Abstract
Purpose
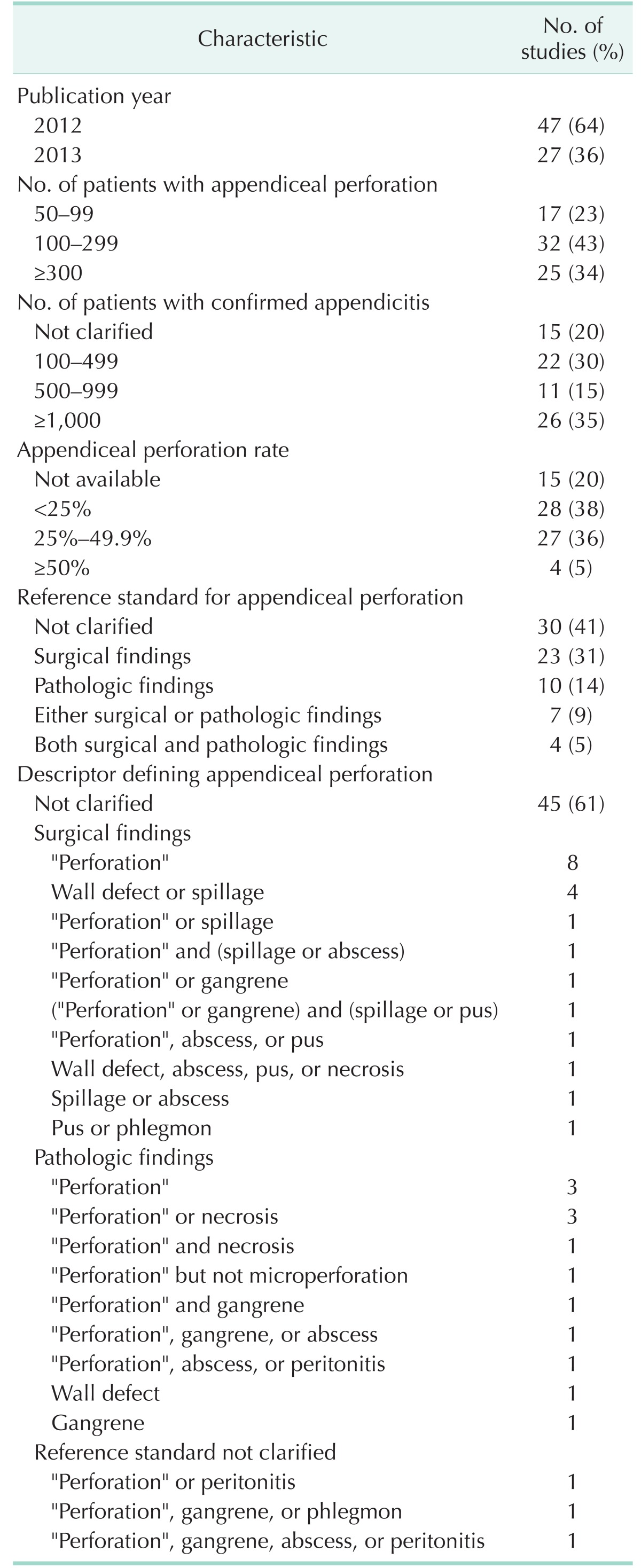
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
References
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 3
Supplementary Table 5
Supplementary Table 7
Fig. 2
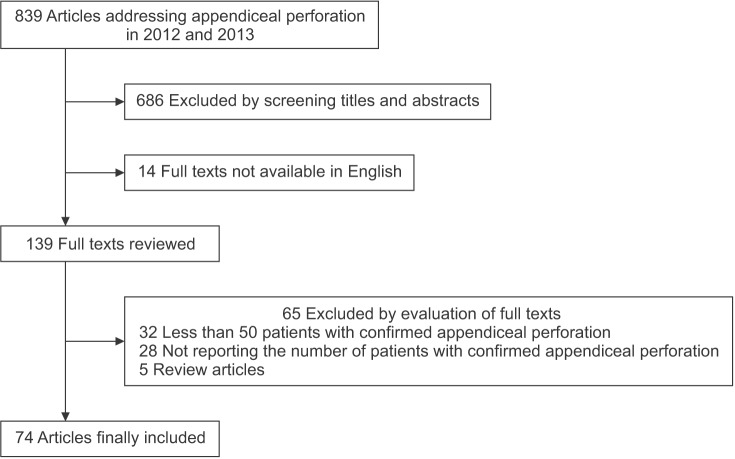
Patient flow diagram. Group 1, nonperforation; group 2, perforation identified pathologically but not surgically; group 3, perforation identified surgically but not pathologically; group 4, perforation identified both pathologically and surgically.
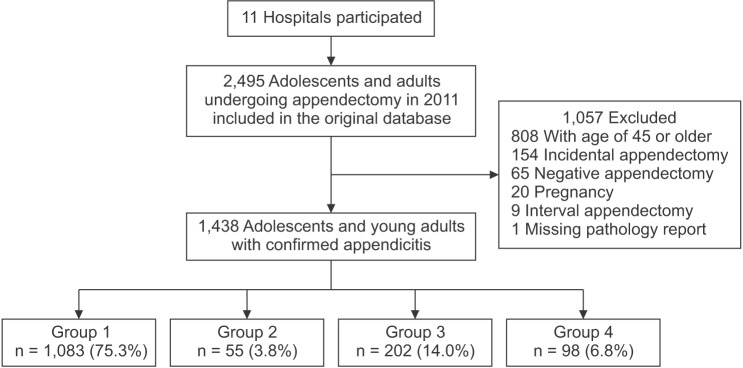
Fig. 3
Length of hospital stay. Group 1, nonperforation; group 2, perforation identified pathologically but not surgically; group 3, perforation identified surgically but not pathologically; group 4, perforation identified both pathologically and surgically. The middle lines in the boxes denote medians, and the upper and lower margins in the boxes represent the upper and lower quartiles, respectively. The ends of the vertical lines indicate 1.5 times the interquartile range. The crosses indicate outliers.
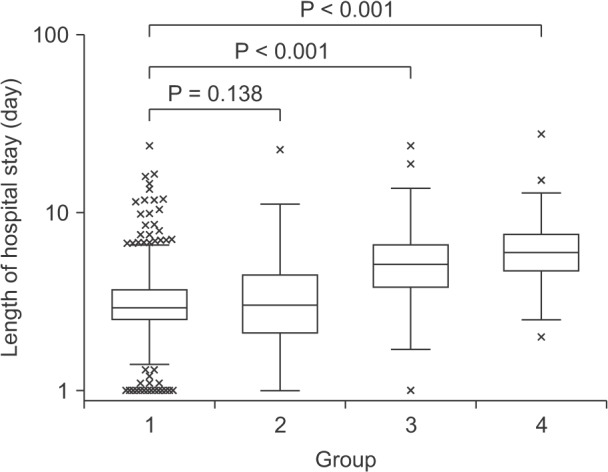
Table 2
Patient characteristics
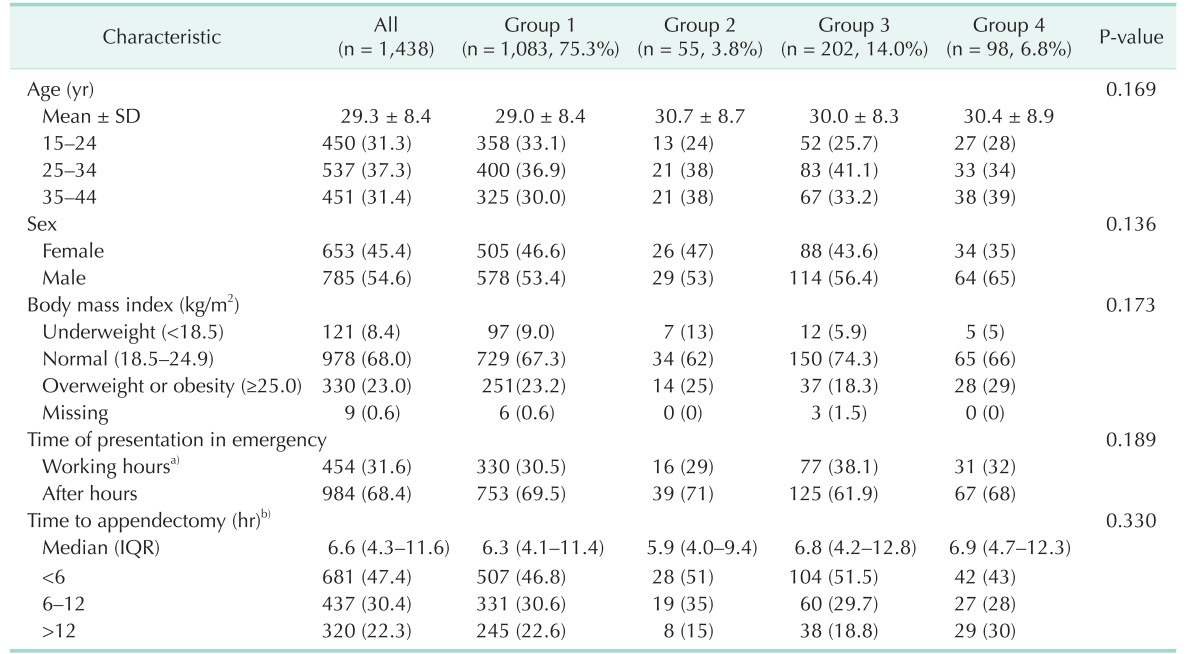
Values are presented as number of patients (%) unless otherwise indicated.
Group 1, nonperforation; group 2, perforation identified pathologically but not surgically; group 3, perforation identified surgically but not pathologically; group 4, perforation identified both pathologically and surgically; SD, standard deviation; IQR, interquartile range. a)8:00 AM to 5:00 PM on work days. b)Defined as the interval from the Emergency Department visit to the induction of anesthesia for appendectomy.
Table 3
Use of laparoscopic appendectomy adjusted for clustering effects by site
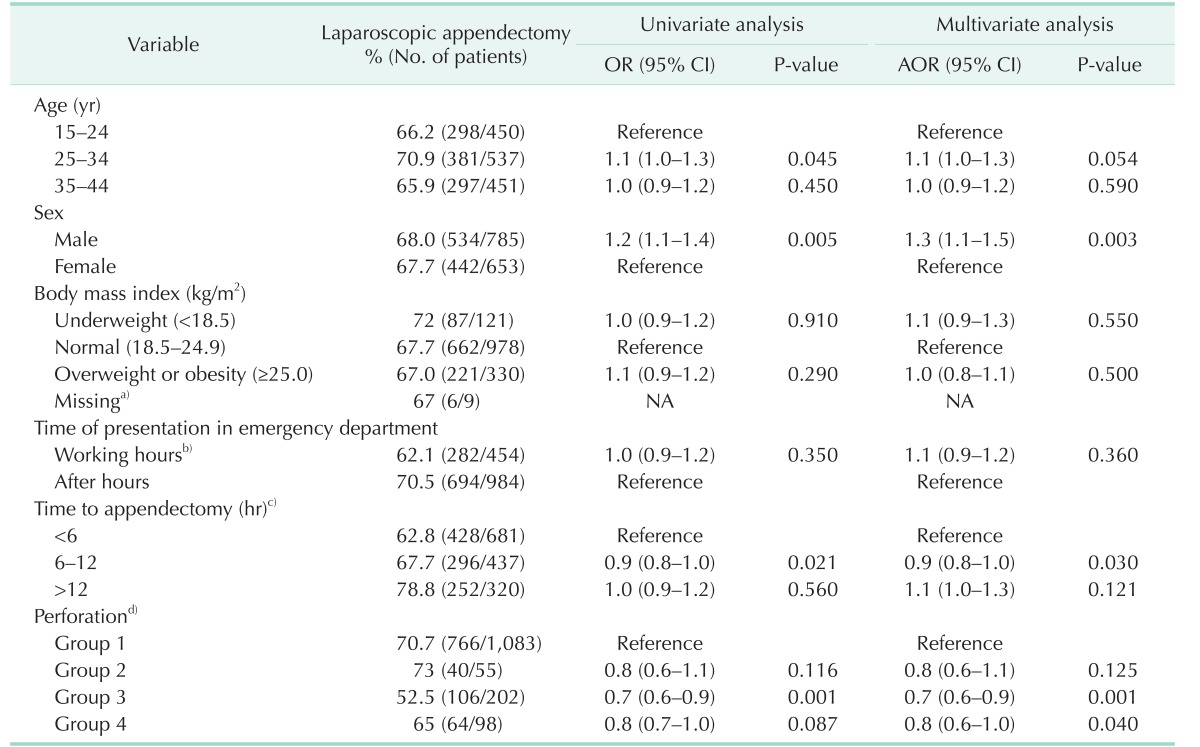
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; AOR, adjusted odds ratio; IQR, interquartile range; NA, not available.
Generalized estimating equations were used to adjust for clustering effects by site. Nine cases with open conversion from initial laparoscopic approach were counted as open appendectomies.
a)Nine cases with missing data were not included in the multivariable analysis. b)8:00 AM to 5:00 PM on work days. c)Defined as the interval from the Emergency Department visit to the induction of anesthesia for appendectomy. d)Group 1, nonperforation; group 2, perforation identified pathologically but not surgically; group 3, perforation identified surgically but not pathologically; group 4, perforation identified both pathologically and surgically.
Table 4
Length of hospital stay
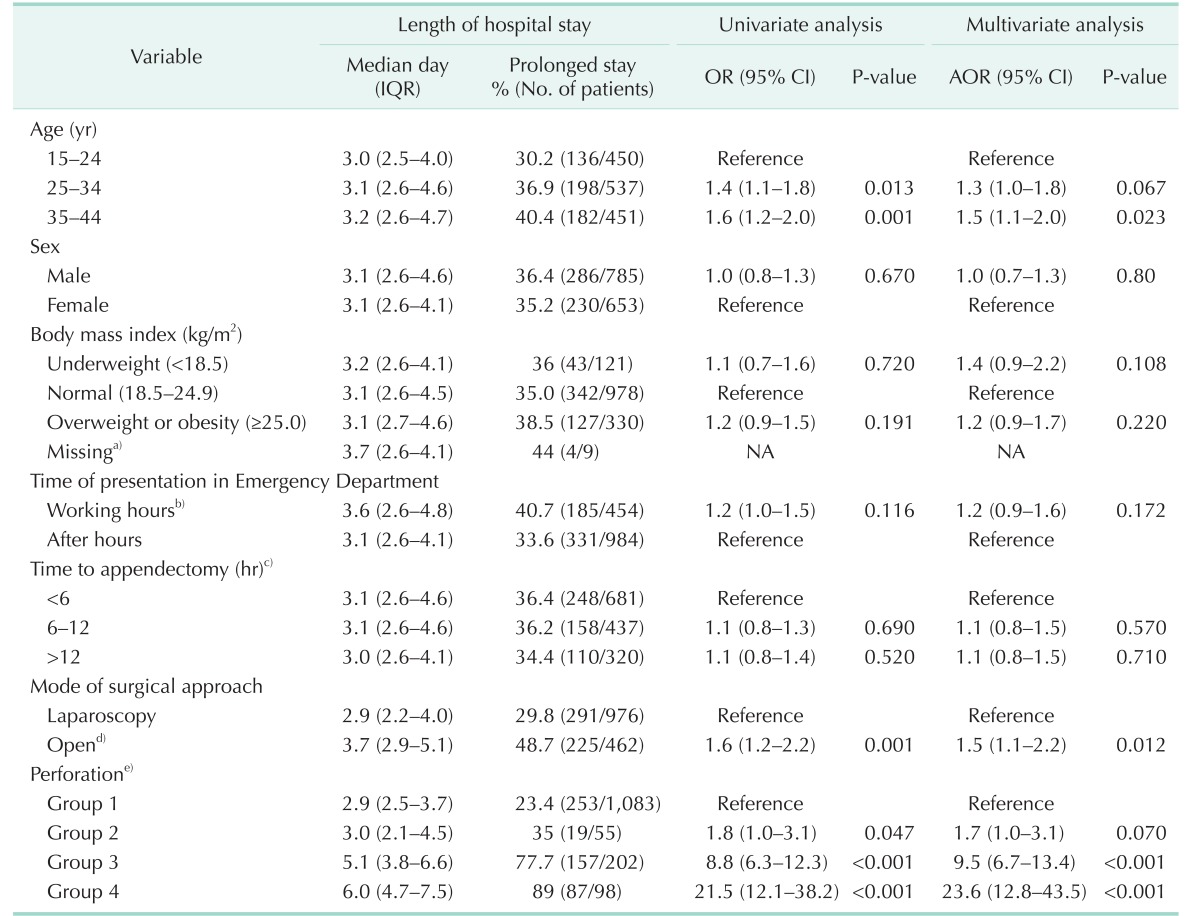
AOR, adjusted odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; IQR, interquartile range; OR, odds ratio.
Generalized estimating equations were used to adjust for clustering effects by site. Prolonged stay was defined as 3.7 days (75th percentile in group 1) or longer.
a)Nine cases with missing data were not included in the multivariable analysis. b)8:00 AM to 5:00 PM on work days. c)Defined as the interval from the Emergency Department visit to the induction of anesthesia for appendectomy. d)Including 9 cases with open conversion from initial laparoscopic approach. e)Group 1, nonperforation; group 2, perforation identified pathologically but not surgically; group 3, perforation identified surgically but not pathologically; group 4, perforation identified both pathologically and surgically.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download