Abstract
Behçet's disease is chronic and systemic inflammatory vasculitis, characterized by immunologically involving in variable size of arteries and veins. Clinically, principal manifestations are recurrent oral ulcer, genital ulcer, skin and eye lesions. Compared to other connective tissue disease, cancer is not accompanied commonly in Behçet's disease. But, immunological confusion such as T cell depletion or B cell hyperplasia, or long-term of immunosuppressive treatment lead to occurrence of malignancy. Recently, we experienced a case of maxillary mass, induced to abrupt headache in Behçet's disease, confirmed diffuse large B cell lymphoma by biopsy, and treated by rituximab-CHOP chemotherapy. Thus we report these with literature review.
References
1. Abe T, Yach A, Yabana T, Ishii Y, Tosaka M, Yoshida Y, et al. Gastric non-Hodgkin's lymphoma associated with Behçet's disease. Intern Med. 1993; 32:663–7.
2. Kaklamani VG, Vaiopoulos G, Kaklamanis PH. Behçet's disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 27:197–217.

4. Direskeneli H. Behcet's disease: infectious aetiology; new autoantigens and HLA-B51. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60:996–1002.

5. Kaklamani VG, Tzonou A, Kaklamanis PG. Behçet's disease associated with malignancies. Report of two cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005; 23(4 Supple 38):S35–41.
6. Ono Y, Yamada M, Kawamura T, Ito J, Kanayama S, Katayama Y, et al. Central nervous system malignant lymphoma associated with Behçet's disease. Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2005; 45:586–90.
7. Black KA, Zilko PJ, Dawkins RL, Armstrong BK, Mastaglia GL. Cancer in connective tissue disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1982; 25:1130–3.

8. Cengiz M, Altundag MK, Zorlu AF, Gullu IH, Ozyar E, Atahan IL. Malingancy in Behçet's disease: a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol. 2001; 20:239–44.
9. Kaneko H, Hojo Y, Nakajima H, Okamura A, Fukase M. Behçet's syndrome associated with nasal malignant lymphoma: report of an autopsy case. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1974; 24:141–50.
10. Celik I, Altundag K, Erman M, Baltali E. Cyclopho-saphamide associated carcinoma of the urinary bladder in Behçet's disease. Nephron. 1999; 81:239.
11. Roitt IM, Brostoff J, Male DK. Immunology. 5th ed.p. 480, Amsterdam, Elsevier Science Health Science;2000.
12. Fukayama M, Ibuka T, Hayashi Y, Ooba T, Koike M, Misutani S. Epstein-Barr virus in pyothorax-associated pleural lymphoma. Am J Pathol. 1993; 143:1044–9.
13. Cote TR, Manns A, Hardy CR, Yellin FJ, Hartge P. Epidemiology of brain lymphoma among people with or without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS/Caner Study Group. J Natl Caner Inst. 1996; 88:675–9.
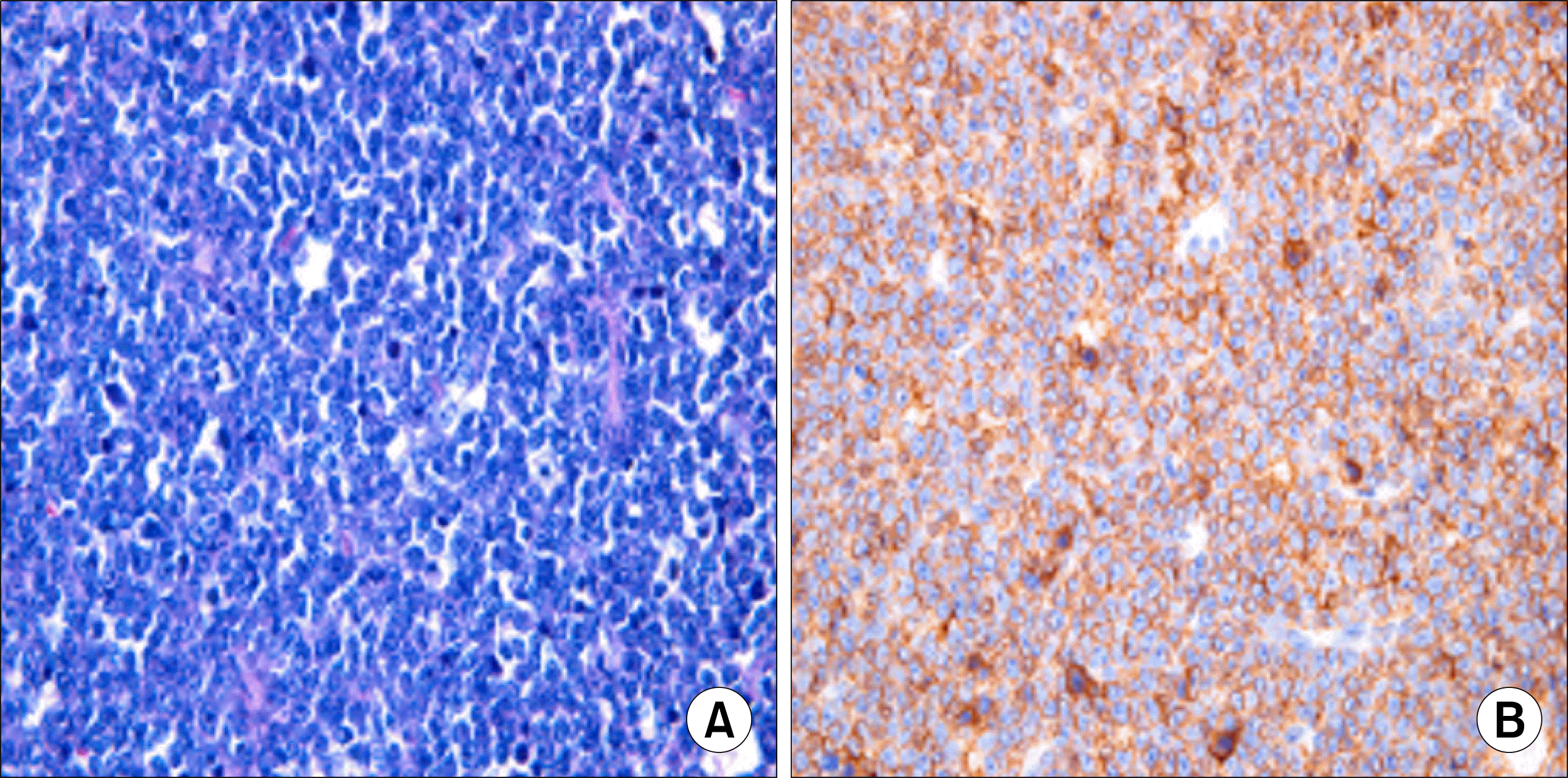
Fig. 1.
A brain MRI shows low signal mass in right maxillary sinus (arrow). (A) T2 weighted image. (B) Gd-DTPA enhanced T1 weighted image.
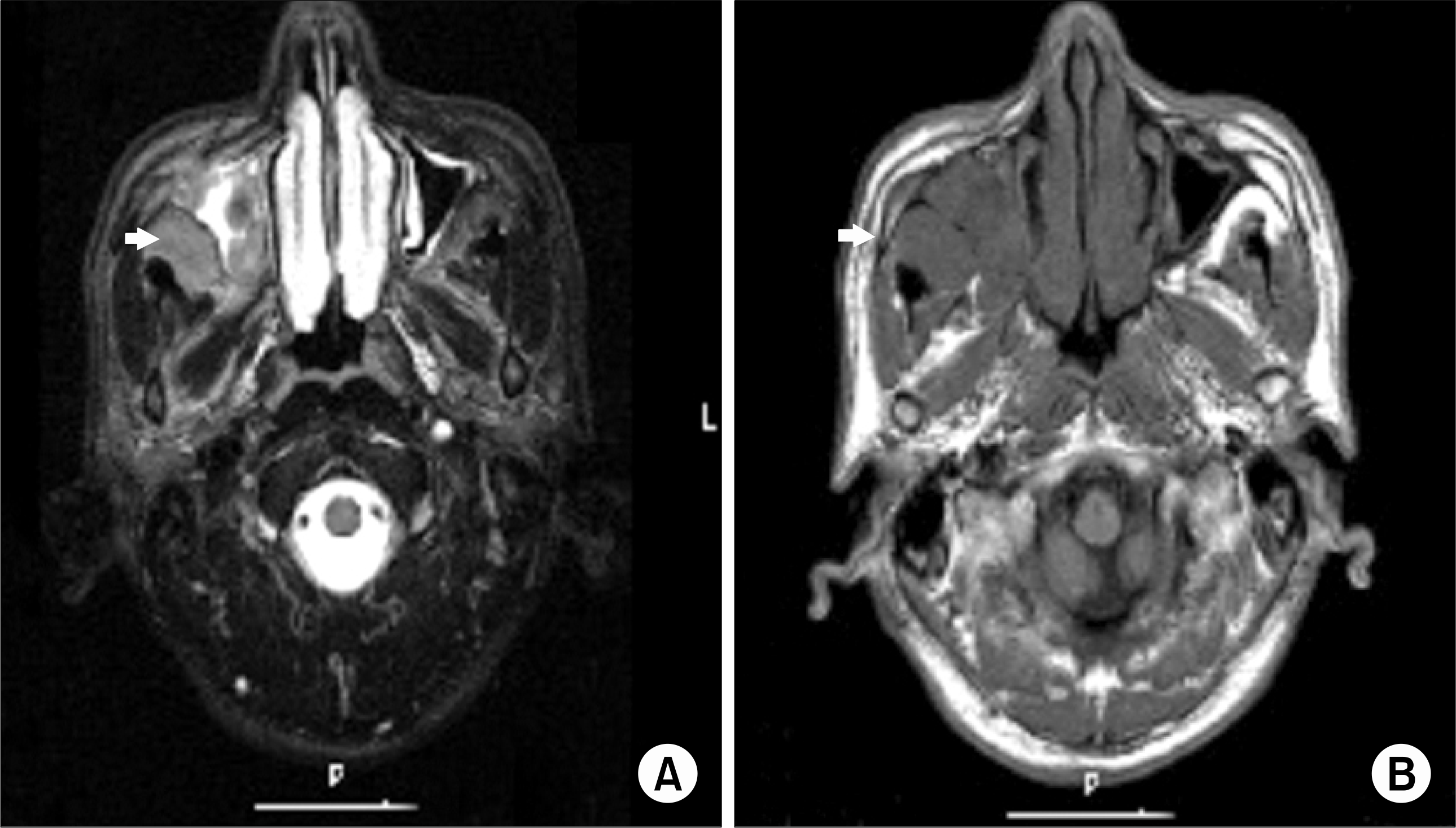
Fig. 2.
A nasopharynx CT shows mass in right maxillary sinus (A: arrow) and invasions of mass to both ethmoidal air cell (B: arrows).
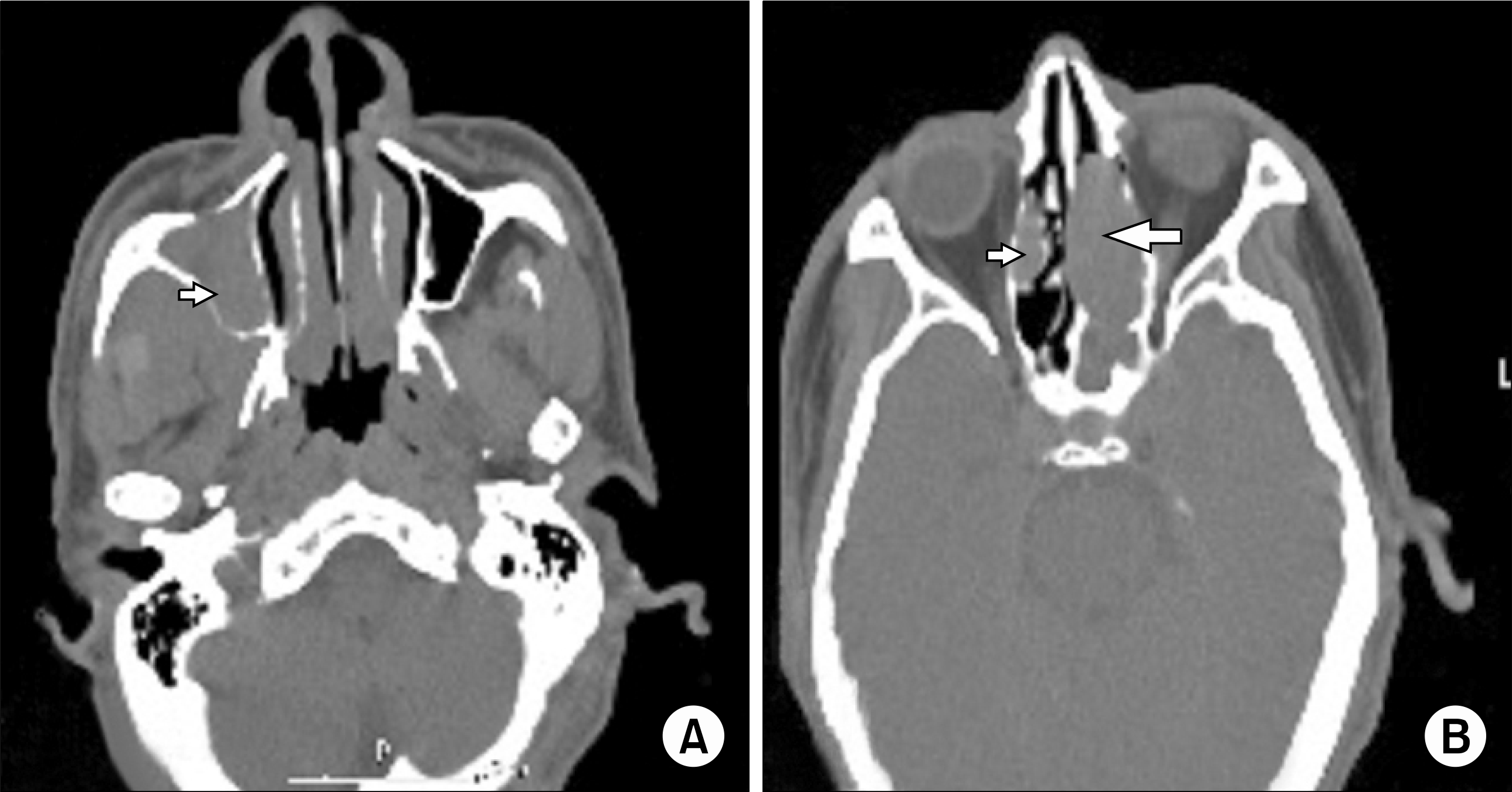
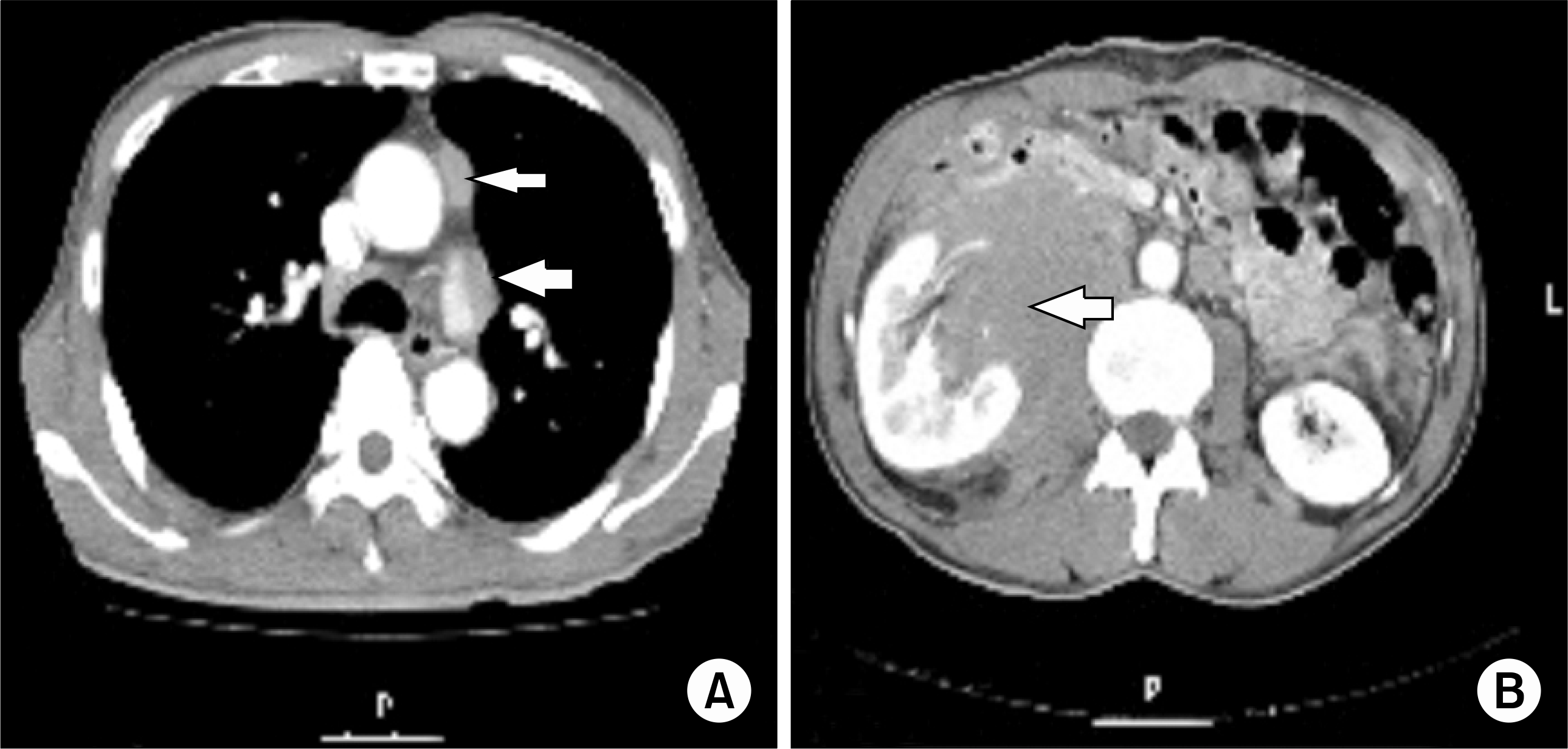
Fig. 3.
A chest CT shows enlarged lymph nodes in para-aortic and left hilar area (A: arrows). and a abdomen CT shows metastatic lymph nodes in right renal hilar and right para-aortic area (B: arrow).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download