Abstract
Objective
The 2010 New American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR) criteria for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was raised to identify patients with early RA and replaced the 1987 ACR classification criteria. The aims of this study are to assess the availability of new classification criteria and to evaluate its potential limitation.
Methods
A total of 408 patients with newly diagnosed RA were included from 13 secondary or tertiary hospitals in South Korea. The symptom duration was less than 12 months before the diagnosis of RA. RA was defined as either 1987 ACR classification criteria or new 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria. We compared the full details of both classification criteria.
Results
The mean symptom duration was 5.1 months. The majority (76.2%) of the patients were female. Two hundred and seventy three patients (66.9%) fulfilled both of the 2010 and 1987 classification criteria. Forty-seven (14.7%) of the 320 patients fulfilling the 1987 criteria did not fulfill the new classification criteria. On the other hand, eighty-eight (24.4%) of the 361 patients fulfilling the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria did not fulfill the 1987 ACR criteria. Thirty-six (55.4%) of the 65 patient with seronegative RA failed to meet the 2010 classification criteria. In case of seropositive RA (n=343), 85 additional patients (24.8%) could be diagnosed as RA using new classification criteria.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Prevalence of each items of 1987 ACR classification criteria for RA according to the three groups.
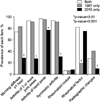
Figure 2
Application of 1987 ACR and 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria according to the seropositivity of patients. (A) seropositive RA, (B) seronegative RA.
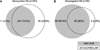
Table 2
Performance of 2010 ACR/EULAR RA classification criteria for patients with newly diagnosed RA

References
1. Raza K. The Michael Mason prize: early rheumatoid arthritis--the window narrows. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010. 49:406–410.
2. Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, Stamm TA, Uffmann M, Smolen JS. Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004. 43:906–914.
3. Banal F, Dougados M, Combescure C, Gossec L. Sensitivity and specificity of the American College of Rheumatology 1987 criteria for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis according to disease duration: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. 68:1184–1191.
4. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988. 31:315–324.
5. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. 62:2569–2581.
6. Funovits J, Aletaha D, Bykerk V, Combe B, Dougados M, Emery P, et al. The 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: methodological report phase I. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. 69:1589–1595.
7. Fautrel B, Combe B, Rincheval N, Dougados M. ESPOIR Scientific Committee. Level of agreement of the 1987 ACR and 2010 ACR/EULAR rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an analysis based on ESPOIR cohort data. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. 71:386–389.
8. Britsemmer K, Ursum J, Gerritsen M, van Tuyl LH, van Schaardenburg D. Validation of the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: slight improvement over the 1987 ACR criteria. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:1468–1470.
9. Jung SJ, Lee SW, Ha YJ, Lee KH, Kang Y, Park MC, et al. Patients with early arthritis who fulfil the 1987 ACR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis but not the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. 71:1097–1098.
10. Saraux A, Berthelot JM, Chalès G, Le Henaff C, Thorel JB, Hoang S, et al. Ability of the American College of Rheumatology 1987 criteria to predict rheumatoid arthritis in patients with early arthritis and classification of these patients two years later. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:2485–2491.
11. Liao KP, Batra KL, Chibnik L, Schur PH, Costenbader KH. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. 67:1557–1561.
12. Kaarela K, Kauppi JE, Kauppi MJ. The 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis in the Heinola inception cohort--diagnoses confirmed by long-term follow-up. Clin Rheumatol. 2012. 31:547–551.
13. Varache S, Cornec D, Morvan J, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Berthelot JM, Le Henaff-Bourhis C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria for rheumatoid arthritis in a 2-year cohort. J Rheumatol. 2011. 38:1250–1257.
14. Cader MZ, Filer A, Hazlehurst J, de Pablo P, Buckley CD, Raza K. Performance of the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with 1987 ACR criteria in a very early synovitis cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:949–955.
15. van der Linden MP, Knevel R, Huizinga TW, van der Helm-van Mil AH. Classification of rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria and the 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:37–42.
16. Zeidler H. How can misclassification be prevented when using the 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria? Comment on the article by van der Linden et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:2544–2546.
17. Rahmani M, Chegini H, Najafizadeh SR, Azimi M, Habibollahi P, Shakiba M. Detection of bone erosion in early rheumatoid arthritis: ultrasonography and conventional radiography versus non-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Rheumatol. 2010. 29:883–891.
18. Bøyesen P, Haavardsholm EA, van der Heijde D, Østergaard M, Hammer HB, Sesseng S, et al. Prediction of MRI erosive progression: a comparison of modern imaging modalities in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:176–179.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download