Abstract
Case summary
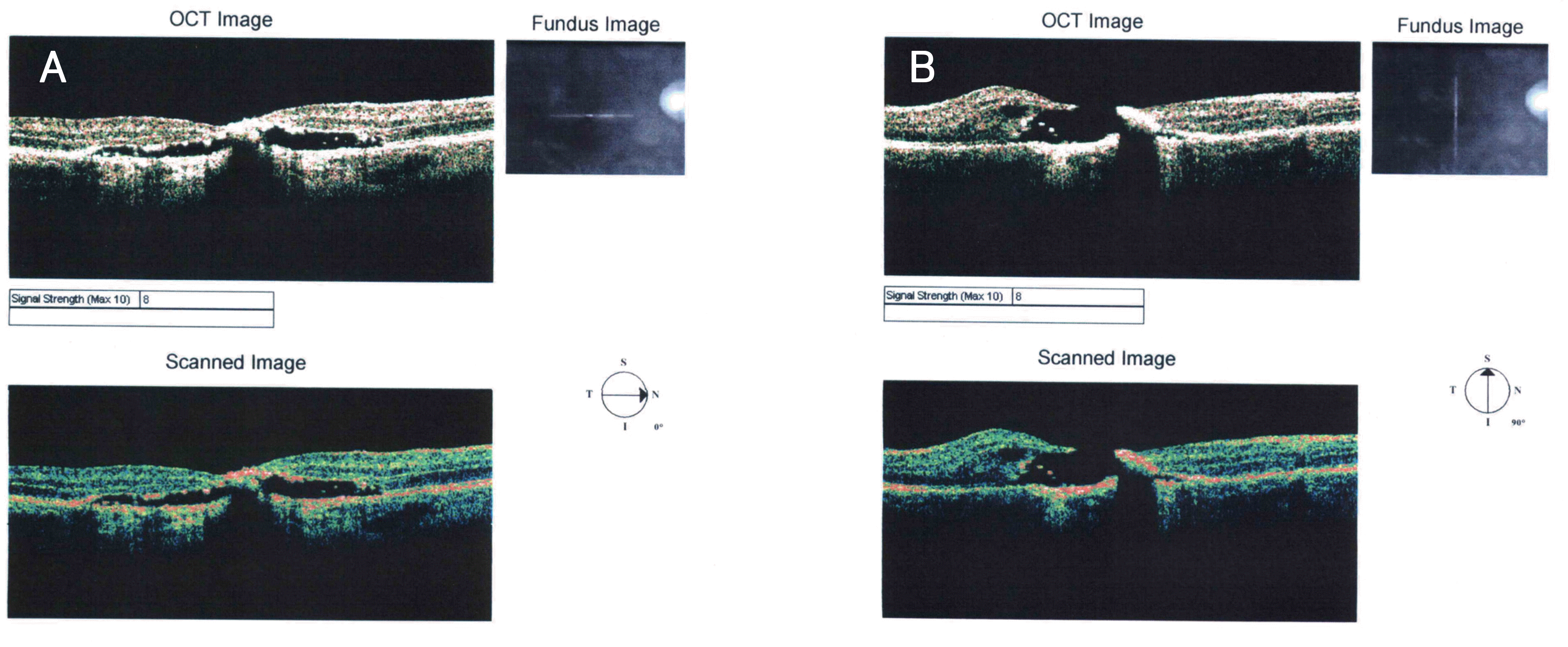
A 25-year-old man had an acute reduction of visual acuity in his right eye two years ago after accidental exposure to a green laser pointer for a few seconds. The patient's best corrected visual acuity was counting fingers in his right eye. Fundus examination and optical coherence tomography showed a macular hole and a linear retinal scar in his right eye.
References
1. Mainster MA. Blinded by the light‐ not! Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:1547–8.
2. Yolton RL, Citek K, Schmeisser E, et al. Laser pointers: toys, nuisances, or significant eye hazards? J Am Optom Assoc. 1999; 70:285–9.
4. Robertson DM, McLaren JW, Salomao DR, Link TP. Retinopathy from a green laser pointer: a clinicopathologic study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:629–33.
5. Namgung M, Park JS, Choi YI. A Case of Nd:YAG laser injury to the macula. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1756–60.
6. Sell CH, Bryan JS. Maculopathy from handheld diode laser pointer. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:1557–8.

8. Robertson DM, Lim TH, Salomao DR, et al. Laser pointers and the human eye: a clinicopathologic study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000; 118:1686–91.
9. Mainster MA. Wavelength selection in macular photocoagulation. Tissue optics, thermal effects, and laser systems. Ophthalmology. 1986; 93:952–8.
10. Alhalel A, Glovinsky Y, Treister G, et al. Long‐ term follow up of accidental parafoveal laser burns. Retina. 1993; 13:152–4.
11. Mainster MA, Timberlake GT, Warren KA, et al. Pointers on laser pointers. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:1213–4.

12. Ham WT Jr, Geeraets WJ, Mueller HA, et al. Retinal burn thresholds for the helium‐ neon laser in the rhesus monkey. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970; 84:797–809.
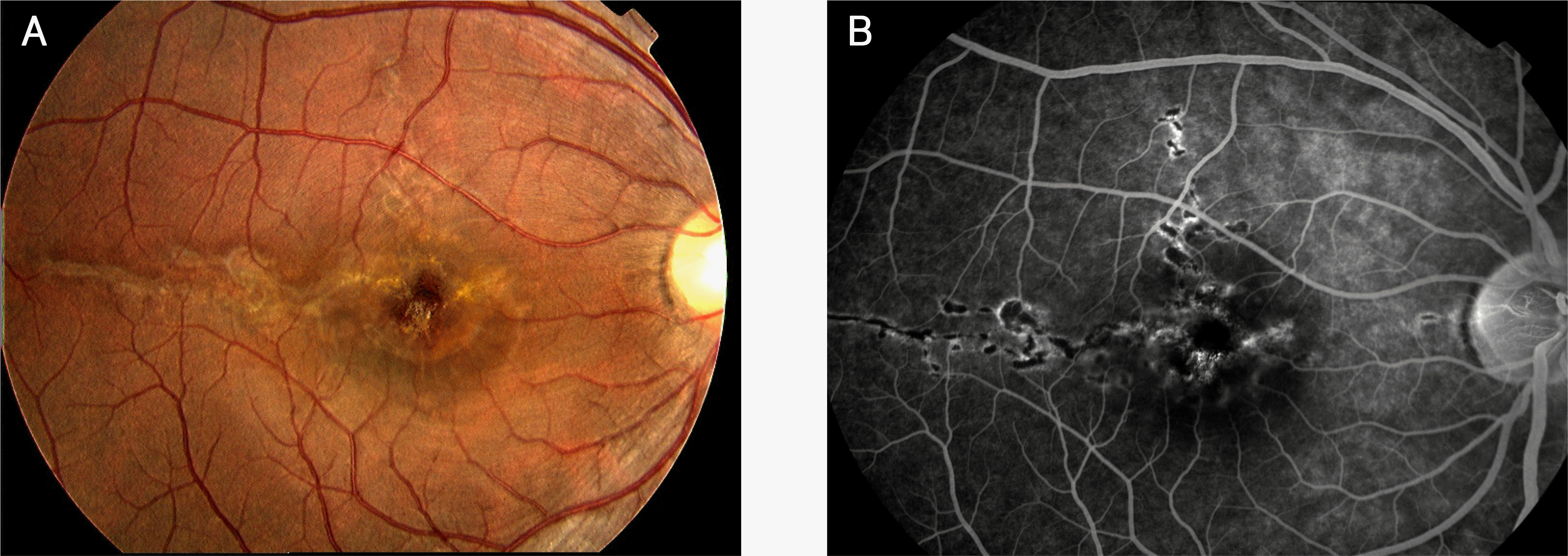
Figure 1.
Fundus photograph shows 1.5 optic disc diameter-sized parafoveal retinal scar with temporally and superiorly extended linear retinal scars (A). Fluorescein angiography shows hyperfluorescence at the margin of the lesions and hypofluorescence in the lesion on the fovea and parafoveal area with superior and temporal lineal extensions (B).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download