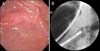
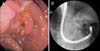
|
|
| 1. |
Mayo CW, Rice RG. Situs inversus totalis; a statistical review of data on 76 cases with special reference to disease of the biliary tract. Arch Surg 1949;58:724–730.
|
|
| 2. |
Moore KL. In: Clinical oriented anatomy. 1st ed. Baltimore, London: William & Wilkins; 1980.
|
|
| 3. |
Chowdhury A, Chatterjee BK, Das U, Dutta P, Dhali GK, Banerjee PK. ERCP in situs inversus: do we need to turn the other way? Indian J Gastroenterol 1997;16:155–156.
|
|
| 4. |
Çoban Ş, Yüksel I, Küçükazman M, Başar Ö. Successful ERCP in a patient with situs inversus. Endoscopy 2014;46 Suppl 1 UCTN:E222.
|
|
| 5. |
Fiocca F, Donatelli G, Ceci V, et al. ERCP in total situs viscerum inversus. Case Rep Gastroenterol 2008;2:116–120.
|
|
| 6. |
Sheikh I, Heard R, Tombazzi C. Technical factors related to endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in patients with situs inversus. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2014;10:277–278.
|
|
| 7. |
Yokoyama T, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Montgomery CA, Elder FF, Overbeek PA. Reversal of left-right asymmetry: a situs inversus mutation. Science 1993;260:679–682.
|
|
| 8. |
Winer-Muram HT. Adult presentation of heterotaxic syndromes and related complexes. J Thorac Imaging 1995;10:43–57.
|
|
| 9. |
Imamura T, Momoi N, Go H, Ogasawara K, Sato M, Hosoya M. Rare case of isolated levocardia with polysplenia including normally structured lung without cardiac anomaly. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 2011;51:187–190.
|
|
| 10. |
Hiraoka K, Haratake J, Horie A, Miyagawa T. Bilateral renal dysplasia, pancreatic fibrosis, intrahepatic biliary dysgenesis, and situs inversus totalis in a boy. Hum Pathol 1988;19:871–873.
|
|
| 11. |
Sadhu S, Jahangir TA, Roy MK. Left-sided gallbladder discovered during laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a patient with dextrocardia. Indian J Surg 2012;74:186–188.
|
|
| 12. |
Applegate KE, Goske MJ, Pierce G, Murphy D. Situs revisited: imaging of the heterotaxy syndrome. Radiographics 1999;19:837–852. discussion 853-854.
|
|
| 13. |
Kim SH, Kong ON, Ha JK, et al. A case of endoscopic removal of choledocholithiasis in a patient with situs inversus totalis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2002;24:59–61.
|
|
| 14. |
García-Fernández FJ, Infantes JM, Torres Y, Mendoza FJ, Alcazar FJ. ERCP in complete situs inversus viscerum using a "mirror image" technique. Endoscopy 2010;42 Suppl 2:E316–E317.
|
|
| 15. |
de la Serna-Higuera C, Perez-Miranda M, Flores-Cruz G, Gil-Simón P, Caro-Patón A. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in situs inversus partialis. Endoscopy 2010;42 Suppl 2:E98.
|
|
| 16. |
Lee JH, Kang DH, Park JH, et al. Endoscopic removal of a bile-duct stone using sphincterotomy and a large-balloon dilator in a patient with situs inversus totalis. Gut Liver 2010;4:110–113.
|
|
| 17. |
Patel KS, Patel JN, Mathur S, Moshenyat Y. To twist or not to twist: a case of ERCP in situs inversus totalis. Endoscopy 2014;46 Suppl 1 UCTN:E304–E305.
|
|
| 18. |
Kim SB, Kim KH, Kim TN. Successful stone removal by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in situs inversus totalis with Billroth-II gastrectomy. Gut Liver 2015;9:118–119.
|
|
| 19. |
Byun JR, Jahng JH, Song JC, Yu JS, Lee DK. Supine position endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in a patient with situs ambiguous with polysplenia. Dig Endosc 2010;22:322–324.
|
|




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print