Abstract
Weber-Christian disease (WCD) is an inflammatory disease of subcutaneous fat tissue which is characterized by relapsing, febrile tender nodules and histologically lobular panniculitis. Any area of the body containing fat can be affected by WCD. Several cases of WCD have been reported as involvement of the heart, lung, liver and kidney. Acute illness (ex. acute myocardiac infarction, infection, etc) can be complicated with stress-related hyperglycemia and increase insulin restistance. Finally this case show that Weber-Christian disease accompanied by marked hyperglycemia and insulin resistance, which resolved soon after corticosteroid.
REFERENCES
2). Oram S., Cochrane GM. Weber-Christian disease with visceral enlargement; an example with hepatic enlargement. Br Med J. 1958. 281–4.
3). Aronson IK., West DP., Variakojis D., Malkinson FD., Wilson HD., Zeitz HJ. Fatal panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985. 12:535–51.

4). Gearhart MM., Parbhoo SK. Hyperglycemia in the critically ill patient. AACN Clin Issues. 2006. 17:50–5.

5). Robinson LE., van Soeren MH. Insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in critical illness: role of insulin in glycemic control. AACN Clin Issues. 2004. 15:45–62.
6). Yang KC., Su TC., Liau CS., Lee YT. Remediable hyperglycaemia in a patient with polymyalgia rhemaica. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005. 34:492–33.
8). Flores EA., Istfan N., Pomposelli JJ., Blackburn GL., Bistrian BR. Effect of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor/cachectin on glucose turnover in the rat. Metabolism. 1990. 39:738–43.

9). Stephens JM., Lee J., Pilch PF. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is accompanied by a loss of insulin receptor substrate-1 and GLUT4 expression without a loss of insulin receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:971–6.
10). Pessin JE. Saltiel AR. Signaling pathways in insulin action: molecular targets of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000. 106:165–9.
11). Ronti T., Lupattelli G., Mannarino E. The endocrine function of adipose tissue: an update. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006. 64:355–65.

12). Drosou A., Kirsner RS., Welsh E., Sullivan TP., Kerdel FA. Use of infliximab, an antitumor necrosis alpha antibody, for inflammatory dermatoses. J Cutan Med Surg. 2003. 7:382–6.

13). 김응호: 신성철: 김형진: 안중경: 전찬홍: 차훈석등. 심한지방간과심낭삼출을동반한Weber-Christian병1예. 대한류마티스학회지. 2003. 10:195–9.
14). Amarapurkar DN., Patel ND., Amarapurkar AD. Panniculitis and liver disease (hepatic Weber Christian disease). J Hepatol. 2005. 42:149–50.

15). Hotamisligil GS., Arner P., Caro JF., Atkinson RL., Spiegelmen BM. Increase adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-a in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1995. 95:2409–15.
Fig. 1.
Multiple nodular lesions with tenderness on anterior side of left leg and right ankle (arrow).
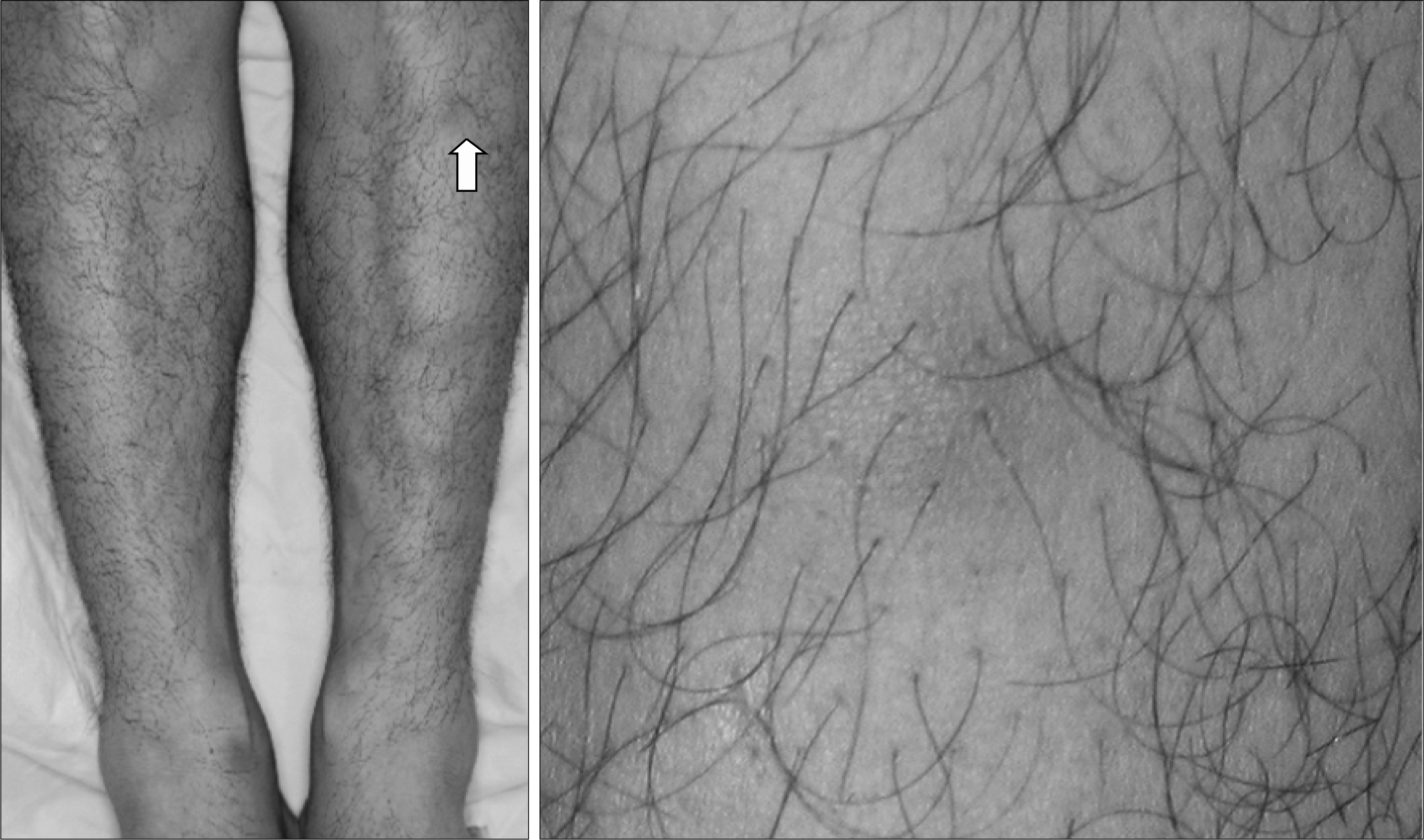
Fig. 2.
The diffusely scattered fat degenerated lesions are observed at low-power field (∗100) and infiltration of lymphocyties, neutrophils and histiocytes is found at high-power field (∗400).
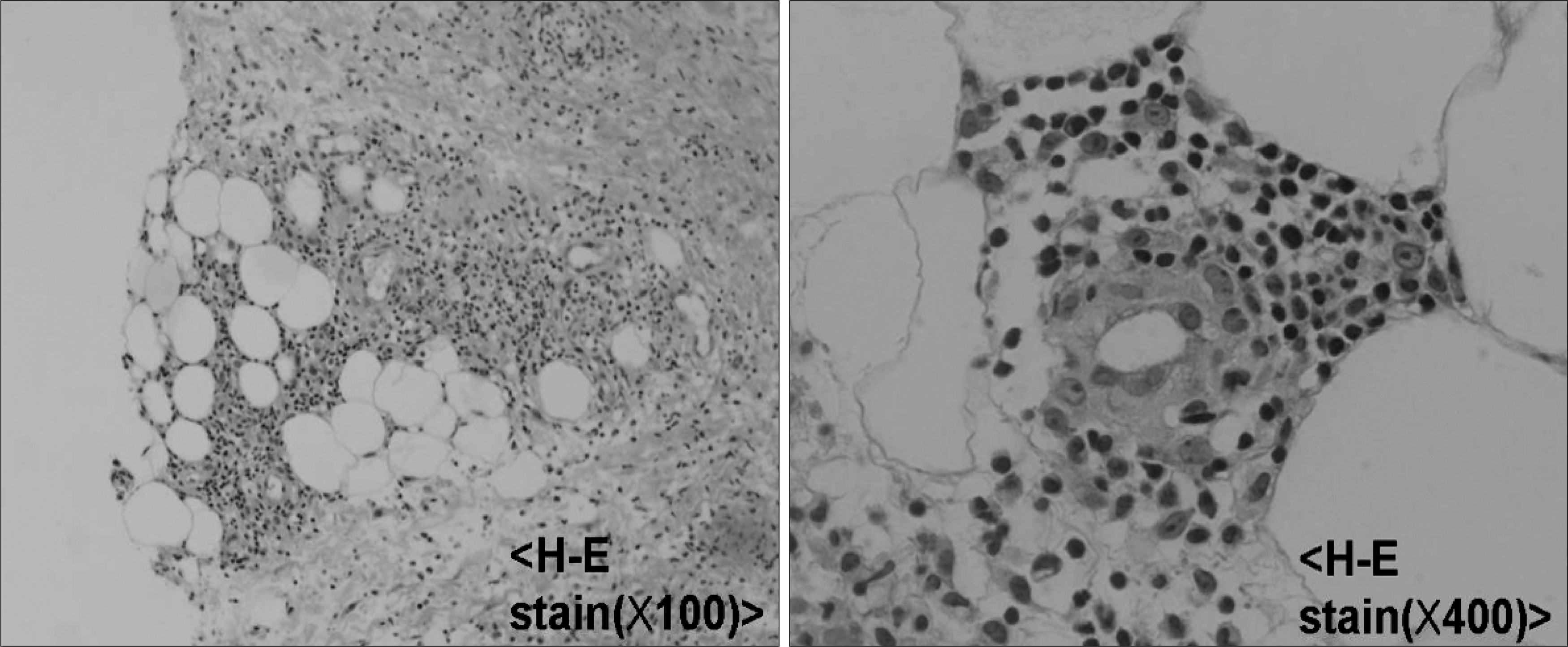
Table 1.
The serial results of laboratory examinations




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download