Abstract
In this research, the glass dosimeter was calibrated to measure the standard absorbed dose of the Cs-137 irradiator and absorbed dose in a biological sample. Absorbed dose in water for Cs-137 gamma ray was determined by the IAEA TRS-277 protocol. The PTW-TM30013 ion chamber and the PTW-TM41023 water phantom were utilized for measuring absorbed dose and the value was compared with the reading from DoseAce GD-302M glass dosimeter from Asahi Techno Glass Corporation for its calibration. The uncertainty of measurement (1σ) of the calibrated glass dosimeter was 2.7% and this result would be applied to improve the accuracy in measurement of absorbed dose in a biological sample.
REFERENCES
1. Jeong DH, Kim JK, Yang KM, et al. Absorbed dose determination for a biological sample irradiated by gamma rays from a Cs-137 source. Korean J Med Phys. 22(3):124–130. 2011.
2. Sabine H. Methods in Radiobiology. Nanodosimetry Workshop. 2009.
3. Kwak DH, Moon YM, Kang YR, Lee CY, Jeong DH, Kim JK. 감마선 조사시 용기의 크기에 따른 흡수선량 평가. KARP 춘계학술대회 논문집. 2011, Seoul, pp.282.
4. Brady SL, Toncheva G, Dewhirst MW, Yoshizumi TT. Characterization of a 137Cs irradiator from a new perspective with modern dosimetric tools. Health Phys. 97(3):195–205. 2009.

5. TRS-277. Absorbed Dose Determination in Photon and Electron Beams: An International Code of Practice. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna. 1997.
6. TRS-398. Absorbed dose determination in external beam radiotherapy: an international code of practice for dosimetry based on standards of absorbed dose to water. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna. 2000.
Fig. 1.
A photography of geometrical setup for measuring absorbed dose to water for a Cs-137 gamma-ray irradiator.
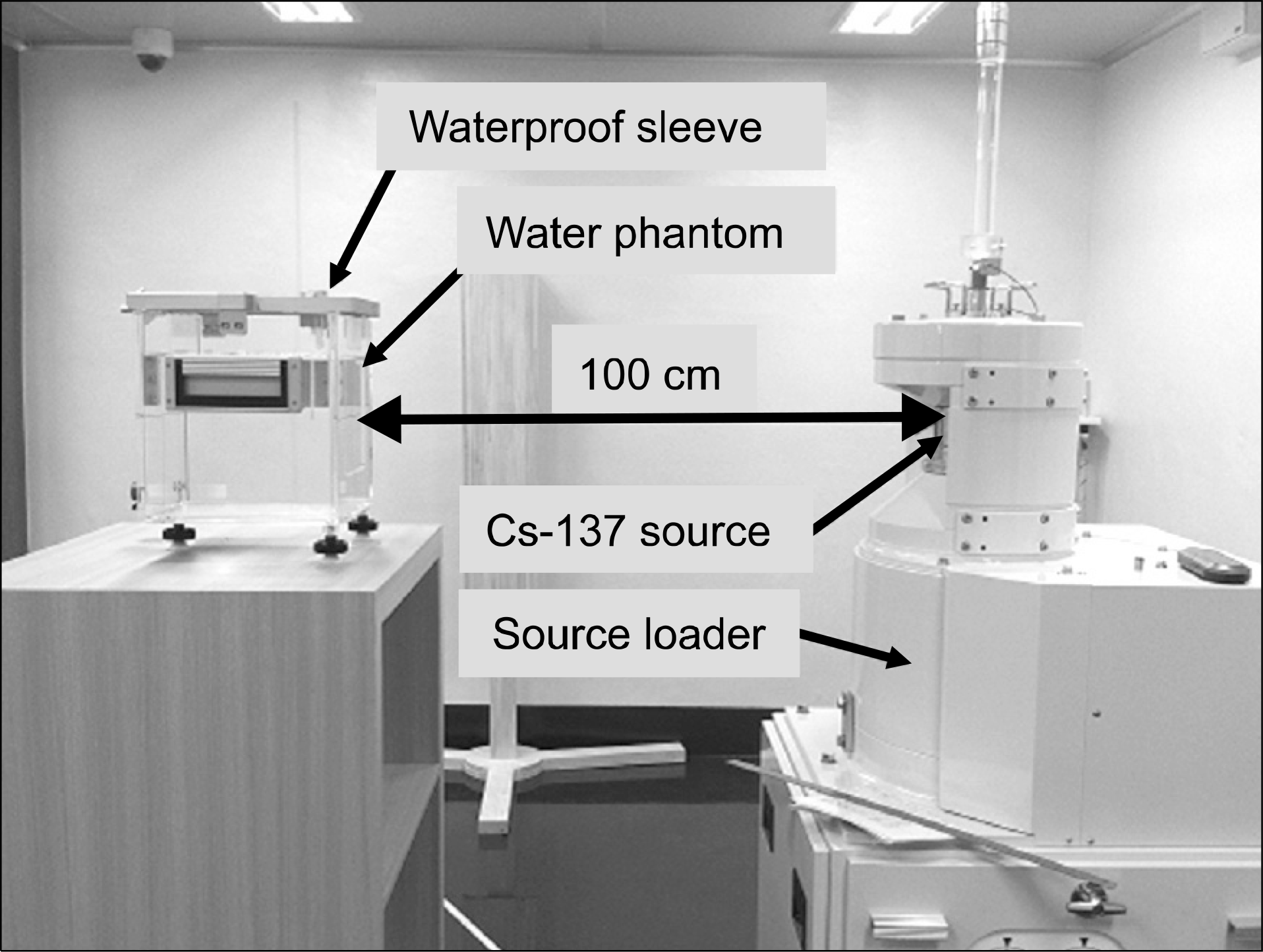
Table 1.
Values for Cs-137 gamma rays in TRS-277 protocol, ∗kTP corrected.
Table 2.
Dosimeter readings, its standard deviations, and calibration factors for 6 glass dosimeters.
Table 3.
Uncertainty estimations of calibration of the glass dosimeters in this study.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download