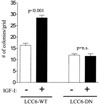
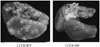
Figures and Tables
References
1. Jenkins PJ, Mukherjee A, Shalet SM. Does growth hormone cause cancer? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006. 64:115 –121.
2. Le Roith D, Bondy C, Yakar S, Liu JL, Butler A. The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr Rev. 2001. 22:53–74.
3. Bustin SA, Jenkins PJ. The growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor-I axis and colorectal cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2001. 7:447–454.
4. Laban C, Bustin SA, Jenkins PJ. The GH-IGF-I axis and breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 14:28–34.
5. Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004. 4:505–518.
6. Tomell J, Carlsson B, Pohjanen P, Wennbo H, Rymo L, Isaksson O. High frequency of mammary adenocarcinomas in metallothionein promoter-human growth hormone transgenic mice created from two different strains of mice. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992. 43:237–242.
7. Bates P, Fisher R, Ward A, Richardson L, Hill DJ, Graham CF. Mammary cancer in transgenic mice expressing insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II). Br J Cancer. 1995. 72:1189–1193.
8. Yang XF, Beamer WG, Huynh H, Pollak M. Reduced growth of human breast cancer xenografts in hosts homozygous for the lit mutation. Cancer Res. 1996. 56:1509–1511.
9. Arteaga CL, Kitten LJ, Coronado EB, Jacobs S, Kull FC, Allred DC, Osborne CK. Blockade of the type I somatomedin receptor inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells in athymic mice. J Clin Inves. 1989. 84:1418–1423.
10. Pollak M, Blouin MJ, Zhang JC, Kopchick JJ. Reduced mammary gland carcinogenesis in transgenic mice expressing a growth hormone antagonist. Br J Cancer. 2001. 85:428–430.
11. Wu Y, Yakar S, Zhao L, Hennighausen L, LeRoith D. Circulating insulin-like growth factor-I levels regulate colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2002. 62:1030–1035.
12. Wu Y, Cui K, Miyoshi K, Hennighausen L, Green JE, Setser J, LeRoith D, Yakar S. Reduced circulating insulin-like growth factor I levels delay the onset of chemically and genetically induced mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:4384–4388.
13. Bustin SA, Dorudi S, Phillips SM, Feakins RM, Jenkins PJ. Local expression of insulin-like growth factor-I affects angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2002. 23:130–138.
14. Sachdev D, Hartell JS, Lee AV, Zhang X, Yee D. A dominant negative type I insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits metastasis of human cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:5017–5024.
15. Gunnell DJ, Smith GD, Frankel SJ, Kemp M, Peters TJ. Socio-economic and dietary influence on leg length and trunk length in childhood; a reanalysis of the Carnegie (Boyd Orr) survey of dier and health in prewar Britain (1937-39). Pediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1998. 12:suppl 1. 96–113.
16. De Stavola BL, dos Santos Silva I, McCormack V, Hardy RJ, Kuh DJ, Wadsworth ME. Childhood growth and breast cancer. Am J Epidemio. 2004. 159:671–682.
17. Stevenaert A, Beckers A. Presurgical Octreotide: treatment in acromegaly. Metabolism. 1996. 45:72–74.
18. Ahlgren M, Melbye M, Wohlfahrt J, Sorensen TI. Growth patterns and the risk of breast cancer in women. N Engl J Med. 2004. 351:1619–1626.
19. Gunnell D, Okasha M, Smith GD, Oliver SE, Sandhu J, Holly JM. Height, leg length, and cancer risk: a systematic review. Epidemiol Rev. 2001. 23:313–342.
20. Taback SP, Dean HJ. Mortality in Canadian children with growth hormone (GH) deficiency receiving GH therapy 1967-1992. The Canadian Growth Hormone Advisory Committee. J Clin Endocrinol Metb. 1996. 81:1693–1696.
21. Swerdlow AJ, Reddingius RE, Higgins CD, Spoudeas HA, Phipps K, Qiao Z, Ryder WD, Brada M, Hayward RD, Brook CG, Hindmarsh PC, Shalet SM. Growth hormone treatment of children with brain tumors and risk of tumor recurrence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:4444–4449.
22. Sklar CA, Mertens AC, Mitby P, Occhiogrosso G, Qin J, Heller G, Yasui Y, Robison LL. Risk of disease recurrence and second neoplasms in survivors of childhood cancer treated with growth hormone: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87:3136–3141.
23. Neglia JP, Friedman DL, Yasui Y, Mertens AC, Hammond S, Stovall M, Donaldson SS, Meadows AT, Robison LL. Second malignant neoplasms in five-year survivors of childhood cancer: childhood cancer survivor study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001. 93:618–629.
24. Wada E, Murata M, Watanabe S. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia following treatment with human growth hormone in a boy with possible preanemic Fanconi's anemia. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1989. 19:36–39.
25. Attanasio AF, Bates PC, Ho KK, Webb SM, Ross RJ, Strasburger CJ, Bouillon R, Crowe B, Selander K, Valle D, Lamberts SW. Human growth hormone replacement in adult hypopituitary patients: long-term effects on body composition and lipid status--3-year results from the HypoCCS Database. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87:1600–1606.
26. Götherstr G, Svensson J, Koranyi J, Alpsten M, Bosaeus I, Bengtsson B, Johannsson G. A prospective study of 5 years of GH replacement therapy in GH-deficient adults: sustained effects on body composition, bone mass, and metabolic indices. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:4657–4665.
27. Monson JP. Long-term experience with GH replacement therapy: efficacy and safety. Eur J Endocrinol. 2003. 148:suppl 2. S9–S14.
28. Sperling MA, Saenger PH, Ray Hintz SR, Tom Wilson SR, Rose SR. Growth hormone treatment and neoplasia-coincidence or consequence? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87:5351–5352.
29. Giovannucci E, Pollak MN, Platz EA, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Majeed N, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Hankinson SE. A prospective study of plasma insulin-likegrowth factor-1 and binding protein-3 and risk of colorectal neoplasia in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000. 9:345–349.
30. Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Pollak M. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet. 1998. 351:1393–1396.
31. Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovannucci E, Chan JM, Tao Y, Hennekens CH, Stampfer MJ. Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men andplasma levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999. 91:620–625.
32. Manousos O, Souglakos J, Bosetti C, Tzonou A, Chatzidakis V, Trichopoulos D, Adami HO, Mantzoros C. IGF-I and IGF-II in relation to colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 1999. 83:15–17.
33. Burroughs KD, Dunn SE, Barrett JC, Taylor JA. Insulin-like growth factor-I: a key regulator of human cancer risk? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999. 91:579–581.
34. el Atiq F, Garrouste F, Remacle-Bonnet M, Sastre B, Pommier G. Alterations in serum levels of insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth-factor-binding proteins in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 1994. 57:491–497.
35. Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O'Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004. 363:1346–1353.
36. Jenkins PJ, Besser M. Clinical perspective: acromegaly and cancer: a problem. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:2935–2941.
37. Renehan AG, O'Connell J, O'Halloran D, Shanahan F, Potten CS, O'Dwyer ST, Shalet SM. Acromegaly and colorectal cancer: a comprehensive review of epidemiology, biological mechanisms, and clinical implications. Horm Metab Res. 2003. 35:712–725.
38. Jenkins PJ, Frajese V, Jones AM, Camacho-Hubner C, Lowe DG, Fairclough PD, Chew SL, Grossman AB, Monson JP, Besser GM. Insulin-like growth factor I and the development of colorectal neoplasia in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:3218–3221.
39. Cats A, Dullaart RP, Kleibeuker JH, Kuipers F, Sluiter WJ, Hardonk MJ, de Vries EG. Increased epithelial cell proliferation in the colon of patients with acromegaly. Cancer Res. 1996. 56:523–526.
40. Nabarro JD. Acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1987. 26:481–512.
41. Orme SM, McNally RJ, Cartwright RA, Belchetz PE. United Kingdom Acromegaly Study Group. Mortality and cancer incidence in acromegaly: a retrospective cohort study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. 83:2730–2734.
42. Dunn SE, Ehrlich M, Sharp NJ, Reiss K, Solomon G, Hawkins R, Baserga R, Barrett JC. A dominant negative mutant of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibits the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:3353–3361.
43. Adachi Y, Lee CT, Coffee K, Yamagata N, Ohm JE, Park KH, Dikov MM, Nadaf SR, Arteaga CL, Carbone DP. Effects of genetic blockade of the insulin-like growth factor receptor in human colon cancer cell lines. Gastroenterology. 2002. 123:1191–1204.
44. Wen B, Deutsch E, Marangoni E, Frascona V, Maggiorella L, Abdulkarim B, Chavaudra N, Bourhis J. Tyrphostin AG 1024 modulates radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2001. 85:2017–2021.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download