Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of corneal ulcer due to Alcaligenes faecalis in a patient with a preexisting corneal ulcer.
Case summary
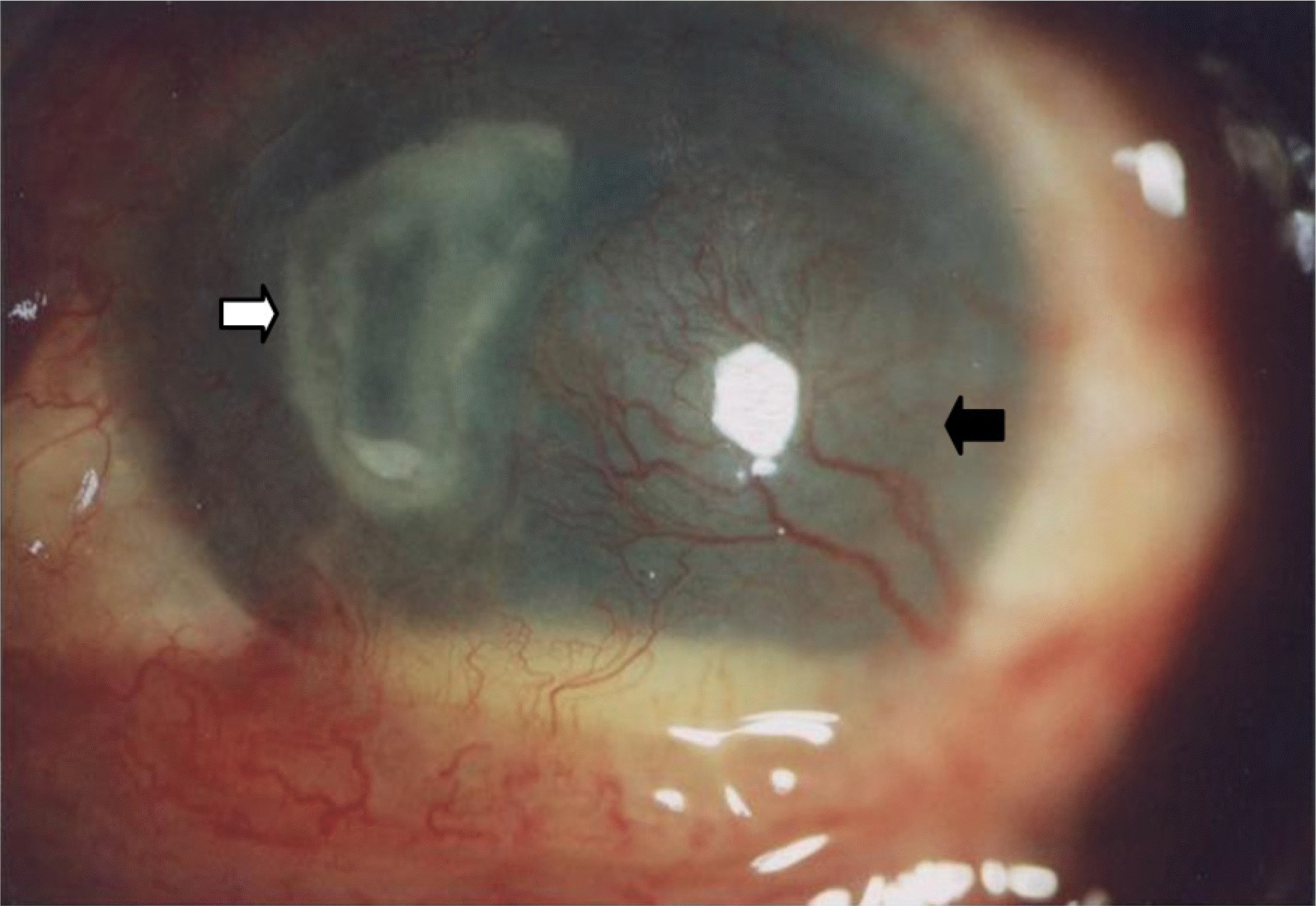
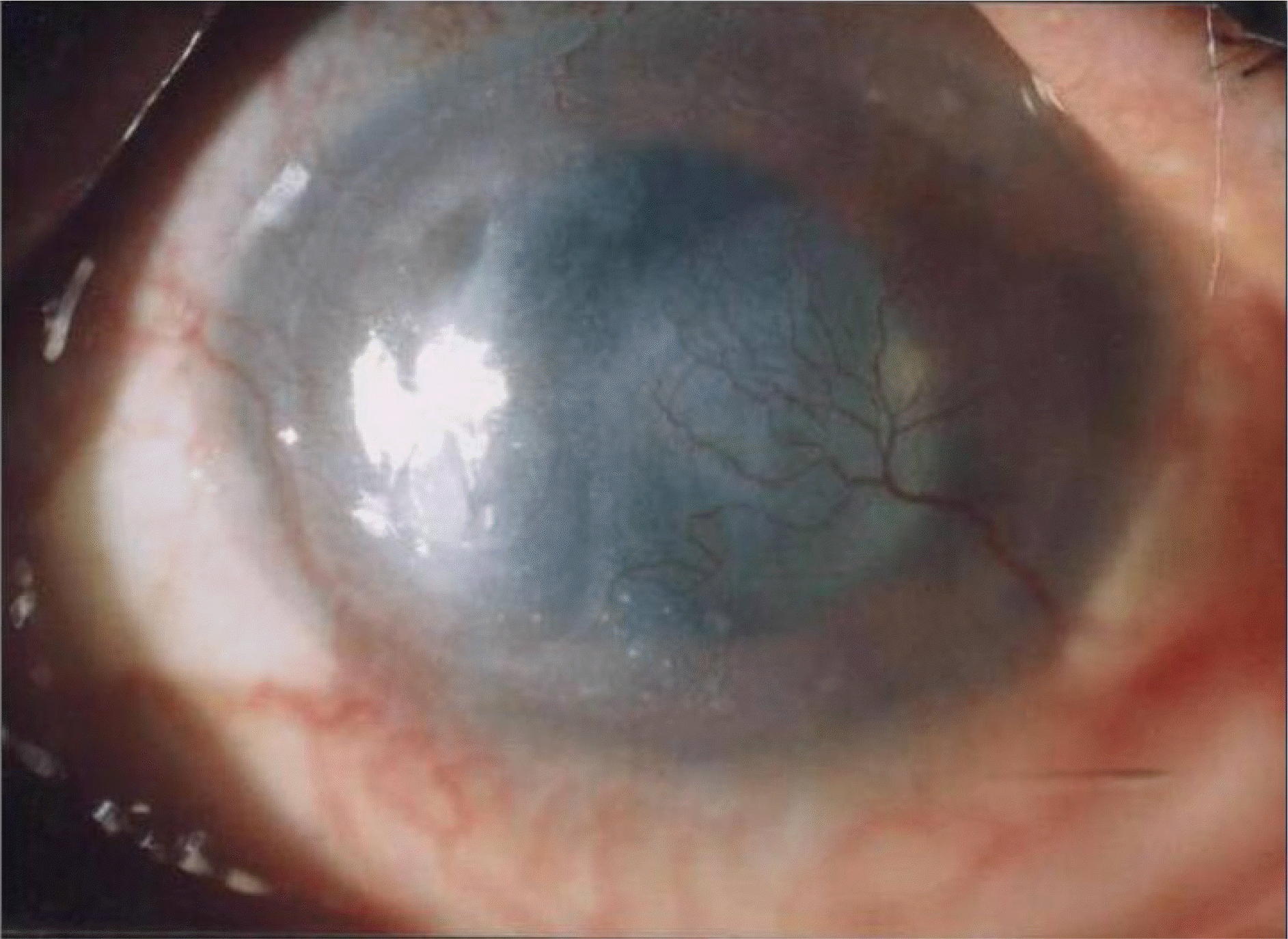
A 58-year-old male patient presented with a corneal ulcer without a history of any trauma. The patient had a history of corneal ulcer 9 months earlier. The patient had previously been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy and neovascular glaucoma, and his visual acuity was no light perception. Corneal scraping and culture yielded Alcaligenes faecalis susceptible to most antibiotics in the antibiotic susceptibility test. After treatment with empirical systemic antibiotics and eyedrops, his eye improved with a remaining corneal scar.
References
1. Davis BD, Dulbecco R, Eisen HN, Ginsberg HS. Microbiology. 4th ed.4. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;1990. p. 595–600.
2. Bizet J, Bizet C. Strains of Alcaligenes faecalis from clinical material. J Infect. 1997; 35:167–9.

3. Tayeri T, Kelly LD. Alcaligenes faecalis corneal ulcer in a patient with cicatricial pemphigoid. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 115:255–6.

4. Khokhar DS, Sethi HS, Kumar H, et al. Postkeratoplasty endophthalmitis by Alcaligenes faecalis: a case report. Cornea. 2002; 21:232–3.
5. Mehrotra A, Gadia R, Venkatesh P, et al. Posttraumatic endophthalmitis due to a rare pathogen, Alcaligenes faecalis. Can J Ophthalmol. 2007; 42:487–8.

6. Kaliaperumal S, Srinivasan R, Gupta A, Parija SC. Postoperative endophthalmitis due to an unusual pathogen: Alcaligenes faecalis. Eye. 2006; 20:968–9.

7. Srinivasan R, Gupta A, Kaliaperumal S, et al. Efficacy of intraoperative vancomycin in irrigating solutions on aqueous contamination during phacoemulsification. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2008; 56:399–402.

8. Han YS, Chung IY, Park JM. A case of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans Endophthalmitis after cataract extraction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:186–9.
9. Pan TH, Heidemann DG, Dunn SP, et al. Delayed onset and recurrent Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratitis. Cornea. 2000; 19:243–5.

10. Weissgold DJ, Kirkoatrick B, Iverson M. Acute postoperative Alcaligenes xylosoxidans endophthalmitis. Retina. 2003; 23:578–80.

11. Rahman MK, Holz ER. Alcaligenus xylosoxidans and propioni-bacterium acnes postoperative endophthalmitis in a pseudophakic eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 129:813–5.
12. Swart J, Völker-Dieben HJ, Reichert-Thoen JW. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans endophthalmitis 8 months after cataract extraction. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 127:345–6.

13. Simmons DG, Rose LP, McCorkle FM, Luginbuhl GH. Histamine sensitizing factor of Alcaligenes faecalis. Avian Dis. 1983; 27:171–7.
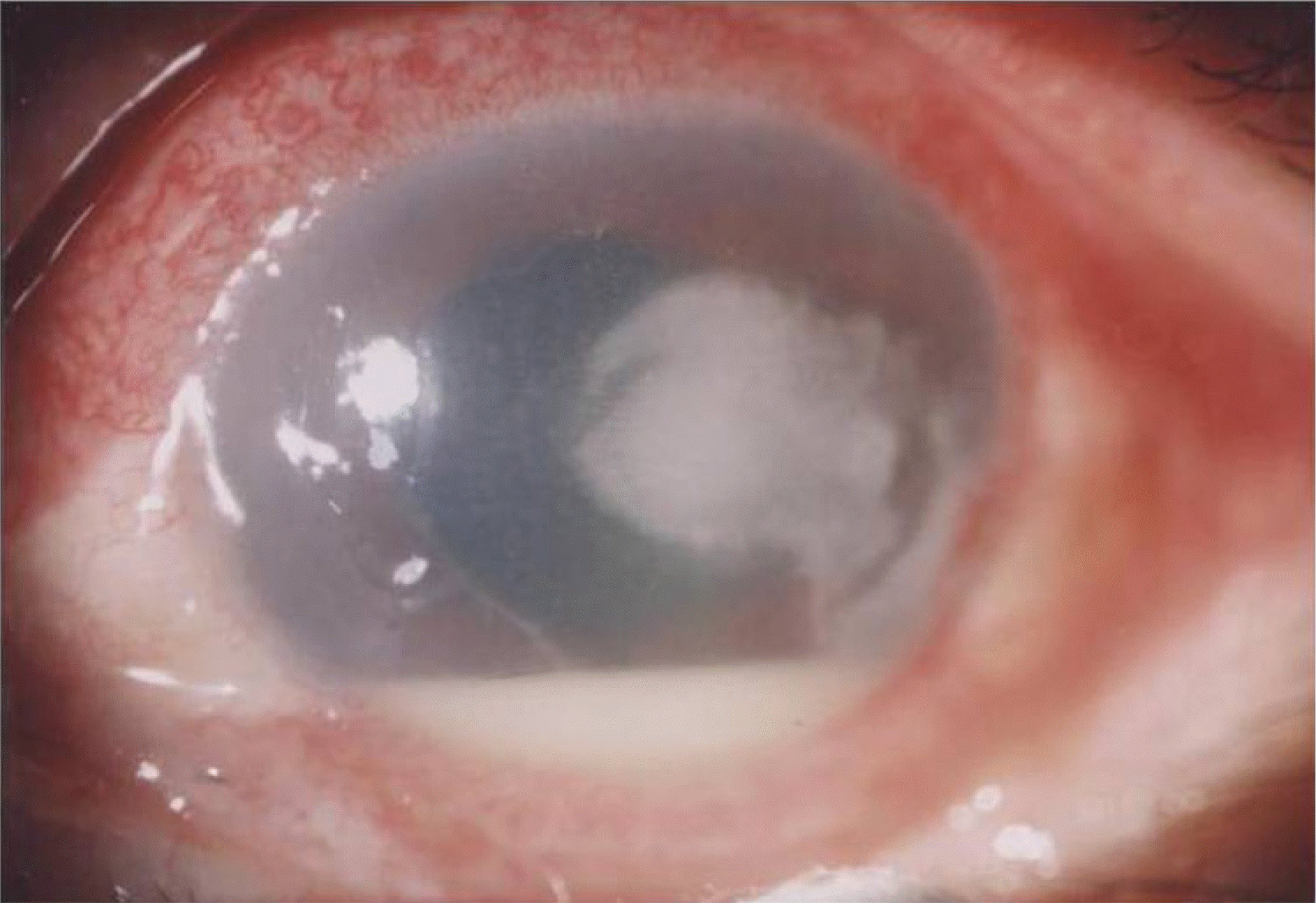
Figure 1.
Preexisting corneal ulcer with deep stromal infiltration and hypopyon in a 58-year-old man with neovascular glaucoma (photograph taken at 9 months earlier).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download