Abstract
Background:
Patient adherence to immunosuppressant regimens after organ transplant is crucial to preserve graft function, and simplifying the regimen improves adherence. In this study, our experience of conversion from twice-daily (b.i.d.) to once-daily (q.d.) tacrolimus (TAC) in stable liver transplant recipients is reviewed and the proper conversion regimen is investigated.
Methods:
Between November 2011 and August 2012, the regimen was converted in 32 stable liver transplant recipients, and data on the conversions gathered retrospectively from medical records. TAC trough level, dose, and laboratory findings were evaluated at preconversion and 1 to 12 months after conversion.
Results:
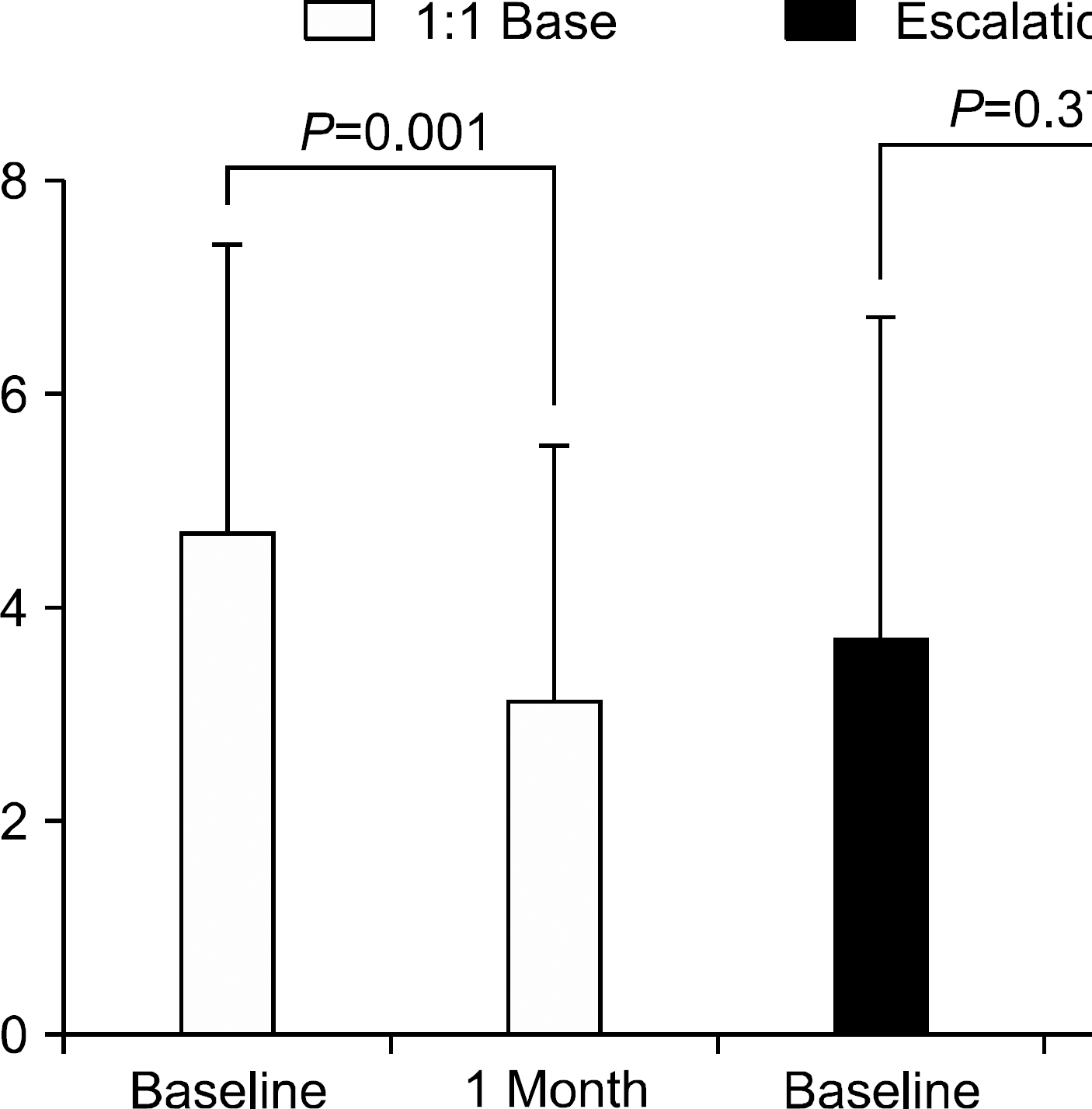
Conversion from b.i.d. to q.d. regimen was based on 1:1 proportion in 16 patients and dose escalation in 16 patients. The mean conversion time after transplant was 56.8 months (range; 21∼94). Reconversion to b.i.d. regimen was needed in nine patients. Among these patients, seven patients needed titration due to elevated liver enzyme. The trough level decreased significantly after conversion (from 4.7 to 3.1 ng/mL) in patients with conversion at 1:1 proportion, while increasing slightly without statistical significance (3.7 to 4.0 ng/mL) in patients with dose escalation. At 1 year after conversion, dose adjustment was required to preserve trough level and graft function in 14 patients.
REFERENCES
1). Chapman JR. Compliance: the patient, the doctor, and the medication? Transplantation. 2004. 77:782–6.

2). Lieber SR., Volk ML. Non-adherence and graft failure in adult liver transplant recipients. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. 58:824–34.

3). Dumortier J., Guillaud O., Boillot O. Conversion from twice daily tacrolimus to once daily tacrolimus in long-term stable liver transplant recipients: a single-center experience with 394 patients. Liver Transpl. 2013. 19:529–33.

4). Beckebaum S., Iacob S., Sweid D., Sotiropoulos GC., Saner F., Kaiser G, et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunosuppressant adherence in stable liver transplant patients converted from a twice-daily tacrolimus-based regimen to once-daily tacrolimus extended-release formulation. Transpl Int. 2011. 24:666–75.

5). Alloway RR., Eckhoff DE., Washburn WK., Teperman LW. Conversion from twice daily tacrolimus capsules to once daily extended-release tacrolimus (LCP-Tacro): phase 2 trial of stable liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2014. 20:564–75.

6). Giannelli V., Rossi M., Giusto M., Lucidi C., Lattanzi B., Ruffa A, et al. Conversion from twice-daily to once-daily Tacrolimus administration in liver transplant patient: results of long term follow-up. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013. 17:2718–20.

7). Valente G., Rinaldi L., Sgambato M., Piai G. Conversion from twice-daily to once-daily tacrolimus in stable liver transplant patients: effectiveness in a real-world setting. Transplant Proc. 2013. 45:1273–5.

8). Jannot M., Masson I., Alamartine E., Mariat C. Early conversion from twice-daily tacrolimus to once-daily extended formulation in renal transplant patients before hospital discharge. Ann Transplant. 2014. 19:320–4.

9). Laederach-Hofmann K., Bunzel B. Noncompliance in organ transplant recipients: a literature review. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2000. 22:412–24.

10). Ichimaru N., Kakuta Y., Abe T., Okumi M., Imamura R., Isaka Y, et al. Treatment adherence in renal transplant recipients: a questionnaire survey on immunosuppressants. Transplant Proc. 2008. 40:1362–5.

11). Trunecka P., Boillot O., Seehofer D., Pinna AD., Fischer L., Ericzon BG, et al. Once-daily prolonged-release tacrolimus (ADVAGRAF) versus twice-daily tacrolimus (PROGRAF) in liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2010. 10:2313–23.
12). Kim SH., Lee SD., Kim YK., Park SJ. Conversion of twice-daily to once-daily tacrolimus is safe in stable adult living donor liver transplant recipients. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015. 14:374–9.

13). Dopazo C., Rodriguez R., Llado L., Calatayud D., Castells L., Ramos E, et al. Successful conversion from twice-daily to once-daily tacrolimus in liver transplantation: observational multicenter study. Clin Transplant. 2012. 26:E32–7.

14). Sanko-Resmer J., Boillot O., Wolf P., Thorburn D. Renal function, efficacy and safety postconversion from twice- to once-daily tacrolimus in stable liver recipients: an open-label multicenter study. Transpl Int. 2012. 25:283–93.
Table 1.
Patients characteristics at the time of conversion (n=32)
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Sex (males/female) | 24/8 |
| Age at conversion (yr) | 55±9.9 (18∼72) |
| Time from LT to conversion | 56.8±19.49 (21∼94) |
| Immunosuppressant regimen | |
| TAC single | 30 |
| TAC+MMF | 2 |
| History of rejection episode | 5 (16) |
| Indications for LT | |
| Hepatitis B virus | 18 (56) |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 10 (31) |
| Others | 4 (13) |
| Mean TAC dose (mg/day) | 2.03±0.60 (1∼4) |
| Baseline mean trough level (ng/mL) | 4.2±1.50 (1.9∼7.4) |
| Reconversion to TAC twice-daily | 9 (28) |
| Time from conversion to reconversion | 4.4±4.12 (0.9∼11.4) |
| Cause of reconversion | |
| Elevated AST or ALT (1:1/escalation) | 7 (5/2) |
| Uncontrolled trough level | 1 |
| Neurologic symptoma | 1 |
Table 2.
Liver function, kidney function, serum trough level, and dose of TAC in patients with successful conversion at baseline and after the conversion from TAC twice-daily to TAC once-daily (n=23)
Table 3.
Comparison of characteristics and results between 1:1 dose group and escalation group




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download