Abstract
Background
Allergen specific IgE (sIgE) assay is an important aid in the diagnosis and treatment of allergy. We evaluated the analytical performance of a quantitative chemiluminescence immunoassay for sIgE using the continuous random access ADVIA Centaur.
Methods
Six ADVIA Centaur sIgE reagents for common inhalant allergens in Korea, d1, d2, e1, e5, t3, and t7, were evaluated for precision, dilution recovery (parallelism), comparison with Pharmacia UniCAP sIgE assay and skin prick test, sample volume, and analytical speed according to the NCCLS guidelines (I/LA20-A, EP5-A2). Commercialized positive and negative quality control materials were used for a precision study, and samples from a total of 110 patients were used for dilution recovery and comparison studies.
Results
Within-run coefficients of variation (CV) of the 6 items were 3.45–6.14% and within-device CVs (total CVs) of all items were below 10%. Interdilutional CVs of all items were 2.84–11.95%, which showed a good linearity and parallelism over its measuring range. Positive/negative concordance rates of the 6 items with UniCAP sIgE assay were 76.3–96.1% (d1, 88.2%; d2, 96.1%; e1, 91.0%; e5, 77.0%; t3, 90.5%; and t7, 76.3%). Concordance rates of the six items with skin prick test were all above 80%. The quantity of sample volume (25 μL/test) needed was relatively small, and a high throughput (120 tests/hr) and rapid turnaround time (47 min) could be achieved.
References
1. Kim SH, Lee JY, Son SW, Chang YS, Jung JW, Kim YK, et al. Prevalence of adult asthma based on questionnaires and methacholine bronchial provocation test in Seoul. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 21:618–27.
2. Kim HS, Park CW, Lee JS, Cho YJ. The sensitization rate to house dust mites and the prevalence of asthma in healthy young women. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 24:103–9.
3. Lee KH. Comparative analyses of prevalence of allergic diseases by countries. New Med J. 2002; 45:181–90.
4. Kim HS, Kim DJ, Lee SG. Analysis of simultaneous positivity to multiple allergens on MAST CLA test. Korean J Lab Med. 2005; 25:448–56.
5. Park DS, Cho JH, Lee KE, Ko OS, Kim HR, Choi SI, et al. Detection rate of allergen-specific IgE by Multiple antigen simultaneous test-immunoblot assay. Korean J Lab Med. 2004; 24:131–8.
6. Johansson SG. ImmunoCAP Specific IgE test: an objective tool for research and routine allergy diagnosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2004; 4:273–9.

7. Petersen AB, Gudmann P, Milvang-Gronager P, Morkeberg R, Bogestrand S, Linneberg A, et al. Performance evaluation of a specific IgE assay developed for the ADVIA centaur immunoassay system. Clin Biochem. 2004; 37:882–92.

8. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of precision performance of quantative measurement methods; Approved quideline-second edition. NCCLS document EP5-A2. NCCLS, Wayne, PA, USA,. 2004.
9. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation methods and analytical performance characteristics of immunological assays for human immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies of defined allergen specificities; Approved guideline. NCCLS document I/LA20-A. NCCLS, Wayne, PA, USA,. 1997.
11. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. User protocol for evaluation of qualitative test performance; Approved guideline. NCCLS document EP12-A.NCCLS, Wayne, PA, USA,. 2002.
12. van der Veen MJ, Mulder M, Witteman AM, van Ree R, Aalberse RC, Jansen HM, et al. False-positive skin prick test responses to commercially available dog dander extracts caused by contamination with house dust mite (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 98:1028–34.
13. Johansen N, Brink-Andersen U. Discordance analysis of dog dander specific IgE assay form tow in vitro systems in XXII EAACI Congress. 2003; 366.
14. Ricci G, Capelli M, Miniero R, Menna G, Zannarini L, Dillon P, et al. A comparison of different allergometric tests, skin prick test, Pharmacia UniCAP and ADVIA Centaur, for diagnosis of allergic diseases in children. Allergy. 2003; 58:38–45.
15. Ollert M, Weissenbacher S, Rakoski J, Ring J. Allergen-specific IgE measured by a continuous random-access immunoanalyzer: interassay comparison and agreement with skin testing. Clin Chem. 2005; 51:1241–9.

16. Kwak YG, Maeng SH, Kim HS, Cho YJ. Comparison of Pharmacia CAP system and Auro Dex(R) Visual ENS(TM) screening test for detecting specific IgE in atopic patients. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 23:53–62.
17. Yoon SY, Suhr KB, Lee JH, Park JK. A study on the reproducibility of allergen skin test in type I hypersensitivity. Korean J Allergy. 1997; 17:549–55.
Fig. 1.
Dilution-recovery analysis for the ADVIA Centaur sIgE assay. D1, house dust mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; D2, house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae; E1, Cat Dander, Felis domesticus; E5, Dog dander, Canis familaris; T3, Birch, Betula verrucosa; T7, White oak, Quercus alba.
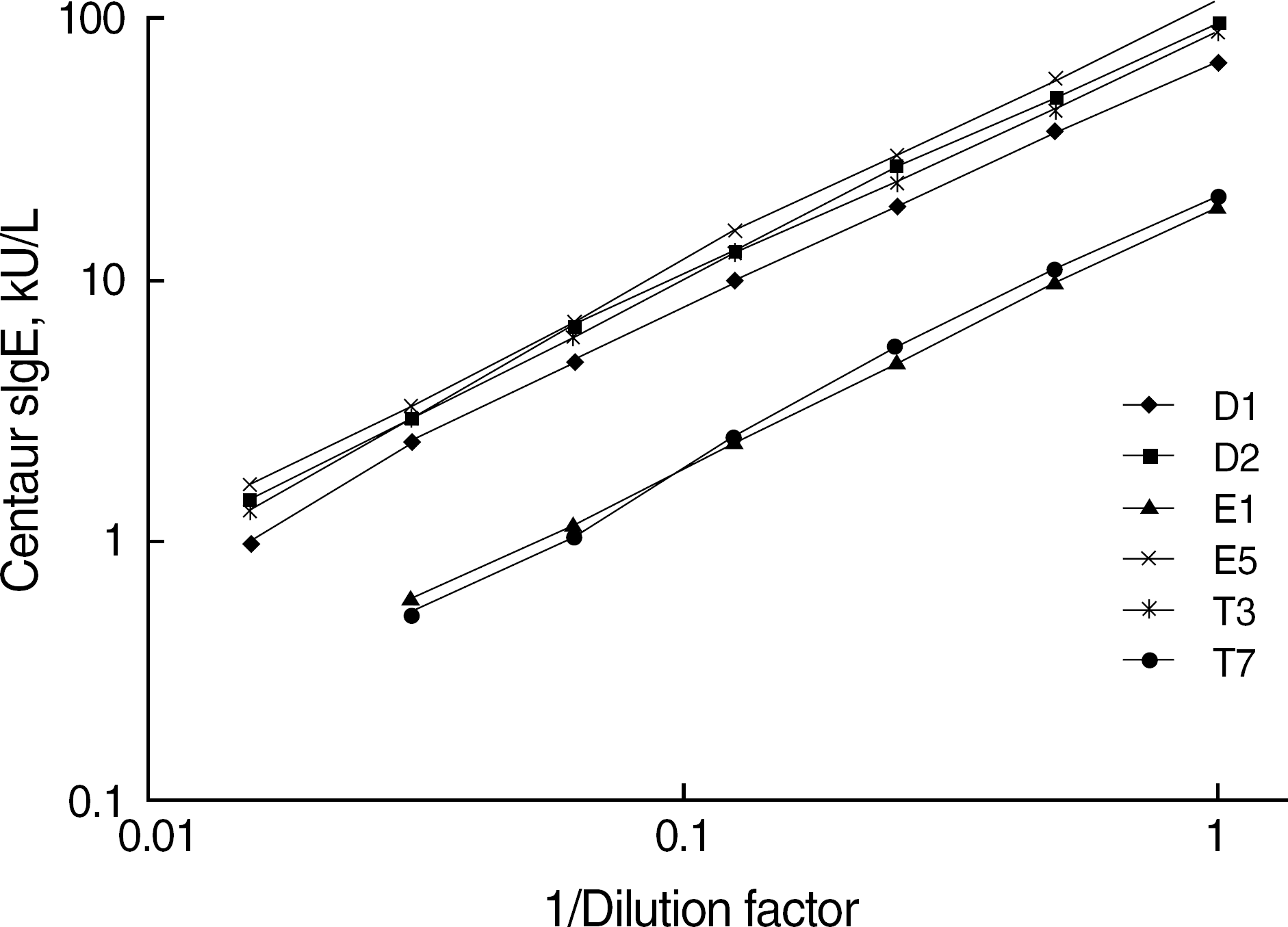
Fig. 2.
Comparison studies between ADVIA Centaur sIgE assay and Pharmacia CAP system for 6 different allergens. The detection limit (0.35 kU/L) is shown by a solid line. D1, house dust mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; D2, house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae; E1, Cat Dander, Felis domesticus; E5, Dog dander, Canis familaris; T3, Birch, Betula verrucosa; T7, White oak, Quercus alba.
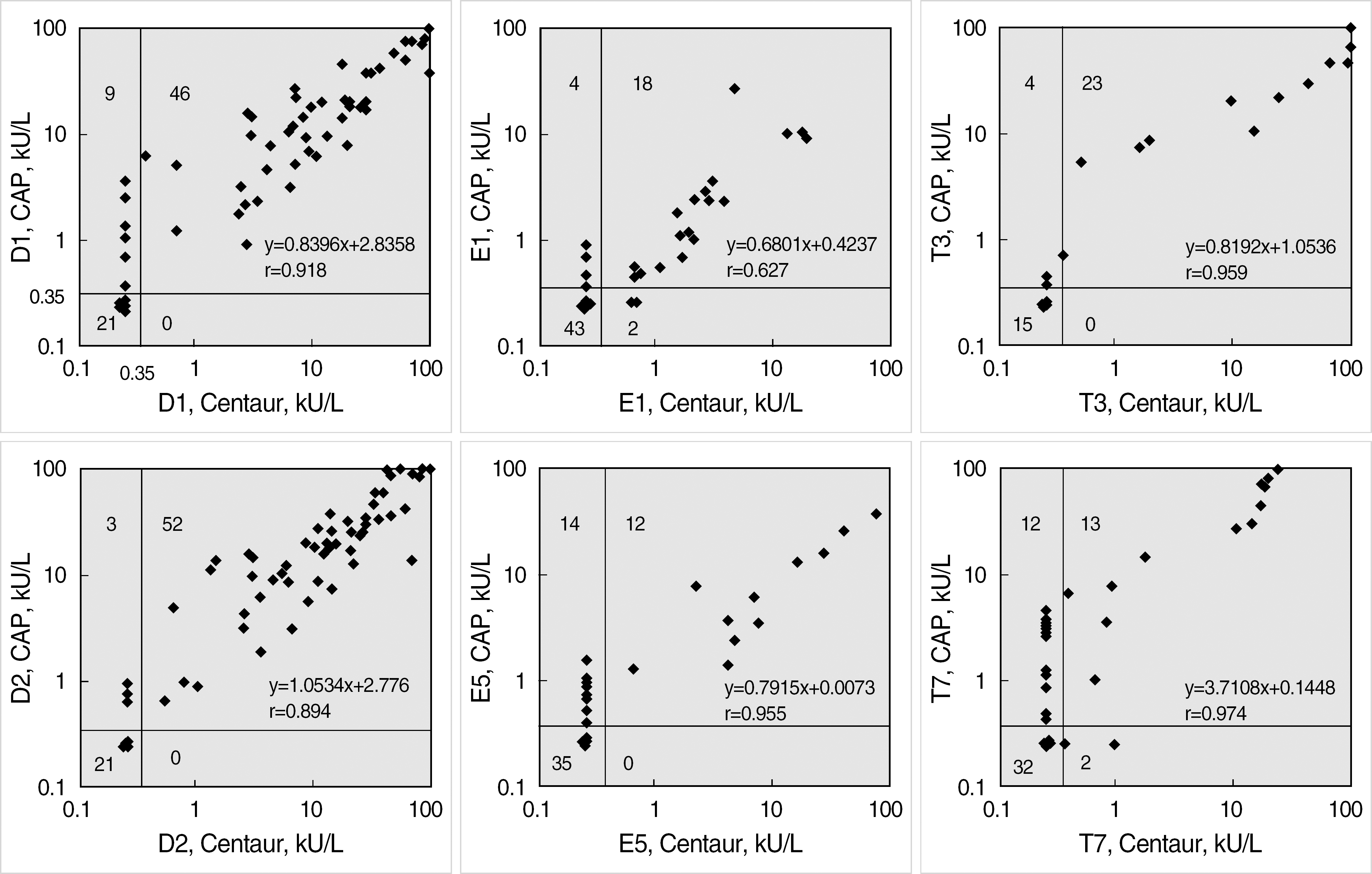
Table 1.
Precisions of ADVIA Centaur sIgE assay using positive controls
Table 2.
Comparison between the results of ADVIA Centaur sIgE assay and Pharmacia UniCAP system, and relative sensitivity, relative specificity and total agreement of ADVIA Centaur sIgE assay with Pharmacia UniCAP system
Table 3.
Relative sensitivity and specificity and total agreement of results of ADVIA Centaur sIgE assay and Pharmacia UniCAP system compared with those of skin prick test (SPT)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download