Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the correlation between preoperative optical coherence tomography (OCT) parameters and pre- and post-operative visual acuity after macular hole surgery.
Methods
Twenty-five eyes of 24 patients who underwent macular hole surgery with a postoperative follow-up longer than 6 months were studied. On enhanced preoperative horizontal and vertical OCT scans, various parameters including hole diameter, base diameter, total lesion diameter, and hole height were measured. Hole form factor (HFF) and macular hole index (MHI) were calculated. The correlation between the parameters and pre- and post-operative visual acuity, as well as visual acuity change, was analyzed.
Results
There was a significant correlation between hole height and preoperative visual acuity (p=0.018). Better postoperative visual outcome was correlated with a smaller hole diameter, smaller total lesion diameter, and greater hole height (p=0.002, 0.043 and 0.037). HFF and MHI were correlated with visual acuity change (p=0.024 and <0.001)
References
1. Gass JD. Idiopathic senile macular hole: its early stages and pathogenesis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988; 106:629–39.

2. Altaweel M, Ip M. Macular hole:improved understanding of pathogenesis, staging, and management based on optical coherence tomography. Semin Ophthalmol. 2003; 18:58–66.
3. Smiddy WE, Flynn HW. Pathogenesis of macular holes and therapeutic implications. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:525–37.

4. Puliafito CA, Hee MR, Lin CP, et al. Imaging of macular diseases with optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 1995; 102:217–29.

5. Hee MR, Puliafito CA, Wong C, et al. Optical coherence tomography of macular holes. Ophthalmology. 1995; 102:748–56.

6. Ullrich S, Haritoglou C, Gass C, et al. Macular hole size as a prognostic factor in macular hole surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:390–3.

7. Kusuhara S, Teraoka Escaño MF, Fujii S, et al. Prediction of postoperative visual outcome based on hole configuration by optical coherence tomography in eyes with idiopathic macular holes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:709–16.

8. Lee JE, Kim EH, Oum BS. Relationship between visual acuity and photoreceptor layer or foveal thickness on optical coherence tomography after macular hole surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1966–71.
9. Villate N, Lee JE, Venkatraman A, Smiddy WE. Photoreceptor layer fearues in eyes with closed macular holes: optical coherence tomography findings and correlation with visual outcomes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:280–9.
10. Takahashi H, Kishi S. Tomographic fearues of a lamellar macular hole formation and a lamellar hole that progressed to a full‐ thickness macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:677–9.
11. Gaudric A, Haouchine B, Massin P. Macular hole formation: new data provided by optical coherence tomography. Arch Opthalmol. 1999; 117:744–51.
12. Sjaarda RN, Frank DA, Glaser BM, et al. Resolution of an absolute scotoma and improvement of relative scotoma after successful macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 116:129–39.
13. Seo MS, Kang SJ. Prognostic factors in idiopathic macular hole surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1746–52.
14. Kim KS, Kim YC. Surgical results of vitrectomy for macular holes, according to the hole size. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:927–32.
Figure 1.
Preoperative parameters of macular hole on optical coherence tomography. HT=height; HD=hole diameter; BD= base diameter; TD=total diameter.
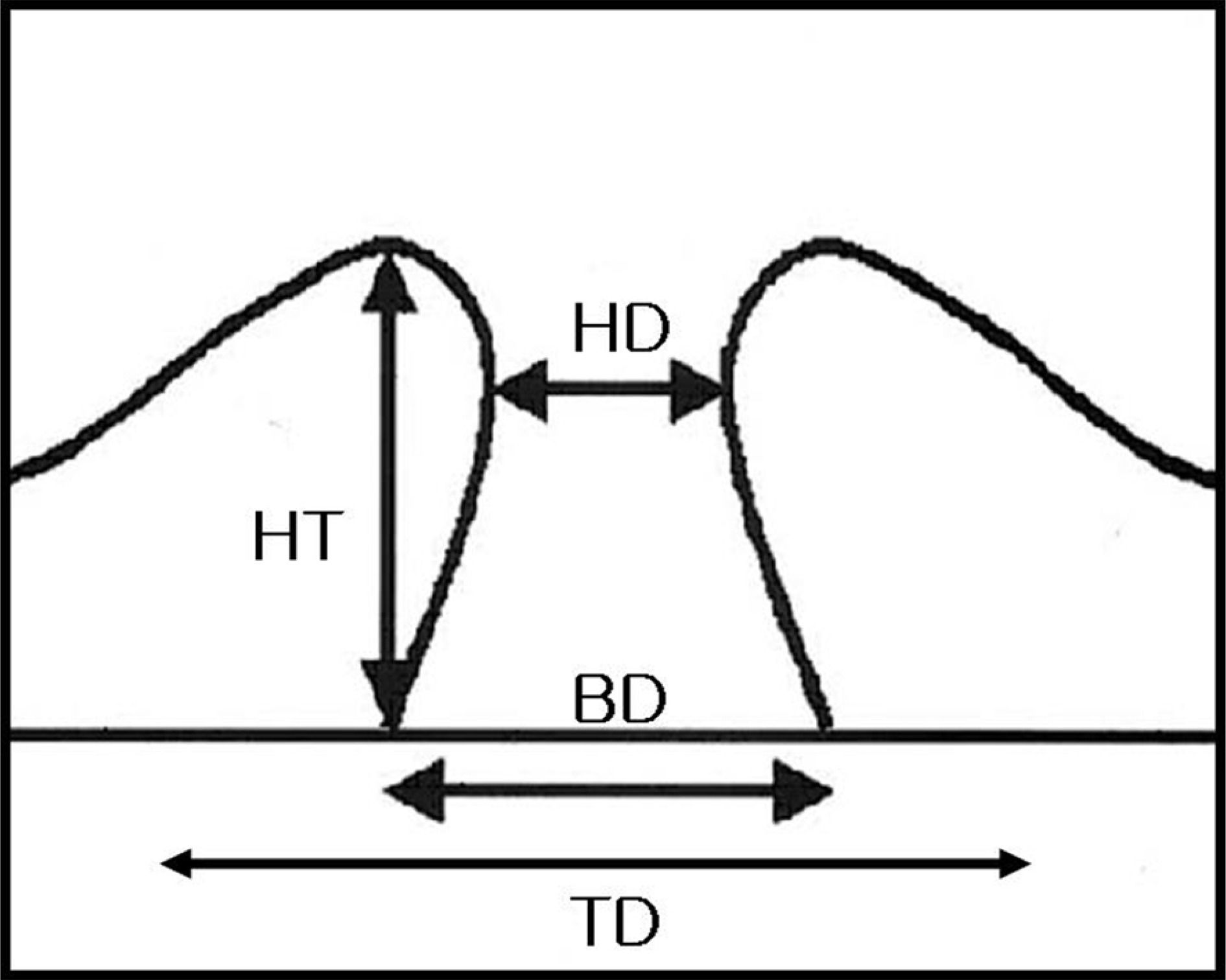
Figure 2.
A case of tall macular hole with high hole form factor (HFF) and macular hole index (MHI). (A) Processed optical coherence tomography (OCT) image shows preoperative parameters. Visual acuity was 0.2. OCT reveals high hole height with extensive cystic changes of the neurosensory retina beyond the extent of the hole base. HFF and MHI were 1.3 and 0.9, respectively. (B) Postoperative 12 months OCT shows normal foveal contour and well‐ organized photoreceptor layer without defect. Visual acuity was 1.0.
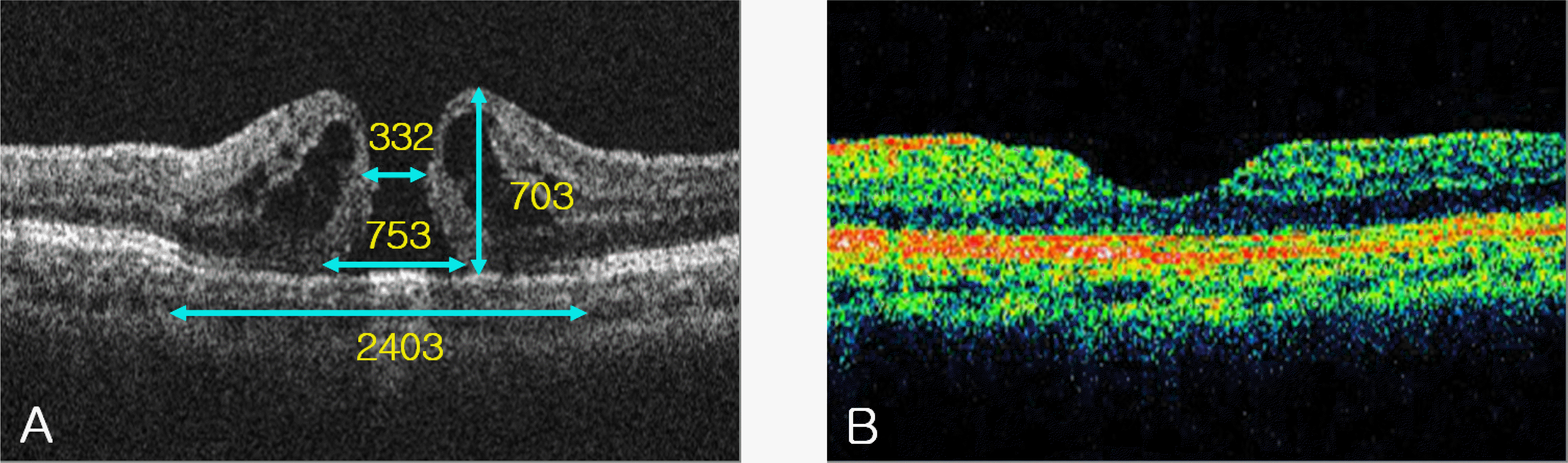
Figure 3.
A case of macular hole with low height, high hole form factor (HFF) and macular hole index (MHI). (A) Processed optical coherence tomography (OCT) image demonstrates a small macular hole with low height. The measured preoperative parameters are shown. Visual acuity was 0.08. HFF was 1.0 and MHI was 0.8. (B) Postoperative 6 month OCT shows residual outer retinal defect. Visual acuity was 0.32.
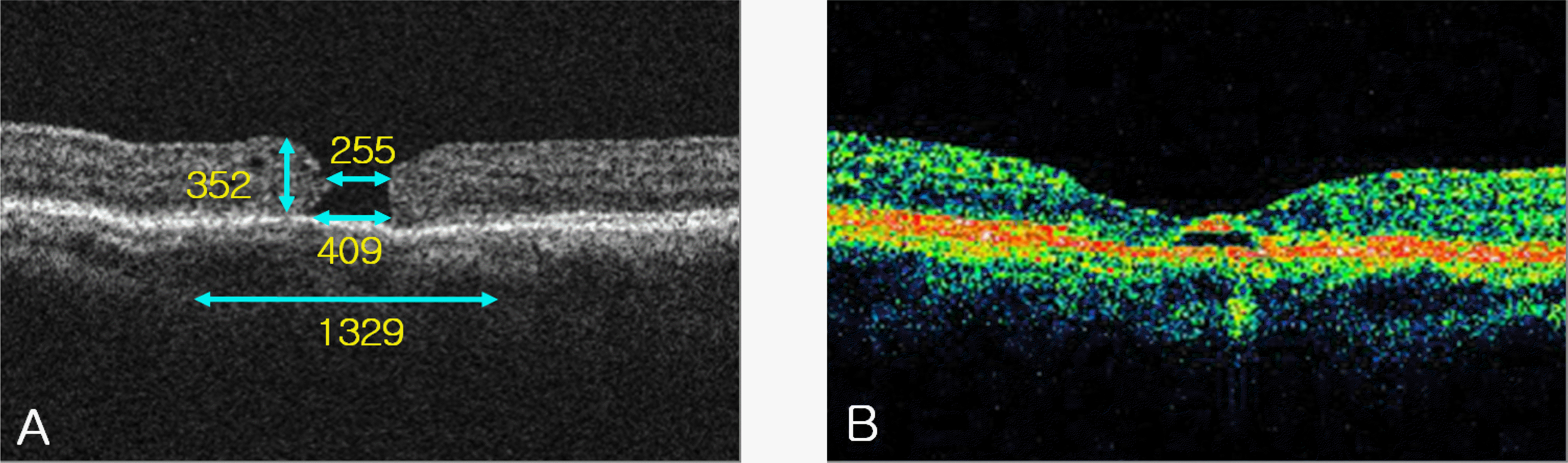
Table 1.
Correlation of macular hole OCT parameter and preoperative best corrected visual acuity (p: Spearman's ran correlation)
| Parameters | Average |
Preoperative visual acuity |
visual acuity Postoperative |
change Visual acuity |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE* | p | CE* | p | CE* | p | ||
| Hole diameter (HD, µm) | 512±206 | −0.325 | 0.112 | −0.590 | 0.002 | 0.174 | 0.406 |
| Base diameter (BD, µm) | 984±389 | 0.173 | 0.407 | −0.189 | 0.366 | 0.336 | 0.101 |
| Total diameter (TD, µm) | 2211±572 | −0.184 | 0.378 | −0.409 | 0.043 | 0.318 | 0.121 |
| Hole height (HT, µm) | 439±125 | 0.470 | 0.018 | 0.419 | 0.037 | 0.047 | 0.824 |
| BD-HD (µm) | 471±336 | 0.343 | 0.093 | 0.082 | 0.696 | 0.341 | 0.095 |
| TD-BD (µm) | 1227±411 | −0.380 | 0.061 | −0.360 | 0.077 | 0.083 | 0.695 |
| TD-HD (µm) | 1699±490 | −0.115 | 0.584 | −0.244 | 0.239 | 0.225 | 0.280 |
| HFF† | 6.60±2.79 | 0.365 | 0.072 | 0.621 | 0.009 | 0.450 | 0.024 |
| MHI‡ | 0.65±0.35 | 0.166 | 0.426 | 0.704 | <0.001 | 0.714 | <0.001 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download