Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop an Allergic Rhinitis-Specific Quality of Life (ARSQOL) scale and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
ARSQOL was developed in 5 steps. Items for the preliminary instrument of ARSQOL were developed through a literature review and deep interviews with allergic rhinitis patients. Face validity with Content Validity Index (CVI), construct validity using factor analysis, and known group comparison, criterion validity test using correlation between ARSQOL and total nasal symptoms score (TNSS) were conducted to evaluate the validity of ARSQOL. Cronbach's α was used to evaluate the reliability of ARSQOL.
Results
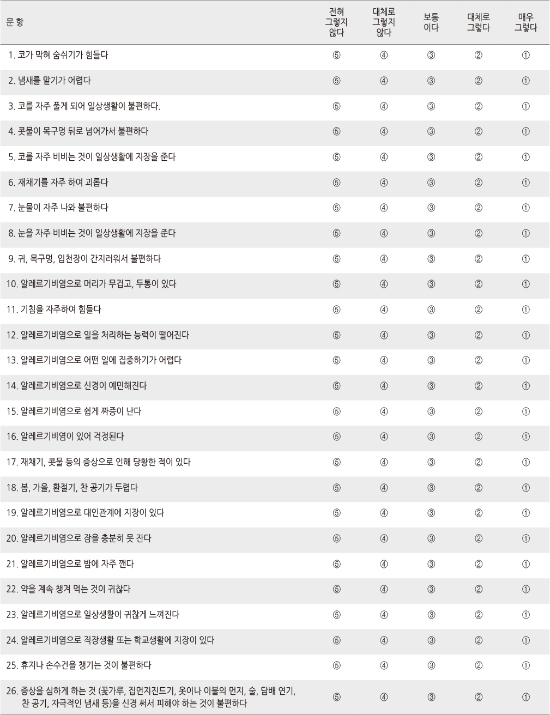
CVI for the items in the final ARSQOL were. 92. Five factors including discomfort associated with nasal symptoms (4 items), physical function (7 items), mental function (5 items), sleep disorder and social function (4 items), and problems of daily life (6 items) were identified through factor analysis and these five factors explained 66.6% of the total variance. The correlation coefficient between TNSS and the total score of life quality was -.69. In the group comparison, the persistent allergic rhinitis group showed lower ARSQOL scores than the intermittent patient group, and moderate to the severe allergic rhinitis patient group presented poorer ARSQOL than the mild symptom patient group. The Cronbach's α reliability coefficient was .95.
Figures and Tables
Notes
References
1. Asher MI, Montefort S, Björkstén B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry crosssectional surveys. Lancet. 2006; 368(9537):733–743. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(06)69283-0.
2. Seong HU, Cho SD, Park SY, Yang JM, Lim DH, Kim JH, et al. Nationwide survey on the prevalence of allergic diseases according to region and age. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012; 22(3):224–231. DOI: 10.7581/pard.2012.22.3.224.
3. Jeong HJ. Health insurance statistical analysis instruction manual. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;2010.
4. Kim CW. Current update on allergic rhinitis. Korean J Med. 2012; 82(3):298–303. DOI: 10.3904/kjm.2012.82.3.298.
5. Ozdoganoglu T, Songu M, Inancli HM. Quality of life in allergic rhinitis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2012; 6(1):25–39. DOI: 10.1177/1753465811424425.
6. Léger D, Annesi-Maesano I, Carat F, Rugina M, Chanal I, Pribil C, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its consequences on quality of sleep: An unexplored area. Arch Intern Med. 2006; 166(16):1744–1748. DOI: 10.1001/archinte.166.16.1744.
7. Kim WK. Therapeutic approaches to allergic rhinitis. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2004; 14(3):183–195.
8. Han SS. The objective and subjective results of radiofrequency ablation in allergic rhinitis based on a 12-month follow-up [dissertation]. Chuncheon: Kangwon National University;2008. 1–61.
9. Jeong JW, Kim WK, Kim SH, Park HW, Chang YS, Kim SH, et al. Measurement of nasal airway conductance in the diagnosis of allergic rhinitis by allergen nasal provocation test. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002; 22(2):446–456.
10. Lee EH, Kim CJ, Cho SY, Chae HJ, Lee S, Kim EJ. Monitoring the use of health-related quality of life measurements in Korean studies of patients with diabetes. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(4):558–567. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.558.
11. Juniper EF, Howland WC, Roberts NB, Thompson AK, King DR. Measuring quality of life in children with rhinoconjunctivitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998; 101(2 Pt 1):163–170. DOI: 10.1016/S0091-6749(98)70380-X.
12. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Dolovich J. Assessment of quality of life in adolescents with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis: Development and testing of a questionnaire for clinical trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994; 93(2):413–423. DOI: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90349-2.
13. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH. Development and testing of a new measure of health status for clinical trials in rhinoconjunctivitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991; 21(1):77–83. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb00807.x.
14. Juniper EF, Thompson AK, Ferrie PJ, Roberts JN. Development and validation of the mini rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000; 30(1):132–140. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2000.00668.x.
15. Juniper EF, Rohrbaugh T, Meltzer EO. A questionnaire to measure quality of life in adults with nocturnal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111(3):484–490. DOI: 10.1067/mai.2003.137.
16. Baiardini I, Pasquali M, Giardini A, Specchia C, Passalacqua G, Venturi S, et al. Rhinasthma: A new specific QoL questionnaire for patients with rhinitis and asthma. Allergy. 2003; 58(4):289–294. DOI: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.2003.00079.x.
17. Jung MK, Hong SJ, Lee SH, Hong SJ, Son JW, Kang W, et al. Development and validation of a Korean allergic rhinitis-specific quality of life questionnaire (KARQLQ). Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 28(2):113–120.
18. Park KH, Cho JS, Lee KH, Shin SY, Moon JH, Cha CI. Rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire (RQLQ) as an evaluator of perennial allergic rhinitis patients: The first report. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2002; 45(3):254–262.
19. Cho YS, Lim MK, Yoo B, Moon HB. Development of a quality of life questionnaire for Korean asthmatics. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 19(5):703–712.
20. Min SK, Lee CI, Kim KI, Suh SY, Kim DK. Development of Korean version of WHO quality of life scale abbreviated version (WHOQOL-BREF). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000; 39(3):571–579.
21. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA (2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.
22. Comrey AL. Factor-analytic methods of scale development in personality and clinical psychology. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1988; 56(5):754–761. DOI: 10.1037/0022-006X.56.5.754.
23. Polit DF, Beck CT.
JW Park
J Kim
H Kim
JH Park
SH Bae
JE Song
. Nursing research: Generating and assessing evidence for nursing practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2012. p. 1–486.
24. Lynn MR. Determination and quantification of content validity. Nurs Res. 1986; 35(6):382–385.
25. DeVellis RF. Scale development: Theory and applications. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage;2012. p. 1–205.
26. Spector SL, Nicklas RA, Chapman JA, Bernstein IL, Berger WE, Blessing-Moore J, et al. Symptom severity assessment of allergic rhinitis: Part 1. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003; 91(2):105–114. DOI: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62160-6.
27. Song JJ. SPSS/AMOS statistical analysis method. Paju: 21cbook;2011. p. 1–441.
28. Seong TJ. Theory and practice of questionnaire construction and analysis. 2nd ed. Seoul: Hakjisa Corp.;2010. p. 1–371.
29. Price D, Bond C, Bouchard J, Costa R, Keenan J, Levy ML, et al. International Primary Care Respiratory Group (IPCRG) Guidelines: Management of allergic rhinitis. Prim Care Respir J. 2006; 15(1):58–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.pcrj.2005.11.002.
30. Chesson A Jr, Hartse K, Anderson WM, Davila D, Johnson S, Littner M, et al. Practice parameters for the evaluation of chronic insomnia. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine report. Standards of practice committee of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Sleep. 2000; 23(2):237–241.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download