers and central catheters. Curr Top Pathol. 1994. 86:199–271.

8. Spittell PC, Hayes DL. Venous complications after insertion of a transvenous pacemaker. Mayo Clin Proc. 1992. 67:258–265.

9. Da Costa A, Lelièvre H, Kirkorian G, Célard M, Chevalier P, Vandenesch F, Etienne J, Touboul P. Role of the preaxillary flora in pacemaker infections: a prospective study. Circulation. 1998. 97:1791–1795.

10. Heilmann C, Schweitzer O, Gerke C, Vanittanakom N, Mack D, Götz F. Molecular basis of intercellular adhesion in the biofilm-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis. Mol Microbiol. 1996. 20:1083–1091.

11. Camus C, Leport C, Raffi F, Michelet C, Cartier F, Vilde JL. Sustained bacteremia in 26 patients with a permanent endocardial pacemaker: assessment of wire removal. Clin Infect Dis. 1993. 17:46–55.

12. Chamis AL, Peterson GE, Cabell CH, Corey GR, Sorrentino RA, Greenfield RA, Ryan T, Reller LB, Fowler VG Jr. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in patients with permanent pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Circulation. 2001. 104:1029–1033.

13. Uslan DZ, Sohail MR, Friedman PA, Hayes DL, Wilson WR, Steckelberg JM, Baddour LM. Frequency of permanent pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator infection in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 43:731–736.

14. Aggarwal RK, Connelly DT, Ray SG, Ball J, Charles RG. Early complications of permanent pacemaker implantation: no difference between dual and single chamber systems. Br Heart J. 1995. 73:571–575.

15. Klug D, Balde M, Pavin D, Hidden-Lucet F, Clementy J, Sadoul N, Rey JL, Lande G, Lazarus A, Victor J, Barnay C, Grandbastien B, Kacet S. PEOPLE Study Group. Risk factors related to infections of implanted pacemakers and cardioverter-defibrillators: results of a large prospective study. Circulation. 2007. 116:1349–1355.

16. Sohail MR, Uslan DZ, Khan AH, Friedman PA, Hayes DL, Wilson WR, Steckelberg JM, Stoner SM, Baddour LM. Risk factor analysis of permanent pacemaker infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 45:166–173.

17. Chua JD, Wilkoff BL, Lee I, Juratli N, Longworth DL, Gordon SM. Diagnosis and management of infections involving implantable electrophysiologic cardiac devices. Ann Intern Med. 2000. 133:604–608.

18. Margey R, McCann H, Blake G, Keelan E, Galvin J, Lynch M, Mahon N, Sugrue D, O'Neill J. Contemporary management of and outcomes from cardiac device related infections. Europace. 2010. 12:64–70.

19. Sohail MR, Uslan DZ, Khan AH, Friedman PA, Hayes DL, Wilson WR, Steckelberg JM, Stoner S, Baddour LM. Management and outcome of permanent pacemaker and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator infections. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. 49:1851–1859.

20. Tascini C, Bongiorni MG, Gemignani G, Soldati E, Leonildi A, Arena G, Doria R, Giannola G, La Pira F, Tagliaferri E, Caravelli P, Dell'Anna R, Menichetti F. Management of cardiac device infections: A retrospective survey of a non-surgical approach combining antibiotic therapy with transvenous removal. J Chemother. 2006. 18:157–163.

21. Karchmer AW, Longworth DL. Infections of intracardiac devices. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2002. 16:477–505. xii

22. Lewis AB, Hayes DL, Holmes DR Jr, Vlietstra RE, Pluth JR, Osborn MJ. Update on infections involving permanent pacemakers. Characterization and management. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1985. 89:758–763.
23. Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 2010. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier.
24. Arber N, Pras E, Copperman Y, Schapiro JM, Meiner V, Lossos IS, Militianu A, Hassin D, Pras E, Shai A, Moshkowitz M, Sidi Y. Pacemaker endocarditis. Report of 44 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1994. 73:299–305.

25. Sohail MR, Uslan DZ, Khan AH, Friedman PA, Hayes DL, Wilson WR, Steckelberg JM, Jenkins SM, Baddour LM. Infective endocarditis complicating permanent pacemaker and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator infection. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008. 83:46–53.

26. Klug D, Lacroix D, Savoye C, Goullard L, Grandmougin D, Hennequin JL, Kacet S, Lekieffre J. Systemic infection related to endocarditis on pacemaker leads: clinical presentation and management. Circulation. 1997. 95:2098–2107.

27. Schulze MR, Ostermaier R, Franke Y, Matschke K, Braun MU, Strasser RH. Images in cardiovascular medicine. Aortic endocarditis caused by inadvertent left ventricular pacemaker lead placement. Circulation. 2005. 112:e361–e363.
28. Cacoub P, Leprince P, Nataf P, Hausfater P, Dorent R, Wechsler B, Bors V, Pavie A, Piette JC, Gandjbakhch I. Pacemaker infective endocarditis. Am J Cardiol. 1998. 82:480–484.

29. Duval X, Selton-Suty C, Alla F, Salvador-Mazenq M, Bernard Y, Weber M, Lacassin F, Nazeyrolas P, Chidiac C, Hoen B, Leport C. Association pour l'Etude et la Prevention de l'Endocardite Infectieuse. Endocarditis in patients with a permanent pacemaker: a 1-year epidemiological survey on infective endocarditis due to valvular and/or pacemaker infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:68–74.

30. Victor F, De Place C, Camus C, Le Breton H, Leclercq C, Pavin D, Mabo P, Daubert C. Pacemaker lead infection: echocardiographic features, management, and outcome. Heart. 1999. 81:82–87.

31. Vilacosta I, Sarriá C, San Román JA, Jiménez J, Castillo JA, Iturralde E, Rollán MJ, Martínez Elbal L. Usefulness of transesophageal echocardiography for diagnosis of infected transvenous permanent pacemakers. Circulation. 1994. 89:2684–2687.

32. Lo R, D'Anca M, Cohen T, Kerwin T. Incidence and prognosis of pacemaker lead-associated masses: a study of 1,569 transesophageal echocardiograms. J Invasive Cardiol. 2006. 18:599–601.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download