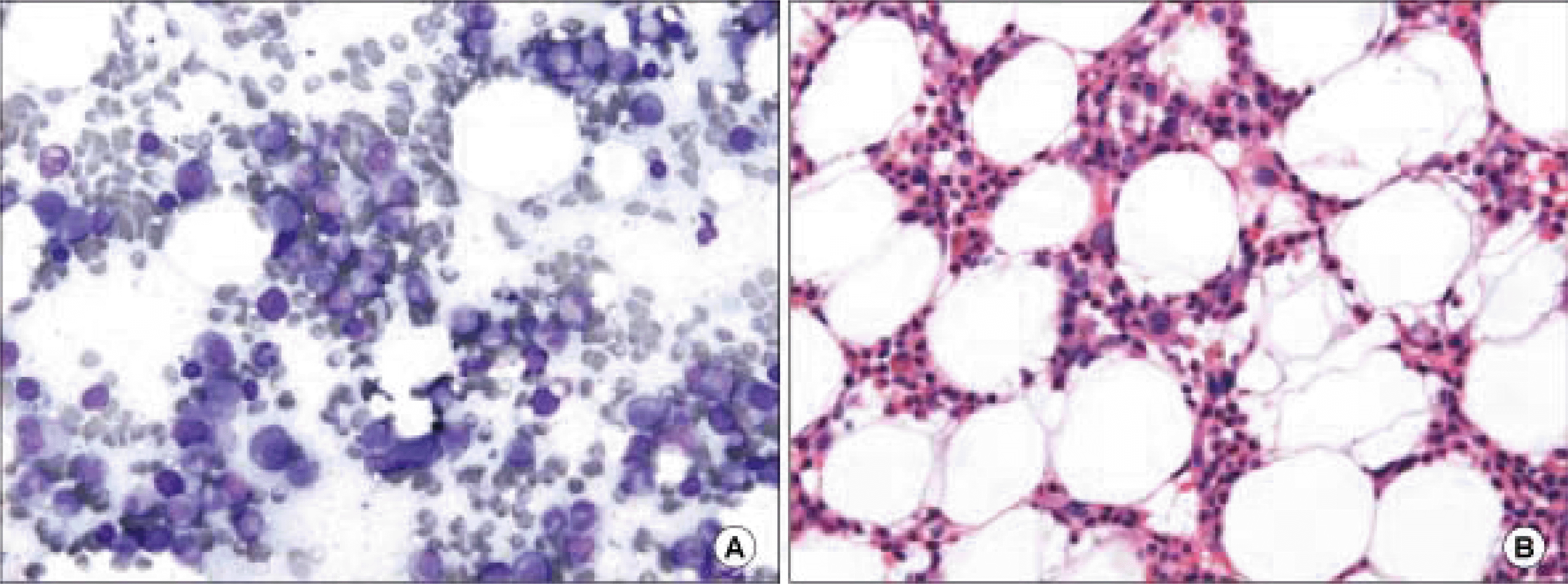
Abstract
A 63-year-old man was placed on hemodialysis for the end-stage of renal disease secondary to renal artery stenosis. He was also regularly given epoetin, subcutaneously, for anemia associated with his renal disease. Rapidly progressing erythropoietin (EPO) resistant anemia and reticulocytopenia developed after 1 year of hemodialysis. The patient required frequent red blood cell transfusions. The bone marrow examination demonstrated selective erythroid hypoplasia. A detailed search for the cause of the erythroblastopenia revealed nothing, with the exception of anti-EPO antibodies (Ab). Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) was suspected due to the anti-EPO Ab. With the immunosuppressive agent and change to the epoetin-therapy, the patient recovered his hemoglobin and reticulocyte counts. Particular attention should be paid for the possibility of PRCA due to anti-EPO Ab in patients undergoing rHuEPO therapy, with an unexplained recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) resistant anemia, especially via the subcutaneous route.
REFERENCES
1). Drueke TB. R-HuEpo hyporesponsiveness–who and why. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995; 10(Suppl 2):62–8.
3). Casadevall N, Nataf J, Viron B, et al. Pure red-cell aplasia and antierythropoietin antibodies in patients treated with recombinant erythropoietin. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:469–75.
4). Quint L, Casadevall N, Giraudier S. Pure red cell aplasia in patients with refractory anaemia treated with two different recombinant erythropoietins. Br J Haematol. 2004; 124:842.

5). Rameshwar P, Ramkissoon SH, Sundararajan S, Gascon P. Defect in the lymphoid compartment might account for CD8+- mediated effects in the pathophysiology of pure red cell aplasia. Clinical Immunol. 2003; 108:248–56.
6). Mamiya S, Itoh T, Miura AB. Acquired pure red cell aplasia in Japan. Eur J Haematol. 1997; 59:199–205.

7). Tanuma Y, Yokoo A, Takashima H. Acquired pure red cell aplasia in a hemodialyzed patient. Int J Urol. 2003; 10:550–3.

8). Schonholzer C, Keusch G, Nigg L, Robert D, Wau-ters JP. High prevalence in Switzerland of pure red-cell aplasia due to anti-erythropoietin antibodies in chronic dialysis patients: report of five cases. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004; 19:2121–5.

9). Locatelli F, Aljama P, Barany P, et al. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and antibody-mediated pure red-cell aplasia: here are we now and where do we go from here? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004; 19:288–93.

10). Eckardt KU, Casadevall N. Pure red-cell aplasia due to anti-erythropoietin antibodies. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003; 18:865–9.

11). Panchapakesan U, Austin SK, Shafransky A, Lawrence JA, Savdie E. Recovery of pure red-cell aplasia secondary to antierythropoietin antibodies after cessation of recombinant human erythropoietin. Intern Med J. 2003; 33:468–71.

12). Summers SA, Matijevic A, Almond MK. Successful reintroduction of recombinant human erythropoietin following antibody induced pure red cell aplasia. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004; 19:2137–9.

13). Vartia A, Asola MR, Tertti R, Kunelius P, Metsarinne KP. Two haemodialysis patients with epoetin alfa-induced pure red-cell aplasia recovered despite treatment with another epoetin preparation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004; 19:1313–6.

14). Casadevall N. Antibodies against rHuEPO: native and recombinant. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002; 17(Suppl 5):42–7.

15). Yang JO, Gil HW, Kwon SH, Choi YJ, Lee EY, Hong SY. Pure red-cell aplasia due to antibodies against erythropoietin. Korean J Nephrol. 2004; 23:528–31.
16). Yang JS, Lee JE, Park DJ, et al. Two cases of pure red cell aplasia due to anti-erythropoietin antibodies. Korean J Nephrol. 2004; 23:809–14.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download