Abstract
The small field dosimetry is very important in modern radiotherapy because it has been frequently used to treat the tumor with high dose hypo-fractionated radiotherapy or high dose single fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) with small size target. But, the dosimetry of a small field (<3×3 cm2) has been great challenges in radiotherapy. Small field dosimetry is difficult because of (a) a lack of lateral electronic equilibrium, (b) steep dose gradients, and (c) partial blocking of the source. The objectives of this study were to measure and verify with the various detectors the output factors in a small field (<3 cm) for the 6 MV photon beams. Output factors were measured using the CC13, CC01, EDGE detector, thermoluminescence dosimeters (TLDs), and Gafchromic EBT2 films at the sizes of field such as 0.5×0.5, 1×1, 2×2, 3×3, 5×5, and 10×10 cm2. The differences in the output factors with the various detectors increased with decreasing field size. Our study demonstrates that the dosimetry for a small photon beam (<3×3 cm2) should use CC01 or EDGE detectors with a small active volume. And also, Output factors with the EDGE detectors in a small field (<3×3 cm2) coincided well with the Gafchromic EBT2 films.
References
1. Rao M, Wu J, Cao D, et al. Dosimetric impact of breathing motion in lung stereotactic body radiotherapy treatment using image-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83(2):e251–e256. 2012.

2. Chan MK, Kwong DL, Ng SC, Tong AS, Tam EK. Experimental evaluations of the accuracy of 3D and 4D planning in robotic tracking stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancers. Med Phys. 40(4):041712. 2013.

3. Matsugi K, Nakamura M, Miyabe Y, et al. Evaluation of 4D dose to a moving target with Monte Carlo dose calculation in stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer. Radiol Phys Technol. 6(1):233–240. 2013.

4. Palm A, Nilsson E, Herrnsdorf L. Absorbed dose and dose rate using Varian OBI 1.3 and 1.4 CBCT system. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 11(1):229–240. 2010.
5. Oh SA, Kang MK, Yea JW, Kim SH, Kim KH, Kim SK. Comparison of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Dose Calculations with a PBC and AAA Algorithms in the Lung Cancer. Kor J Med Phys. 23(1):48–53. 2012.
6. Chetty IJ, BCurran , Cygler JE, et al. Report of the AAPM Task Group No. 105: Issues associated with clinical implementation of Monte Carlo-based photon and electron external beam treatment planning. Med Phys. 34(12):4818–4853. 2007.
7. IPEM Report 103: Small field MV photon dosimetry. International Symposium on Standards, Applications and Quality Assurance in Medical Radiation Dosimetry, Vienna, Austria (. 2010.
8. Larraga-Gutierrez JM, Garcia-Hernandez D, Garcia-Garduno OA, Galvan de la Cruz OO, Ballesteros-Zebadua P, Esparza-Moreno KP. Evaluation of the GafchromicⓇ EBT2 film for the dosimetry of radiosurgical beams. Med Phys. 39(10):6111–6117. 2012.
9. Hardcastle N, Basavatia A, Bayliss A, Tome WA. High dose per fraction dosimetry of small field with Gafchromic EBT2 film. Med Phys. 38(7):4081–4085. 2011.
10. Laub WU, Wong T. The volume effect of detectors in the dosimetry of small fields used in IMRT. Med Phys. 30(3):341–347. 2003.

11. Chung H, Lynch B, Samant S. High-precision GAFCHROMIC EBT film-based absolute clinical dosimetry using a standard flatbed scanner without the use of a scanner non-uniformity correction. J appl clin med phys/AAPM. 11(2):3112. 2010.

12. Bassinet C, Huet C, Derreumaux S, et al. Small fields output factors measuremets and correction factors determination for several detectors for CyberKnifeⓇ and linear accelerators equipped with microMLC and circular cones. Med Phys. 40(7):071725. 2013.
13. Das IJ, Ding GX, Ahnesjo A. Small fields: Nonequilibrium radiation dosimetry. Med Phys. 35(1):206–215. 2008.

14. Sanchez-Doblado F, Andreo P, Capote R, et al. Ionization chamber dosimetry of small photon fields: a Monte Carlo study on stopping-power ratios for radiosurgery and IMRT beams. Phys Med Biol. 48(14):2081–2099. 2003.
15. Vlamynck K De. Palmans H, Verhaegen F, De Wagter C, De Neve W, Thierens H. Dose measurements compared with Monte Carlo simulations of narrow 6 MV multileaf collimator shaped photon beams. Med Phys. 26(9):1874–1882. 1999.
16. Verhaegen F, Das IJ, Palmans H. Monte Carlo dosimetry study of a 6 MV stereotactic radiosurgery unit. Phys Med Biol. 43(10):2755–2768. 1998.
17. Sauer OA, Wilbert J. Measurement of output factors for small photon beams. Med Phys. 34(6):1983–1988. 2007.

18. Haryanto F, Fippel M, Laub W, Dohm O, Nusslin F. Investigation of photon beam output factors for conformal radiation therapy – Monte Carlo simulations and measurements. Phys Med Biol. 47(11):N133–N143. 2002.
19. Francescon P, Cora S, Cavedon C. Total scatter factors of small beams: A multidetector and Monte Carlo study. Med Phys. 35(2):504–513. 2008.

20. Lee HJ, Choi TJ, Oh YK, et al. The Output Factor of Small Field in Multileaf Collimator of 6MV Photon Beams. Progress in Medical Physics. 25(1):15–22. 2014.
21. Oh SA, Kang MK, Yea JW, Kim SK, Oh YK. Study of the penumbra for high-energy photon beams with GafchromicTM EBT2 films. J Kor Phys Soc. 60(11):1973–1976. 2012.
22. Cranmer-Sargison G, Weston S, Sidhu NP, Thwaites DI. Experimental small field 6 MV output ratio analysis for various diode detector and accelerator combinations. Radiother Oncol. 100(3):429–435. 2011.
Fig. 1.
Photograph of the Novalis Tx for a medical linear accelerator: (a) side view, (b) front view.

Fig. 2.
Photograph of the detectors combined with the blue phantom; (a) CC13 ion chamber, (b) EDGE detector.
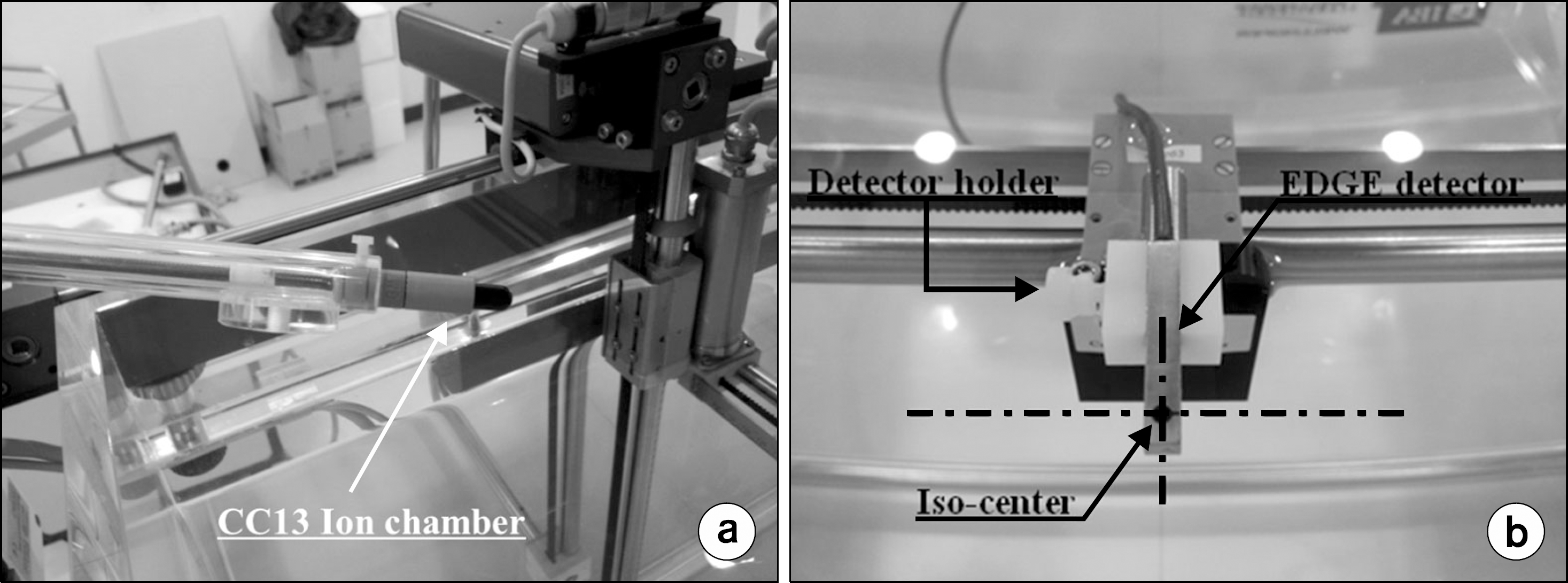
Fig. 3.
Photograph of the Gafchromic EBT2 films for the dose calibration. (a) Background film; (b) Cut-calibration film (#1∼ #16, #24, #25: 0, 10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 100, 120, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500, 700, and 1000 cGy, respectively; #17∼#22 (exposed film for output factors in each field): 5×5, 10×10, 20×20, 30×30, 50×50, and 100 mm×100 mm, respectively. #23 is a re-measurement of #11.

Fig. 4.
Calibration curve for the 6 MV photon beam with R, G, B channel (0, 10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 100, 120, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500, 700, and 1000 cGy).
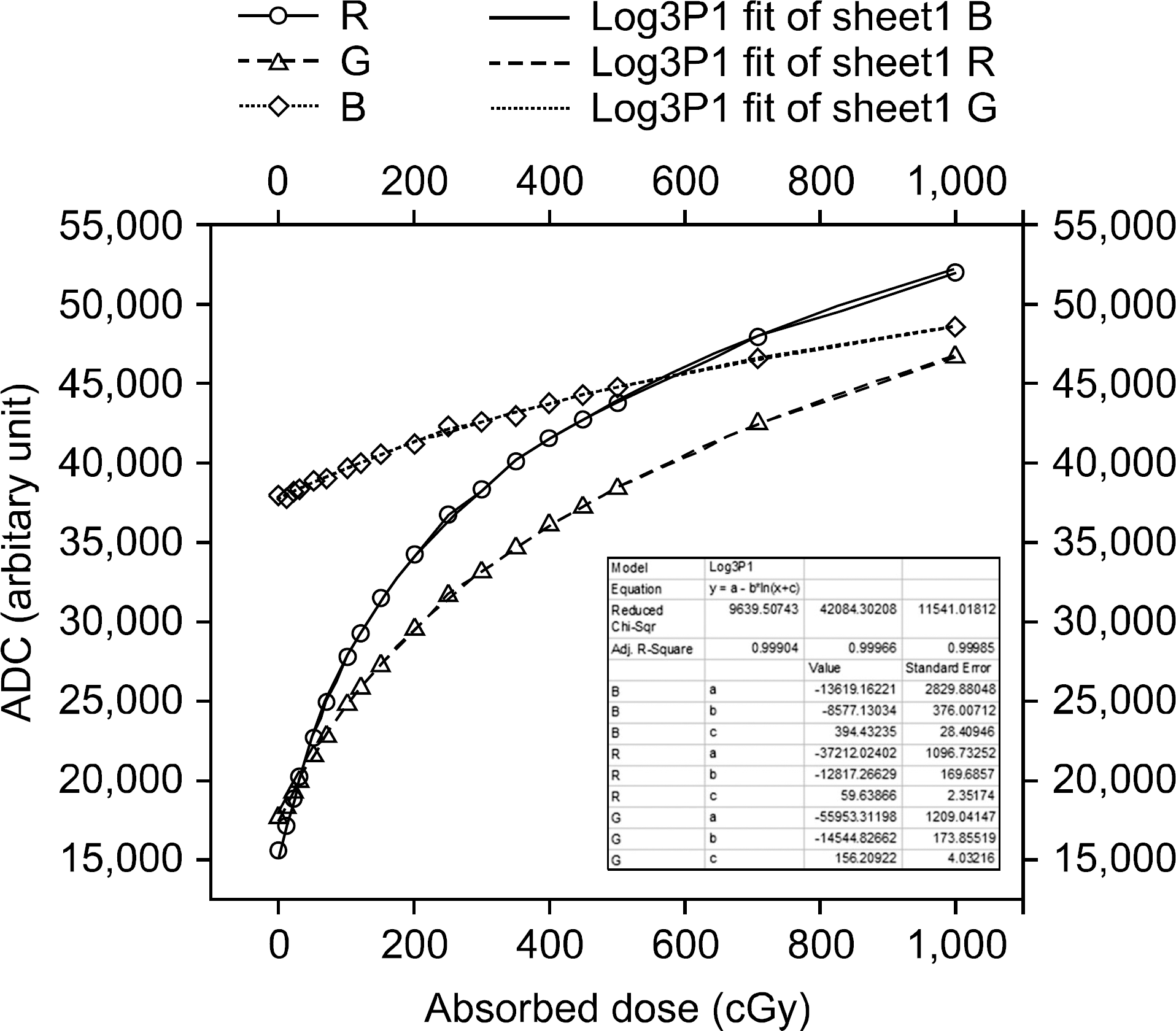
Fig. 5.
Output factor measured with CC13, CC01, EDGE, TLD and EBT2 film for photon beam from a 6 MV accelerator for field sizes ranging from 0.5×0.5 cm2 to 10×10 cm2.
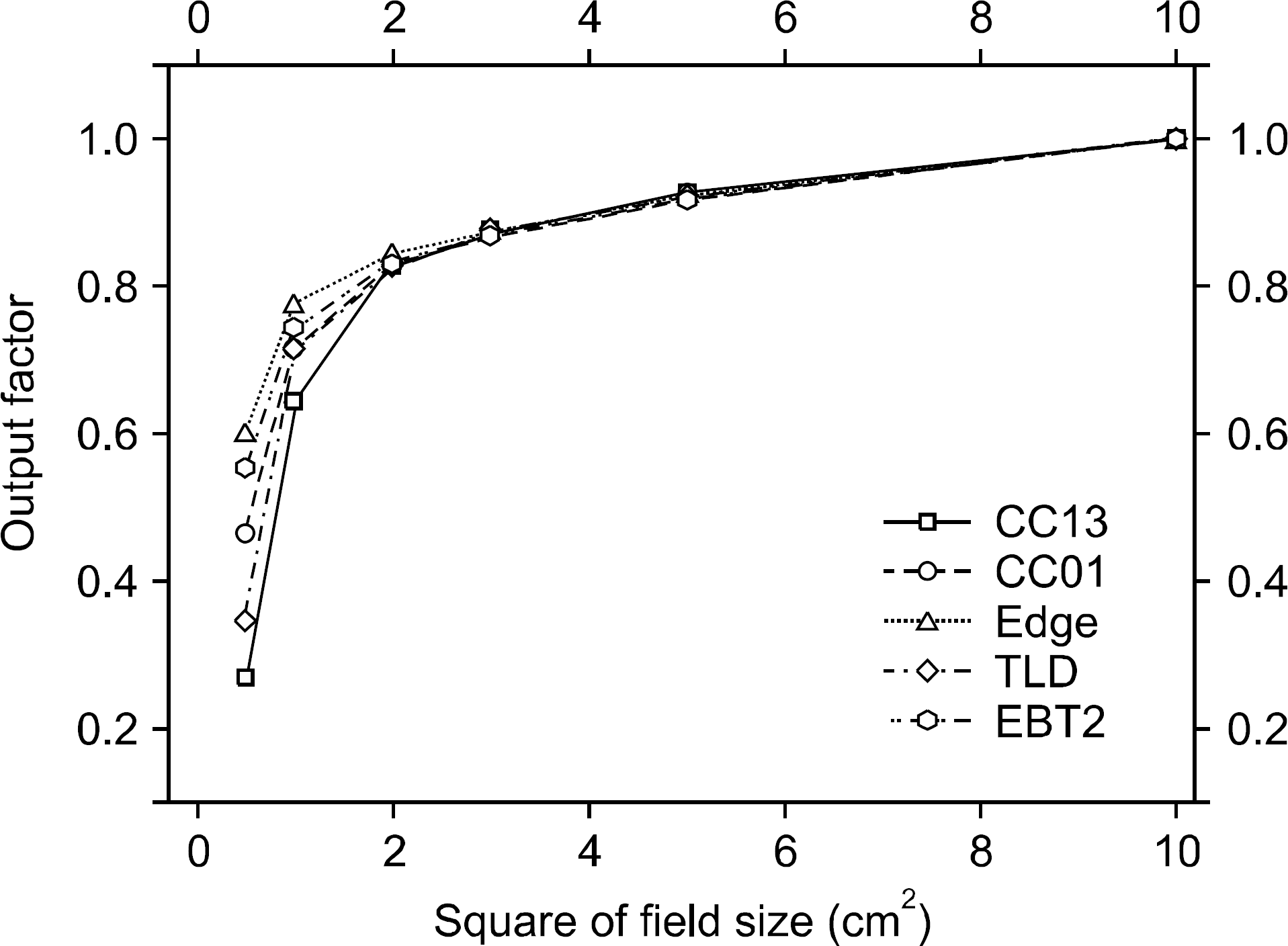
Table 1.
Specifications of the CC13, CC01, and EDGE detectors.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download