Abstract
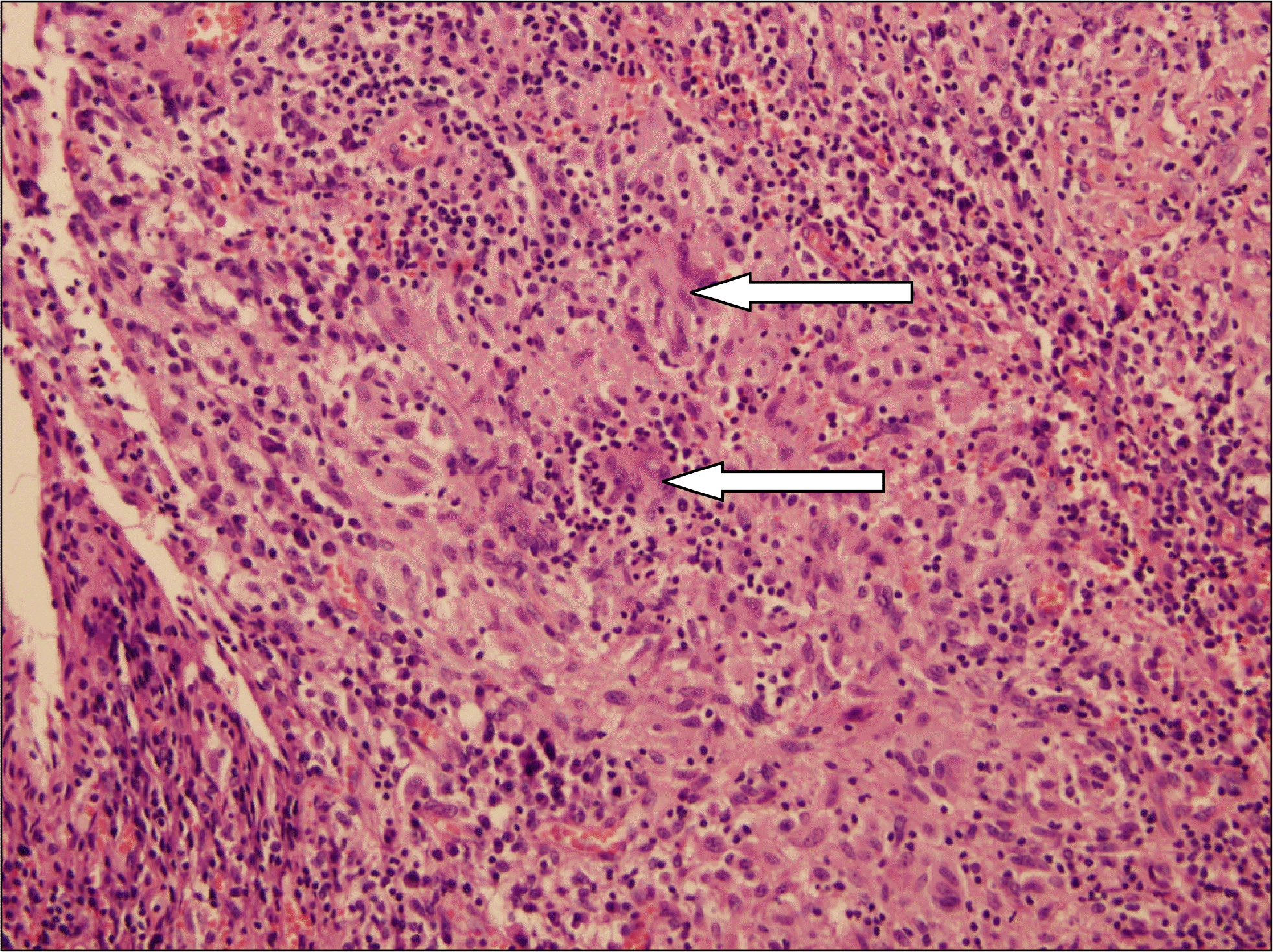
Tuberculosis of the penis is rare. The clinical features of penile tuberculosis are usually manifested as ulceration or scars. However, the authors encountered a case of penile tuberculosis that presented as a mass. A painless nodule at the base of the penis was noted in a 63-year-old male patient. Surgical excision was recommended, and pathologic finding revealed granulomatous inflammation in the mass. Acid fast bacilli stain and culture were negative, but a positive result was found in urine polymerase chain reaction for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. He was diagnosed with tuberculosis of the penis and underwent anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy.
REFERENCES
1.Daher Ede F., da Silva GB Jr., Barros EJ. Renal tuberculosis in the modern era. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013. 88:54–64.
3.Narayanaswamy S., Krishnappa P., Bandaru T. Unproved tuberculous lesion of penis: a rare cause of saxophone penis treated by a therapeutic trial of anti-tubercular therapy. Indian J Med Sci. 2011. 65:112–5.

4.Mylarappa P., Srikantaiah HC. Acute retention of urine, tubercular prostatitis: a rare case. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013. 7:2992–3.
5.Dahl DM., Klein D., Morgentaler A. Penile mass caused by the newly described organism Mycobacterium celatum. Urology. 1996. 47:266–8.

6.Wolf JS Jr., McAninch JW. Tuberculous epididymo-orchitis: diagnosis by fine needle aspiration. J Urol. 1991. 145:836–8.
7.Wise GJ., Marella VK. Genitourinary manifestations of tuberculosis. Urol Clin North Am. 2003. 30:111–21.

8.Baveja CP., Vidyanidhi G., Jain M., Kumari T., Sharma VK. Drug-resistant genital tuberculosis of the penis in a human immunodeficiency virus non-reactive individual. J Med Microbiol. 2007. 56:694–5.

9.Zajaczkowski T. Genitourinary tuberculosis: historical and basic science review: past and present. Cent European J Urol. 2012. 65:182–7.
Fig. 1.
Abdomino-pelvic computed tomography showed a 15×15×17 mm sized non-enhancing cystic mass with wall enhancement on the dorsal aspect of the penis base (arrow).
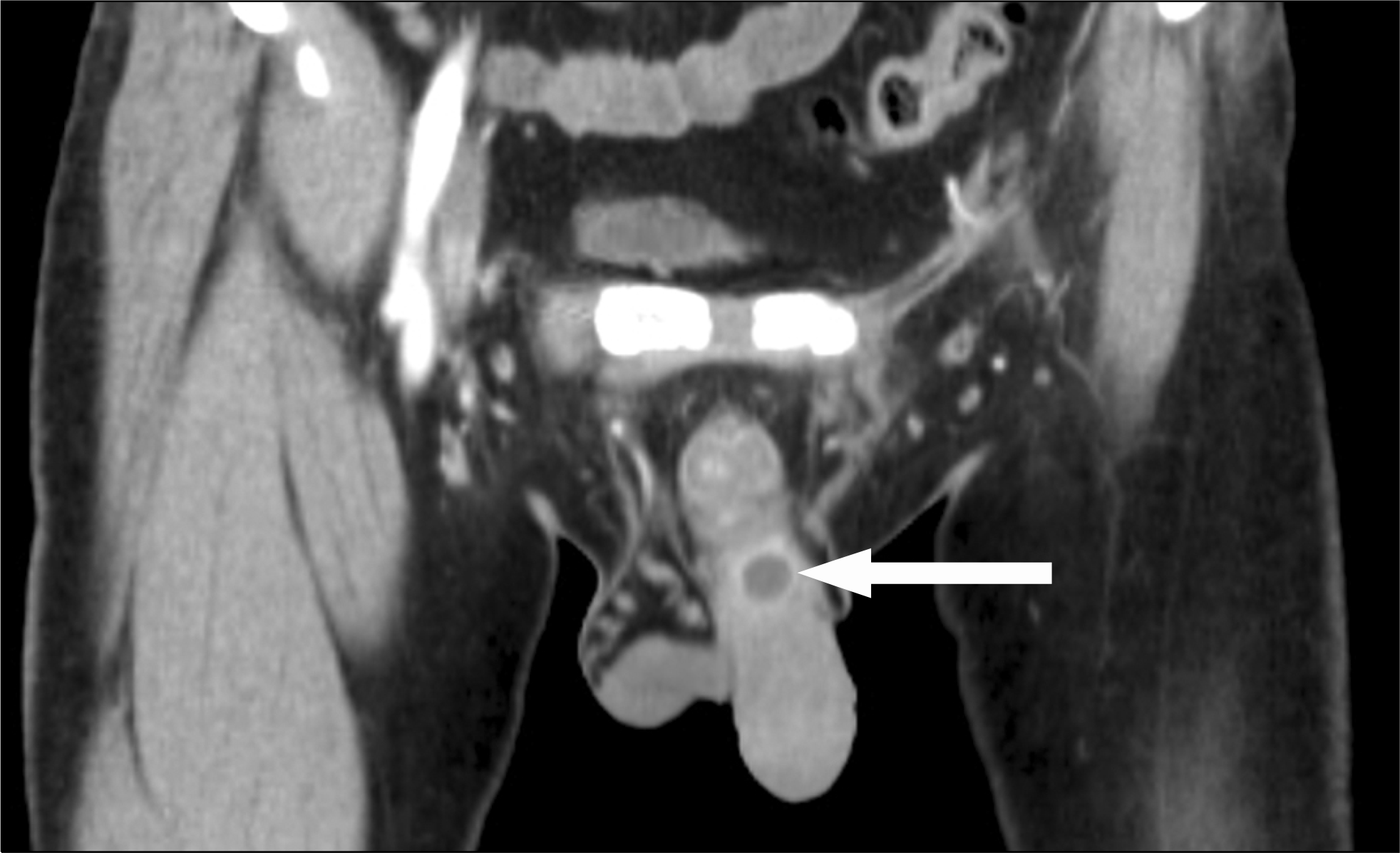
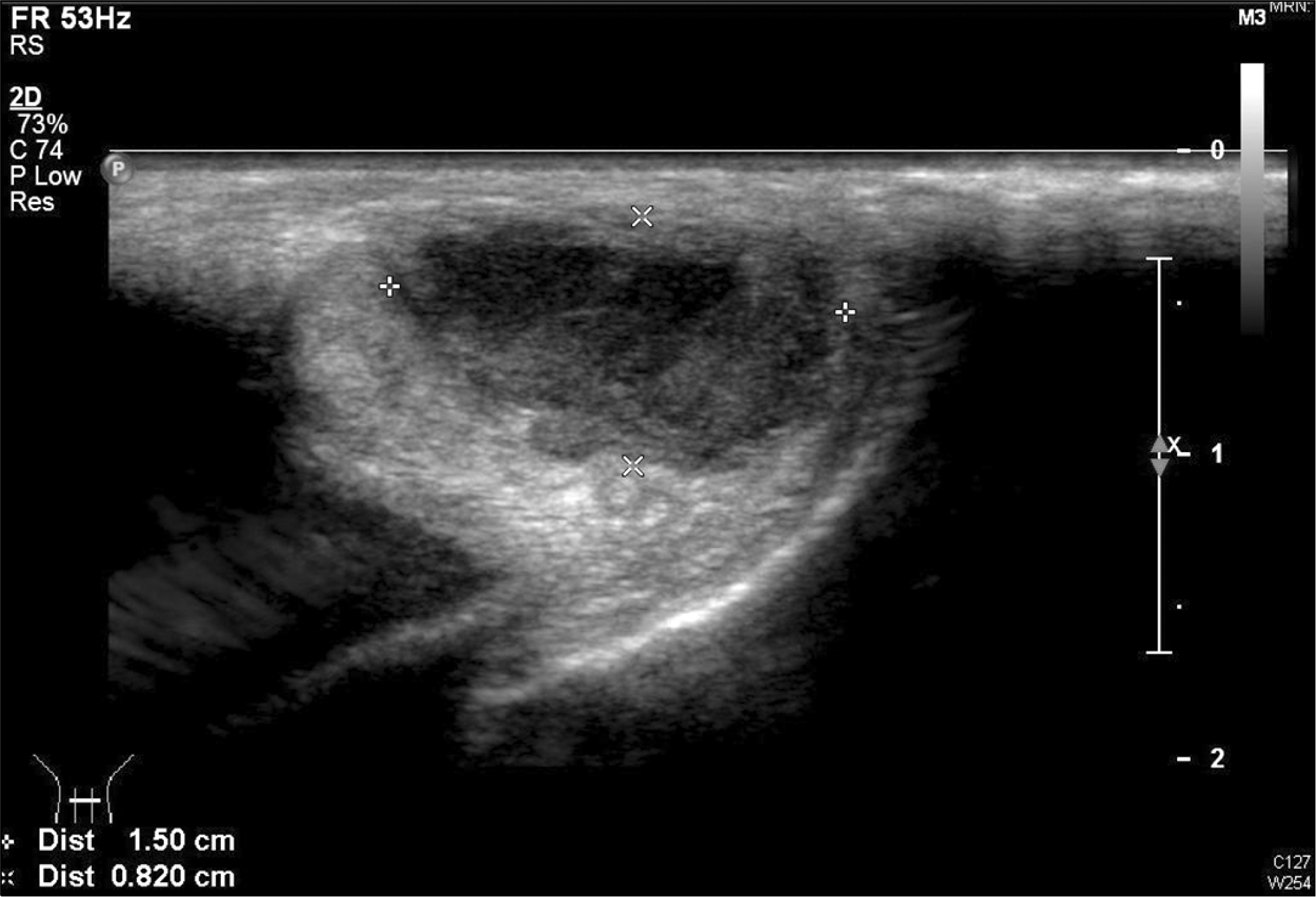
Fig. 2.
Penile ultrasonography showed a 15×8×17 mm sized heterogeneous hypoechoic mass with irregular wall thickening in the penile base.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download