Abstract
Purpose
We report here on the safety and efficacy of nephron-sparing radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for treating renal tumor.
Materials and Methods
Starting June 2004, a total of 14 patients underwent RFA for renal tumor during the following 3 years. Of these, 12 cases were followed up for at least 6 months postoperatively. Eight cases of combined computed tomography (CT) and ultrasonogram-guided percutaneous RFA, and four cases of intraoperative ultrasonography-guided laparo-scopic RFA were performed with mean follow-up of 18.2 months (range: 4-27 months). The treatment indications were a localized, small (<4cm), solid renal mass in the elderly patients and those patients with co-morbid conditions. Physical examination, CBC, determining the serum creatinine levels and urine analysis were performed for the follow-up laboratory study and kidney CT was performed at day 1, 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months and 1 year after ablation and thereafter semi-annually. The mean follow-up duration was 18.2 months (range: 4-27 months).
Results
All the patients underwent successful RFA without any serious events. Four patients had mild perinephric hematoma on the follow-up CT scan and there was one case of mild gross hematuria postoperatively. With a mean follow-up of 18.2 months, two patients showed residual tumor at 3 months & 22 months, respectively, on the follow-up contrast-enhanced CT after the first tumor ablation. One patient underwent a second RFA and another patient underwent laparoscopic radical nephrectomy, and no residual tumor was seen on the follow-up CT. Distant metastasis was not found in any cases and all the patients are alive on serial follow-up.
REFERENCES
1.Moll V., Becht E., Ziegler M. Kidney preserving surgery in renal cell tumors: indications, techniques and results in 152 patients. J Urol. 1993. 150:319–23.

2.Livraghi T., Goldberg SN., Lazzaroni S., Meloni F., Ierace T., Solbiati L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: radio-frequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology. 2000. 214:761–8.

3.Martin AP., Goldstein RM., Dempster J., Netto GJ., Katabi N., Derrick HC, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma before liver transplantation - a clinical and histological examination. Clin Transplant. 2006. 20:695–705.

4.Zlotta AR., Wildschutz T., Raviv G., Peny MO., van Gansbeke D., Noel JC, et al. Radiofrequency interstitial tumour ablation (RITA) is a possible new modality for treatment of renal cancer: ex vivo and in vivo experience. J Endourol. 1997. 11:251–8.
5.Yohannes P., Pinto P., Rotariu P., Smith AD., Lee BR. Retro-peritoneoscopic radiofrequency ablation of a solid renal mass. J Endourol. 2001. 15:845–9.

6.Gervais DA., McGovern FJ., Arellano RS., McDougal WS., Mueller PR. Radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma: part 1, indications, results, and role in patient management over a 6-year period and ablation of 100 tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 185:64–71.

7.Matsumoto ED., Johnson DB., Ogan K., Trimmer C., Sagalowsky A., Margulis V, et al. Short-term efficacy of temperature-based radiofrequency ablation of small renal tumors. Urology. 2005. 65:877–81.

8.Jacomides L., Ogan K., Watumull L., Cadeddu JA. Laparoscopic application of radio frequency energy enables in situ renal tumor ablation and partial nephrectomy. J Urol. 2003. 169:49–53.

9.Zagoria RJ. Imaging-guided radiofrequency ablation of renal masses. Radiographics. 2004. 24(Suppl 1):S59–71.

10.Uzzo RG., Novick AC. Nephron sparing surgery for renal tumors: indications, techniques and outcomes. J Urol. 2001. 166:6–18.

11.Ljungberg B., Alamdari FI., Holmberg G., Granfors T., Duchek M. Radical nephrectomy is still preferable in the treatment of localized renal cell carcinoma. A long-term follow-up study. Eur Urol. 1998. 33:79–85.
12.Leach GE., Lieber MM. Partial nephrectomy: Mayo Clinic experience 1957-1977. Urology. 1980. 15:219–28.

13.Siqueira TM Jr., Kuo RL., Gardner TA., Paterson RF., Stevens LH., Lingeman JE, et al. Major complications in 213 laparo-scopic nephrectomy cases: the Indianapolis experience. J Urol. 2002. 168:1361–5.

14.Delakas D., Karyotis I., Daskalopoulos G., Terhorst B., Lymber-opoulos S., Cranidis A. Nephron-sparing surgery for localized renal cell carcinoma with a normal contralateral kidney: a European three-center experience. Urology. 2002. 60:998–1002.

15.Mahnken AH., Gunther RW., Tacke J. Radiofrequency ablation of renal tumors. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:1449–55.

16.Ogan K., Jacomides L., Dolmatch BL., Rivera FJ., Dellaria MF., Josephs SC, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal tumors: technique, limitations, and morbidity. Urology. 2002. 60:954–8.

17.Gervais DA., McGovern FJ., Wood BJ., Goldberg SN., McDougal WS., Mueller PR. Radio-frequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma: early clinical experience. Radiology. 2000. 217:665–72.

18.Su LM., Jarrett TW., Chan DY., Kavoussi LR., Solomon SB. Percutaneous computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation of renal masses in high surgical risk patients: preliminary results. Urology. 2003. 61(4 Suppl 1):26–33.

19.Walther MM., Shawker TH., Libutti SK., Lubensky I., Choyke PL., Venzon D, et al. A phase 2 study of radio frequency interstitial tissue ablation of localized renal tumors. J Urol. 2000. 163:1424–7.

20.Pavlovich CP., Walther MM., Choyke PL., Pautler SE., Chang R., Linehan WM, et al. Percutaneous radio frequency ablation of small renal tumors: initial results. J Urol. 2002. 167:10–5.

21.Li QL., Guan HW., Zhang QP., Zhang LZ., Wang FP., Liu YJ. Optimal margin in nephron-sparing surgery for renal cell carcinoma 4cm or less. Eur Urol. 2003. 44:448–51.
22.Rendon RA., Kachura JR., Sweet JM., Gertner MR., Sherar MD., Robinette M, et al. The uncertainty of radio frequency treatment of renal cell carcinoma: findings at immediate and delayed nephrectomy. J Urol. 2002. 167:1587–92.

23.Zagoria RJ., Hawkins AD., Clark PE., Hall MC., Matlaga BR., Dyer RB, et al. Percutaneous CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of renal neoplasms: factors influencing success. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:201–7.

Fig. 1.
(A) The follow up CT scan image 24 hours after radiofrequency ablation (RFA) shows slightly enhanced peripheral lesion. (B) The follow up CT image 1 month after RFA shows no contrast enhancement of the left renal tumor, but a slightly increased size. (C) The follow up CT image 6 month after RFA shows a decreased tumor size compared to that immediately after RFA. (D) The follow up CT image 9 month after RFA shows a more decreased tumor size.
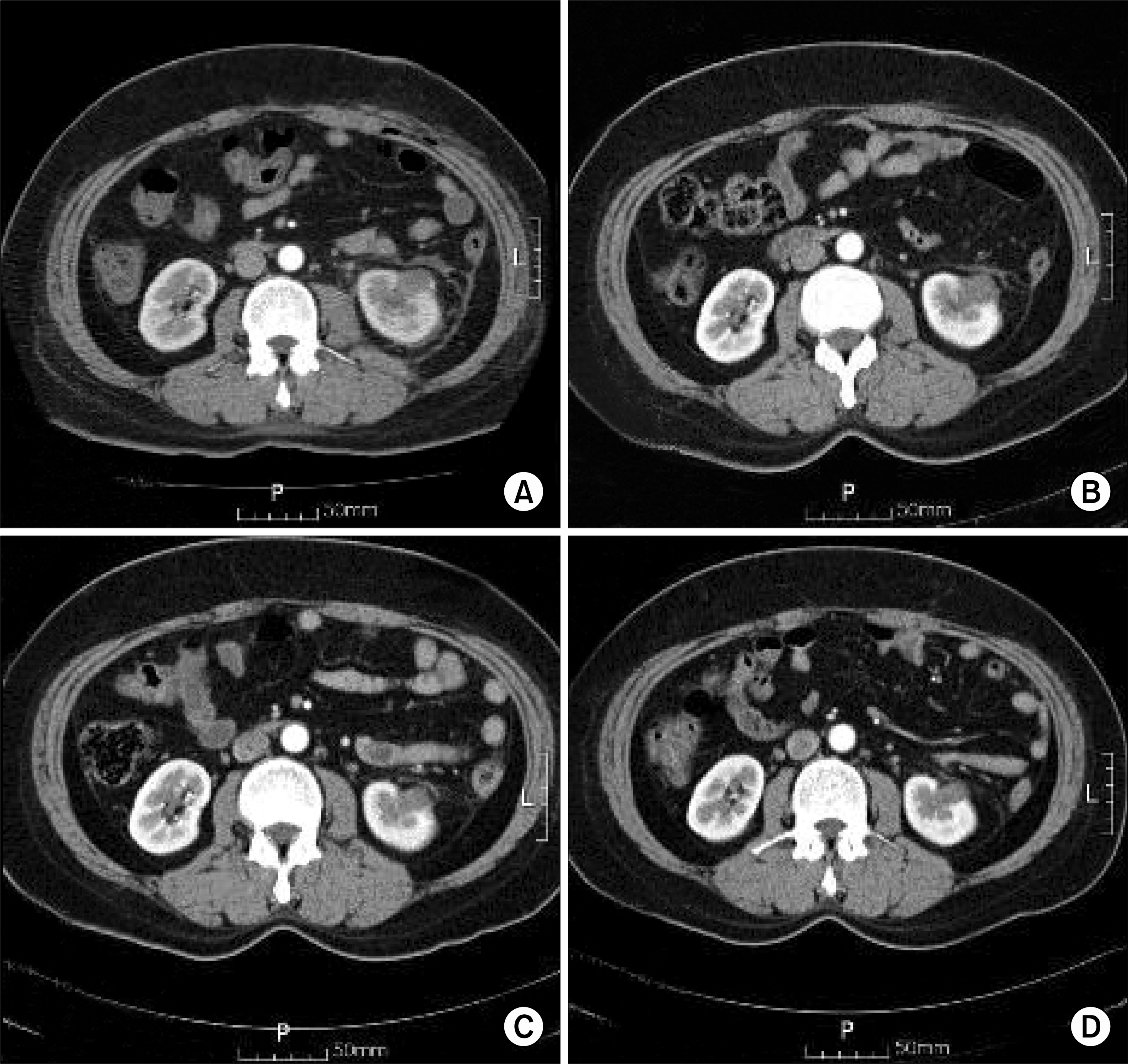
Table 1.
The patient characteristics and pre-operative status of the 12 cases
Table 2.
Results of radiofrequency ablation in the 12 patients




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download