Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
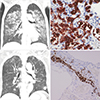
Journal List > J Korean Med Sci > v.31(7) > 1023008

Ji Young Moon 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2768-7810
Won Hong Park 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0716-7914
Jin Man Kim 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3129-3355
Yoon Seok Choi 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0054-3641
Ik-Chan Song 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6938-970X
Hyo Jin Lee 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8378-3001
Deog-Yeon Jo 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8267-4214
Samyong Kim 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5993-1430
Young Jun Yang 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4394-7993
Song Soo Kim 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3078-2184
Jin Hwan Kim 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1632-2421
Hwan-Jung Yun 
https://orcid.org/http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0696-1235