Abstract
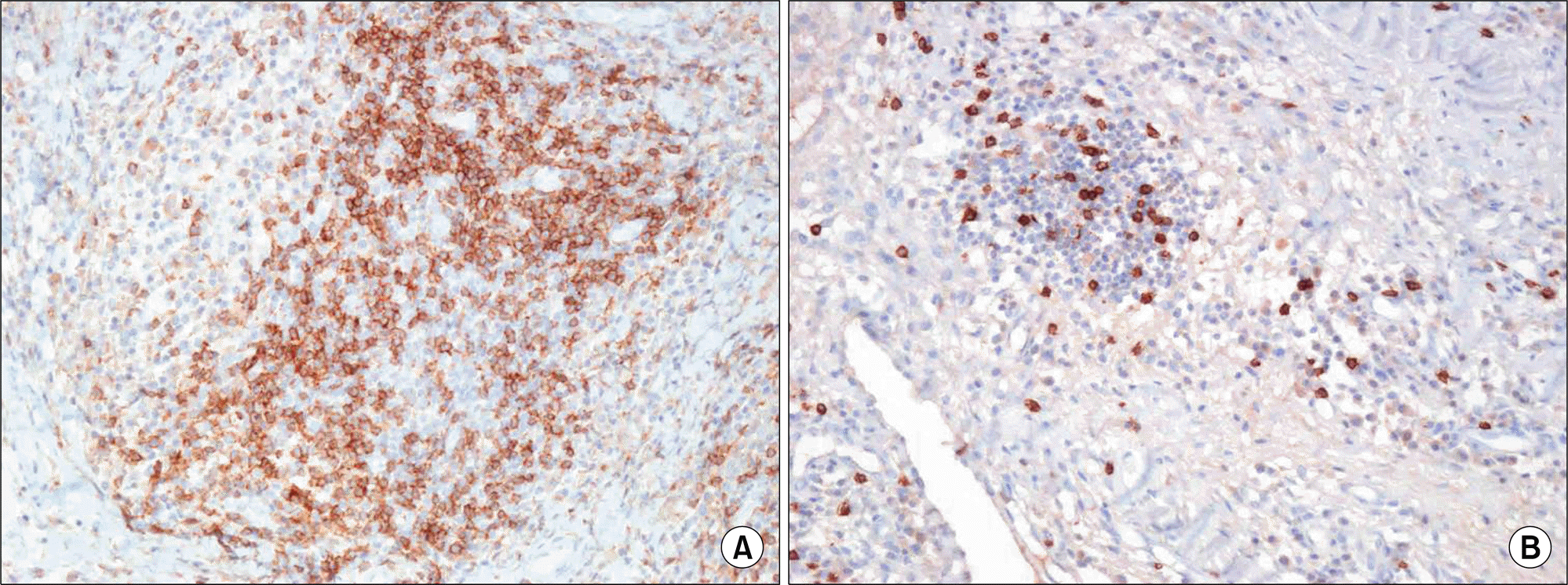
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) mainly affects polyarticular joints and is characterized by inflammation of the synovial membrane leading to joint destruction. We report on an unusual case of RA presenting as an intra-articular mass invading bone of the wrist joint in a patient with chronic monoarthritis. A 43-year-old man presented with left wrist joint pain and swelling lasting several years. A plain radiograph showed a non-specific osteolytic lesion in the distal ulna but a magnetic resonance image demonstrated an intra-articular irregular mass-like lesion with eccentric bone erosion the distal radioulnar joint. Synovial biopsy detected hyperplasia of the synovial lining cell layer and finger-like protrusions of inflamed and edematous fibrovascular stroma containing dense inflammatory infiltrates, mainly plasma cells, B cells, and CD4+ T cells. Rheumatoid factor and anticitrullinated protein antibody were highly positive. The patient was diagnosed with RA and treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, showing a good response on further follow-up.
REFERENCES
2. Hülsemann JL, Zeidler H. Undifferentiated arthritis in an early synovitis outpatient clinic. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1995; 13:37–43.
3. Binard A, Alassane S, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Berthelot JM, Jousse-Joulin S, Chalés G, et al. Outcome of early monoarthritis: a followup study. J Rheumatol. 2007; 34:2351–7.
4. Jeong H, Kim AY, Yoon HJ, Park EJ, Hwang J, Kim H, et al. Clinical courses and predictors of outcomes in patients with monoarthritis: a retrospective study of 171 cases. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014; 17:502–10.

5. Machado P, Castrejon I, Katchamart W, Koevoets R, Kuriya B, Schoels M, et al. Multinational evidence-based recommendations on how to investigate and follow-up undifferentiated peripheral inflammatory arthritis: integrating systematic literature research and expert opinion of a broad international panel of rheumatologists in the 3E Initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:15–24.

6. Iguchi T, Matsubara T, Kawai K, Hirohata K. Clinical and histologic observations of monoarthritis. Anticipation of its progression to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (250):241–9.
7. Foocharoen C, Nanagara R, Foocharoen T, Mootsikapun P, Suwannaroj S, Mahakkanukrauh A. Clinical features of tuberculous septic arthritis in Khon Kaen, Thailand: a 10-year retrospective study. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2010; 41:1438–46.
9. Kraan MC, Haringman JJ, Post WJ, Versendaal J, Breedveld FC, Tak PP. Immunohistological analysis of synovial tissue for differential diagnosis in early arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38:1074–80.

10. Cañete JD, Rodríguez JR, Salvador G, Gómez-Centeno A, Muñoz-Gómez J, Sanmartí R. Diagnostic usefulness of synovial vascular morphology in chronic arthritis. A systematic survey of 100 cases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 32:378–87.

11. Bugatti S, Manzo A, Bombardieri M, Vitolo B, Humby F, Kelly S, et al. Synovial tissue heterogeneity and peripheral blood biomarkers. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011; 13:440–8.

12. Pitzalis C, Kelly S, Humby F. New learnings on the pathophysiology of RA from synovial biopsies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013; 25:334–44.

13. Johansson JE, Ajjoub S, Coughlin LP, Wener JA, Cruess RL. Pigmented villonodular synovitis of joints. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982; (163):159–66.

Figure 1.
Abnormalties of the distal end and styloid process of the ulna. Radiolucent osteolytic lesion in ulnar head with sub-jacent resorption of bone on plain radiograph of the left wrist joint. Alterations on apposing surface of the distal ends of the radius and ulna.
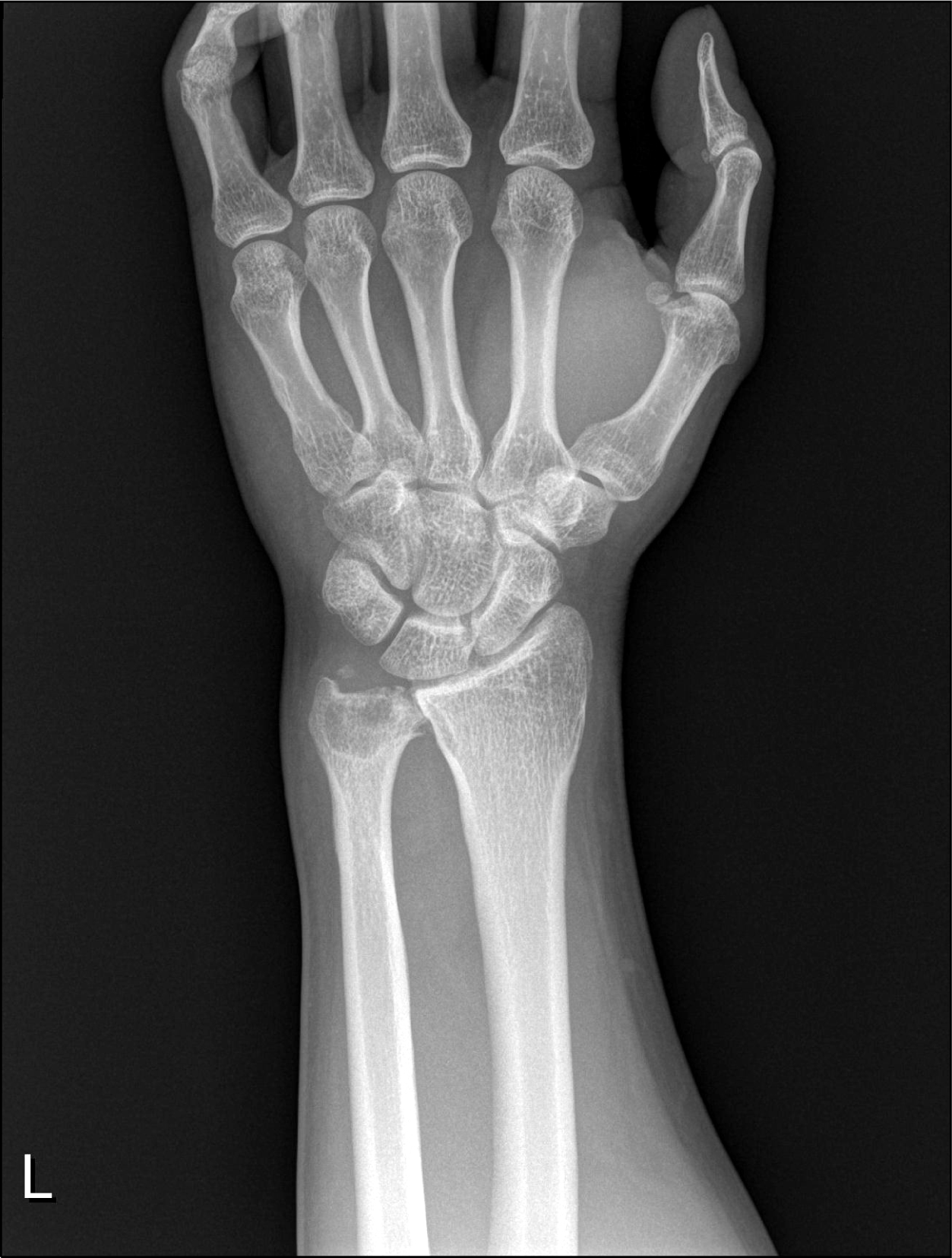
Figure 2.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) abnormalities. (A) Coronal T1-weighted, (B) T1-weighted with enhancement, and (C) sagittal T2-weighted MRI of intra-articular irregular mas-like lesion of left distal ulna including extensive osseous involvement with enhancement. Eccentric bone erosion with suspicious overhanging edge at distal ulna and radioulnar joint. (D) Proton density-weighted image of bone marrow edema and marginal erosion with synovial hyperplasia at distal end of radio-unlar joint.

Figure 3.
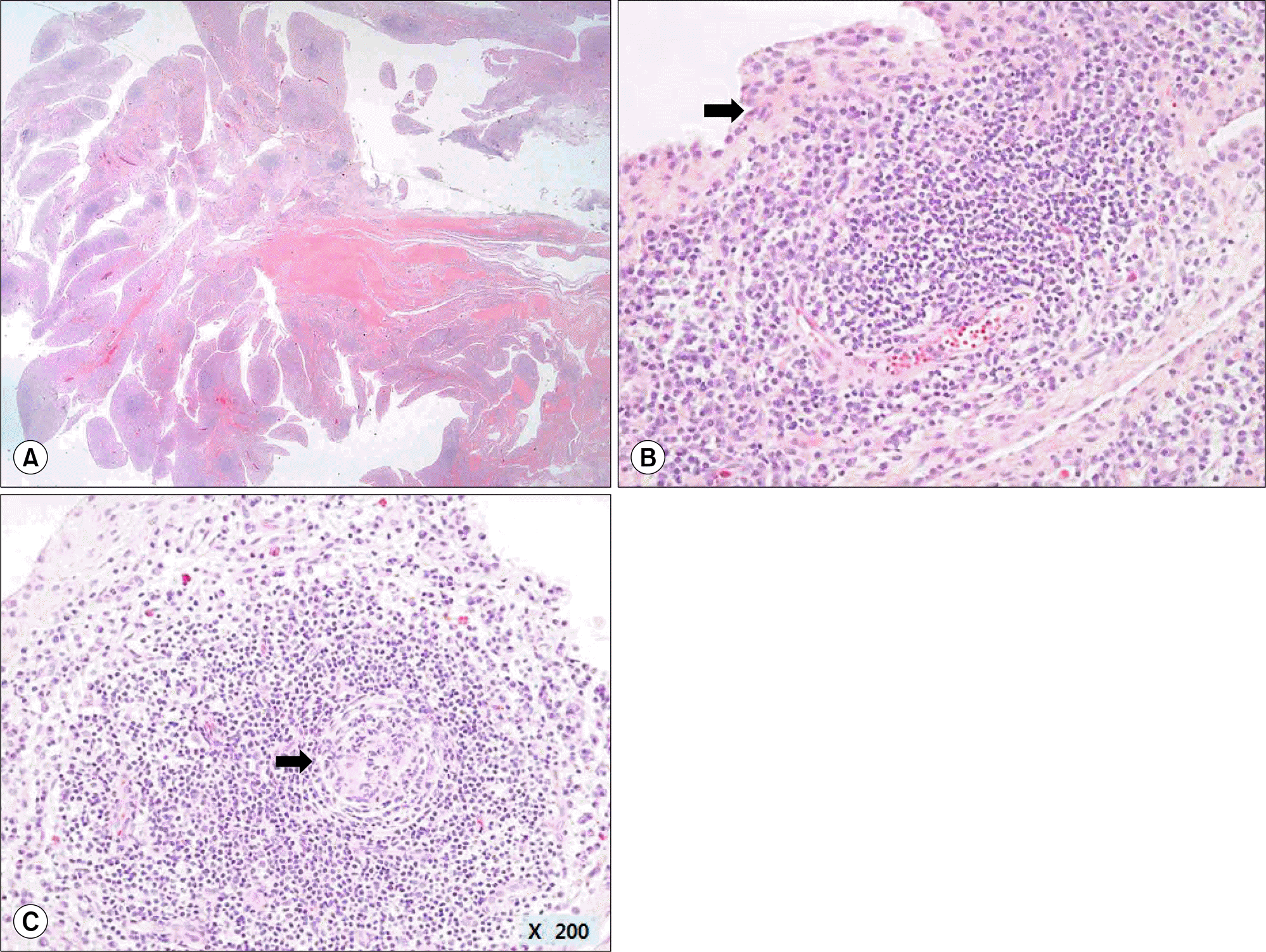
Histopathology of synovial tissue (H&E). (A) Marked synovial hyperplasia with formation of villi (×10) and (B) marked proliferation of synovial lining cells and dense inflammatory infiltrates (arrow), (C) predominantly plasma cells and lymphocytes with germinal center formation (arrow) (B, C: ×200).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download