Abstract
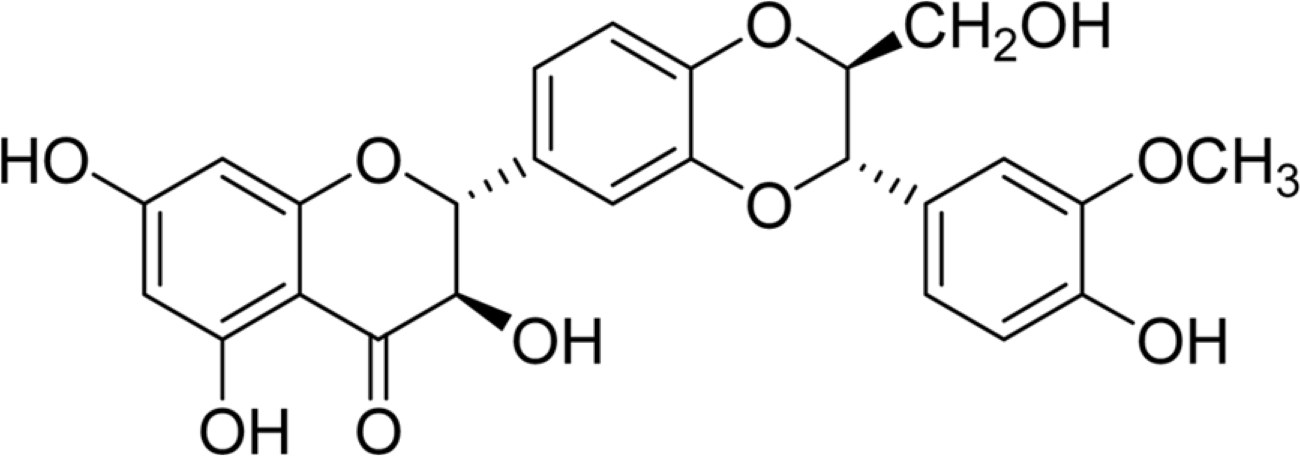
Silymarin is the standardized extract from Silybum marianum which consists mainly of flavonoids and polyphenols. It is highly regarded for its hepatoprotective ability. Silybin B is a flavonolignan and one of the active components of silymarin. The content of silybin B in various parts of S. marianum was analyzed by HPLC-UV. Results show that the extract of seeds contain the highest amount of silybin B (7.434 mg/g DW). The petioles of S. marianum showed a low content of silybin B. This study revealed that seeds of S. marianum contain high amount of silybin B and could be a good source of the compound.
References
(1). Elwekeel A.., Elfishawy A.., AbouZid S. J.Med. Plants Res. 2013. 7:1665–1669.
(2). AbouZid S. F.., Chen S. N.., Pauli G. F.Ind. Crops Prod. 2016. 83:729–737.
(3). Abenavoli L.., Capasso R.., Milic N.., Capasso F.Phytother. Res. 2010. 24:1423–1432. . ê.
(4). K en V.., Walterová D.Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky r Olomouc Czech Repub. 2005. 149:29–41. . ê ê ê.
(5). Kvasni ka F.., Bíba B.., Šev ík R.., Vold ich M.., Krátká J. J.c c Chromatogr. A. 2003. 990:239–245. . ê r Chromatogr. A. 2003 990.
(6). Saller R.., Meier R.., Brignoli R.Drugs. 2001. 61:2035–2063.
(7). Hwang I. -S.., Han E. -J.., Bak J. -S.., Kim J. -G.., Chough N.J. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2006. 12:166–173.
(8). Kim N. C.., Graf T. N.., Sparacino C. M.., Wani M. C.., Wall M. E.Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003. 1:1684–1689.
(9). Shaker E.., Mahmoud H.., Mnaa S.Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010. 48:803–806.
(10). Tamayo C.., Diamond S.Integr. Cancer Ther. 2007. 6:146–157.
(11). Csupor D.., Csorba A.., Hohmann J. J.Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016. 130:301–317.
(12). Loguercio C.., Festi D.World J. Gastroenterol. 2011. 17:2288–2301.
(13). Trouillas P.., Marsal P.., Svobodová A.., Vostálová J.., Gažák R.., ê Hrbác J.., Sedmera P.., K en V.., Lazzaroni R.., Duroux J. L.., Walterová r D. J.Phys. Chem. A. 2008. 112:1054–1063.
(14). Trappoliere M.., Caligiuri A.., Schmid M.., Bertolani C.., Failli P.., Vizzutti F.., Novo E.., di Manzano C.., Marra F.., Loguercio C.., Pinzani M. J.Hepatol. 2009. 50:1102–1111.
(15). Scambia G.., De Vincenzo R.., Ranelletti P. O.., Panici P. B.., Ferrandina G.., D'Agostino G.., Fattorossi A.., Bombardelli E.., Mancuso S.Eur. J. Cancer. 1996. 32:877–882.
(16). Tyagi A.., Bhatia N.., Condon M. S.., Bosland M. C.., Agarwal C.., Agarwal R.Prostate. 2002. 53:211–217.
(17). Zheng D.., Wang Y.., Zhang D.., Liu Z.., Duan C.., Jia L.., Wang F.., Liu Y.., Liu G.., Hao L.., Zhang Q.Cancer Lett. 2011. 307:158–164.
(18). Lee D. G.., Kim H. K.., Park Y.., Park S. C.., Woo E. R.., Jeong H. G.., Hahm K. S.Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003. 26:597–600.
(19). Cappelletti E. M.., Caniato R.Herba Hung. 1984. 23:53–66.
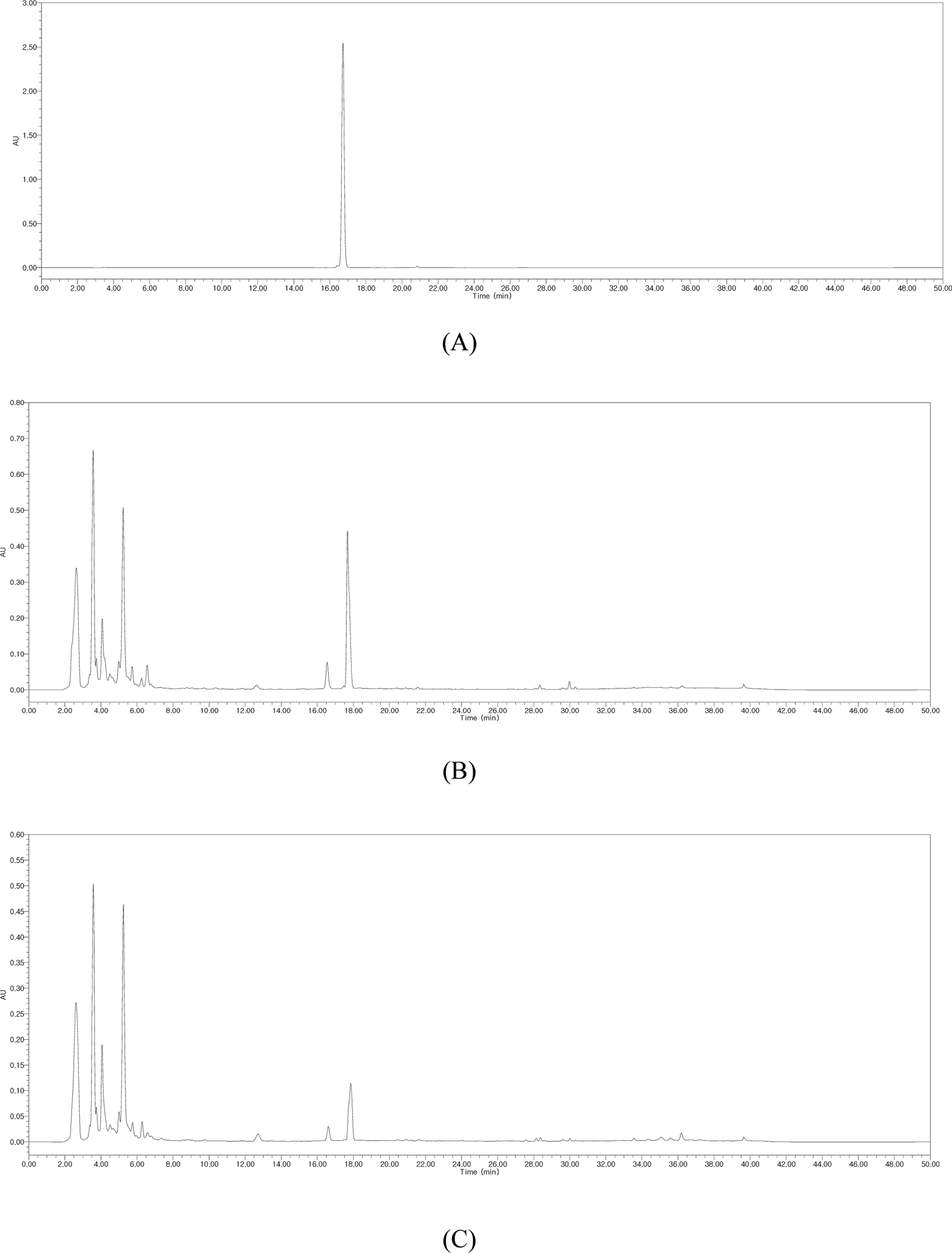
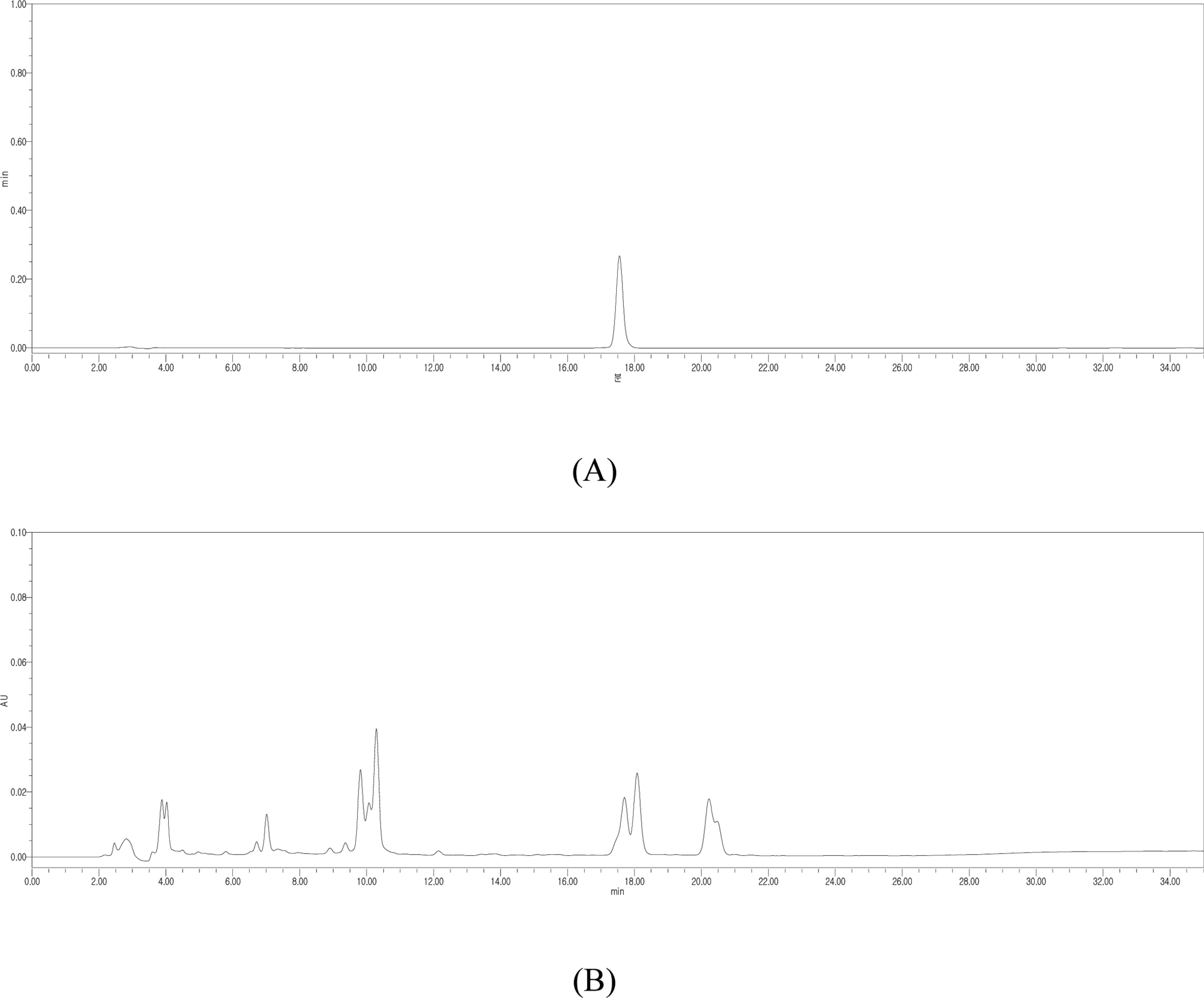
Fig. 2.
HPLC chromatograms of silybin B (A) and the EtOH extracts of leaves (B), petioles (C), flowers (D), stems (E), seeds (F), and germinated seeds (G) of S. marianum.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download