Abstract
Purpose
To compare visual performance after microincision cataract surgery (MICS) with the implantation of the Akreos MI-60 (MI-60) intraocular lens (IOL) through a 1.8-mm microincision with that after conventional cataract surgery with implantation of the Akreos Adapt-AO IOL (Adapt-AO).
Methods
All MICS procedures were performed by the same surgeon. The MI-60 was implanted into 25 eyes, and the Adapt-AO was place in 28 eyes. Best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), total high-order-aberration (HOA), contrast sensitivity, and surgi-cally-induced astigmatism (SIA) were recorded one-week, one-month, and four-months postoperatively.
Results
There were no statistically significant differences in BCVA between eyes implanted with the MI-60 or those with the Adapt-AO (MI-60 vs. Adapt-AO, 0.09±0.11 at baseline (logMAR), 0.11±0.08 at one-week, 0.06±0.07, 0.06±0.06 at one-month, 0.05±0.06, 0.06±0.05 at four-months according to the Mann-Whitney U test, p>0.05). Refractive errors were significantly less with the Adapt-AO than with the MI-60 (MI-60 vs. Adapt-AO, −0.50±0.43 at baseline (diopter), −0.06±0.39 at one-week, −0.50±0.41, 0.01±0.57 at one-month, −0.46±0.36, 0.08±0.58 at four-months according to the Mann-Whitney U test, p<0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in total HOA or contrast sensitivity between eyes implanted with the MI-60 and those implanted with the Adapt-AO. SIAs were significantly reduced in eyes implanted with the MI-60 than in those with the Adapt-AO at one-month and four-months postoperatively (Mann-Whitney U test, p<0.05).
Conclusions
Implantation with either the MI-60 or the Adapt-AO produced clinically acceptable outcomes, including good spherical aberration and contrast sensitivity. Furthermore, implantation with the MI-60 caused less SIA at one- and four-months postoperation, as compared to that with the Adapt-AO.
References
1. Ginsberg AP, Evans DW, Sekuler R, et al. Contrast sensitivity predicts pilots' performance in aircraft simulation. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1982; 59:105–9.
2. Pesudovs K, Hazel CA, Doran RM, Elliot DB. The usefulness of Vistech and FACT contrast sensitivity charts for cataract and abdominal surgery outcomes research. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:11–6.
3. Applegate RA, Hilmantel G, Howland HC, et al. Corneal surface abdominal aberrations and visual performance. J Refract Surg. 2000; 16:507–14.
4. Mierdel P, Kaemmerer M, Mrochen M, et al. Ocular optical aberr-ometer for clinical use. J Biomed Opt. 2001; 6:200–4.

5. Bhattacharjee H, Bhattacharjee K, Medhi J. Visual performance: abdominal of foldable intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:451–5.
6. Agarwal A, Agarwal A, Agarwal S, et al. Phakonit: phacoemulsification through a 0.9 mm corneal incision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1548–52.

8. Fine IH, Hoffman RS, Packer M. Optimizing refractive lens exchange with bimanual microincision phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:550–4.

9. Braga-Mele R, Liu E. Feasibility of sleeveless bimanual abdominal with the Millenium microsurgical system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:2199–203.
10. Mackool RJ. Temperature during bimanual phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:732.

11. Soscia W, Howard J, Olson R. Bimanual phacoemulsification through 2 stab incision a woundtemperature study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1039–43.
12. Soscia W, Howard JG, Olson RJ. Microphacoemulsification with WhiteStar. A woundtemperature study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1044–6.
13. Olson RJ. Clinical experience with 21-gauge manual microphacoemulsification using Sovereign Whitestar technology in eyes with dense cataract. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:168–72.

14. Alio JL, Rodriguez Prats JL, Galal A. Advances in microincision abdominal surgery intraocular lenses. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006; 17:80–93.
15. Hill W. Expected effects of surgically induced astigmatism on AcrySof toric intraocular lens results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:364–7.

16. Donnenfeld ED, Olson RJ, Solomon R, et al. Efficacy and woundtemperature gradient of whitestar phacoemulsification through a 1.2 mm incision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1097–100.

17. Steinert RF, Brint SF, White SM, et al. Astigmatism after small incision cataract surgery. A prospective, randomized, multicenter comparison of 4- and 6.5 mm incisions. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:417–23.
18. Alió JL, Piñero DP, Ortiz D, Montalbán R. Clinical outcomes and postoperative intraocular optical quality with a microincision aberration-free aspheric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1548–54.

19. Tong N, He JC, Lu F, et al. Changes in corneal wavefront aberrations in microincision andsmall-incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:2085–90.
20. Denoyer A, Denoyer L, Marotte D, et al. Intraindividual comparative study of corneal and ocular wavefront aberrations after biaxial abdominal versus coaxial small-incision cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 92:1679–84.
21. Wilczynski M, Supady E, Piotr L, et al. Comparison of surgically abdominal astigmatism after coaxial phacoemulsification through 1.8 mm microincision and bimanual phacoemulsification through 1.7 mm microincision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1563–9.
22. Milla E, Verges C, Cipres M. Corneal endothelium evaluation after phaocoemulsification with continuous anterior chamber infusion. Cornea. 2005; 24:278–82.
23. Choi JA, Kim CY, Na KS, et al. Clinical results after implantation of a spherical aberration-free intraocular lens: Effect of contrast sensitivity and wavefront aberration-a clinical comparative study. Ophthalmologica. 2009; 223:320–5.
Figure 1.
(A) Contrast sensitivity test results of Akreos MI-60 and Akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted groups in photopic condition at postoperative 1 month (Mann-Whitney U test, P>0.05). (B) Contrast sensitivity test result of Akreos MI-60 and Akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted groups in mesopic condition at postoperative 1 month (Mann-Whitney U test, * P=0.03).
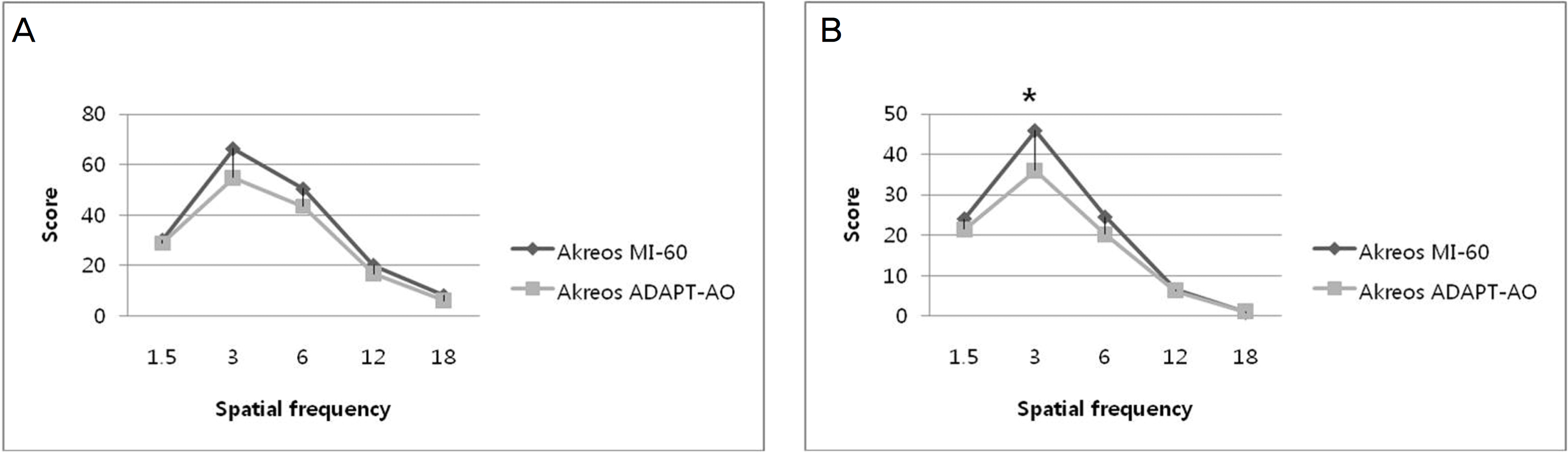
Figure 2.
(A) Contrast sensitivity test result of Akreos MI-60 and Akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted groups in photopic condition at postoperative 4 months (Mann-Whitney U test, P>0.05). (B) Contrast sensitivity test result of Akreos MI-60 and Akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted groups in mesopic condition at postoperative 4 months (Mann-Whitney U test, P>0.05).
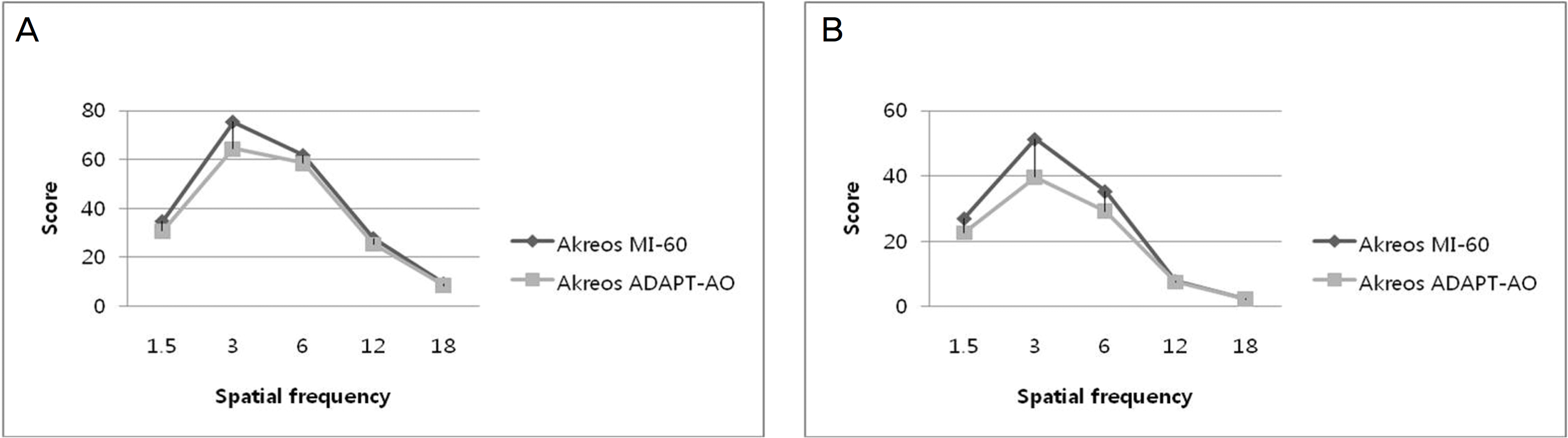
Figure 3.
Comparison of preoperative and postoperative astigmatism between Akreos MI-60 IOL-implanted group and Akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted group. (* Mann-Whitney U test, P<0.05)
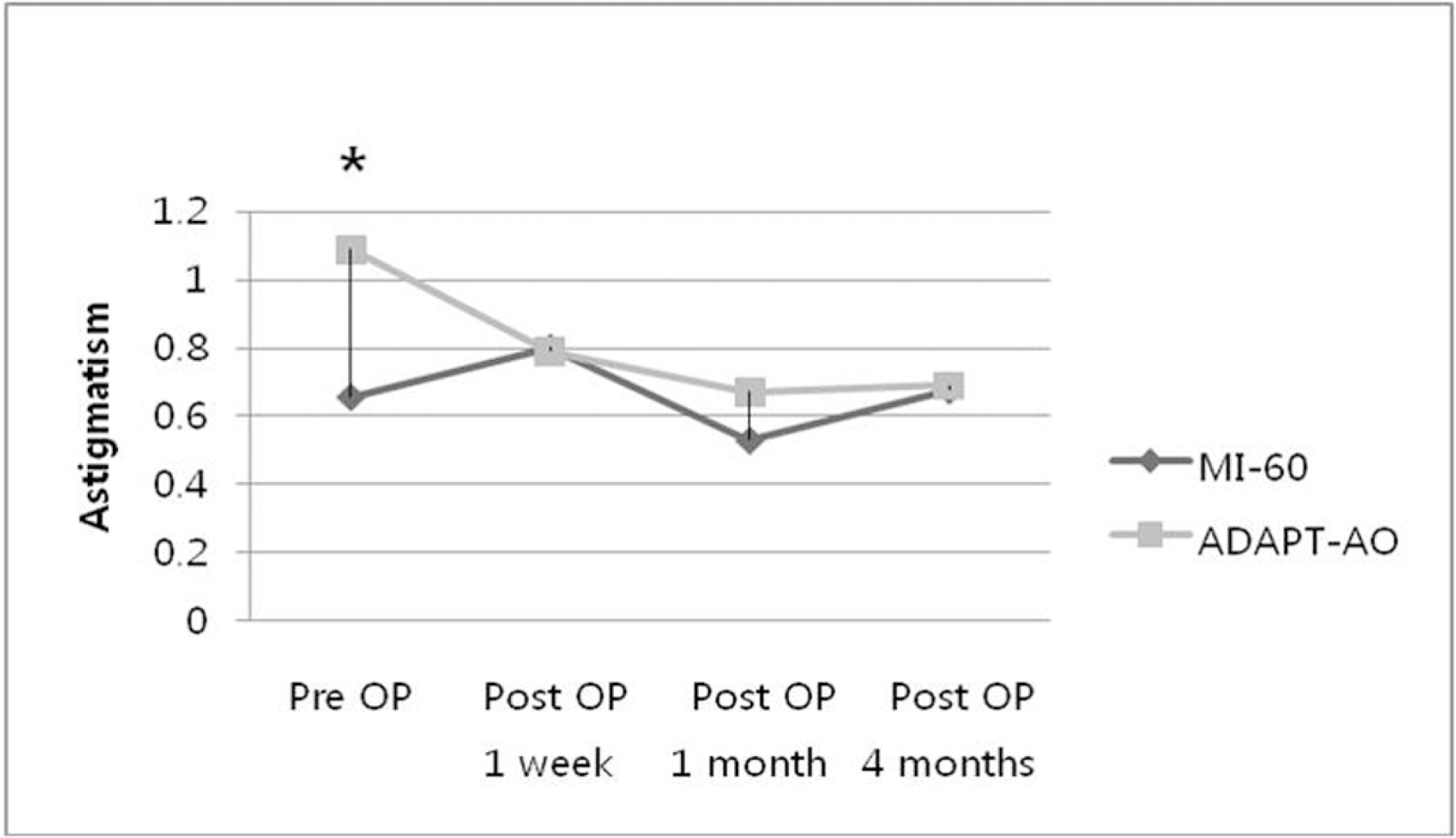
Table 1.
Comparison of sex, age, preoperative BCVA, axial length, IOL power between akreos MI-60 IOL-im-planted group and akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted group (Mean± SD†)
| Akreos MI-60 | Akreos Adapt-AO | P value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of eyes | 25 | 28 | |
| Age (years) | 67.88±8.97 | 69.96±6.34 | P>0.05 |
| BCVA‡ (logMAR) | 0.39±0.15 | 0.38±0.21 | P>0.05 |
| Axial length (mm) | 23.51±0.72 | 23.19±0.51 | P>0.05 |
| IOL Power§ (diopter) | 21.00±1.46 | 20.93±1.04 | P>0.05 |
| Sex (M:F) | 1:1 | 3:4 |
Table 2.
Comparison of postoperative BCVA, spherical equivalent, refractive error between akreos MI-60 IOL-implanted group and akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted group (Mean± SD†)
| Results | Group | Post OP 1week | Post OP 1month | Post OP 4months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCVA‡ (logMAR) | MI-60 | 0.09±0.11 | 0.06±0.07 | 0.05±0.06 |
| ADAPT-AO | 0.11±0.08 | 0.06±0.06 | 0.06±0.05 | |
| Spherical equivalent (diopter) | MI-60 | –0.86±0.85* | –0.83±0.78* | –0.74±0.85* |
| ADAPT-AO | –0.36±0.70* | –0.25±0.81* | –0.21±0.90* | |
| Refractive error§ (diopter) | MI-60 | –0.50±0.43* | –0.50±0.41* | –0.46±0.36* |
| ADAPT-AO | –0.06±0.39* | 0.01±0.57* | 0.08±0.58* |
Table 3.
Comparison of postoperative total high order aberration, spherical aberration, coma aberration between akreos MI-60 IOL-implanted group and akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted group (Mean± SD†)
| Results | Group | Post OP 1week | Post OP 1month | Post OP 4months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS HoA‡ | MI-60 | 0.657±0.153** | 0.649±0.188** | 0.753±0.251** |
| ADAPT-AO | 0.755±0.102* | 0.826±0.262* | 0.643±0.163* | |
| Spherical aberration | MI-60 | 0.394±0.110** | 0.399±0.147** | 0.424±0.110** |
| ADAPT-AO | 0.412±0.141* | 0.413±0.134* | 0.408±0.103* | |
| Coma aberration | MI-60 | 0.233±0.140** | 0.286±0.126** | 0.338±0.243** |
| Coma aberration | ADAPT-AO | 0.328±0.150* | 0.370±0.326* | 0.311±0.225* |
Table 4.
Comparison of postoperative surgically induced astigmatism between Akreos MI-60 IOL-implanted group and akreos Adapt-AO IOL-implanted group (Mean± SD†)
| Results | Group | Post OP 1week | Post OP 1month | Post OP 4months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIA‡ | MI-60 | 0.662±0.685 | 0.417±0.503** | 0.394±0.235** |
| ADAPT-AO | 0.936±0.863 | 1.040±0.857* | 0.594±0.299* |
Table 5.
Comparison of preoperative and postoperative astigmatism between akreos MI-60 IOL-implanted group and akreos adapt-AO IOL-implanted group (Mean± SD†)
| Results | Group | Pre OP | Post OP 1week | Post OP 1month | Post OP 4months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astigmatism | MI-60 | 0.656±0.659** | 0.800±0.655 | 0.530±0.565 | 0.676±0.524 |
| Astigmatism | ADAPT-AO | 1.090±0.767* | 0.790±0.612 | 0.670±0.681 | 0.691±0.524 |
Table 6.
Comparison of postoperative anterior chamber depth between akreos MI-60 IOL-implanted group and akreos adapt-AO IOL-implanted group (Mean± SD†)
| Results | Group | Post OP 1week | Post OP 1month | Post OP 4months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACD‡ | MI-60 | 3.948±0.288** | 3.858±0.496 | 3.682±0.664 |
| ACD | ADAPT-AO | 3.721±0.376* | 3.762±0.459 | 3.784±0.488 |
Table 7.
Comparison of postoperative refractive error and anterior chamber depth between akreos MI-60 IOL-implanted group A and B (Mean± SD†)
| Akreos MI-60 A‡ | Akreos MI-60 B§ | P value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 17 | 8 | |
| RE∏ post OP 1week | –0.399±0.369 | –0.733±0.684 | P=0.198 |
| RE∏ post OP 1month | –0.383±0.423 | –0.719±0.404 | P=0.076 |
| RE∏ post OP 4months | –0.383±0.406 | –0.528±0.520 | P=0.904 |
| ACD∏ post OP 1week | 3.935±0.353 | 3.973±0.081 | P=0.743 |
| ACD∏ post OP 1month | 3.813±0.549 | 3.949±0.393 | P=1.000 |
| ACD∏ post OP 4months | 3.677±0.582 | 3.698±0.955 | P=0.933 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download