Abstract
Purpose
The study was done to identify lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and to evaluate the factors affecting LUTS for the people with Parkinson's disease.
Methods
The research design was a cross-sectional study with interviews using a structured questionnaire. The participants were 72 patients with Parkinson's disease who were seen in the Neurology clinic of a university hospital from September to November 2005.
Results
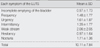
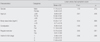
Mean score of LUTS for the participants was 10.11. In each symptom score of LUTS (range 0-5), weak stream was the highest 2.06, followed by nocturia 1.71, and urgency 1.61. The severity of LUTS was moderate to severe group for 51%. LUTS were significantly different by regular exercise. Positive correlations were observed between Hoehn and Yahr stage (stage of disease severity) and frequency and between Hoehn and Yahr stage and urgency (r=.280, p=.018; r=.328, p=.005). LUTS were significantly predicted by regular exercise (p=.001) which explained 15.0% of the variance in LUTS.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Andersen JT. Disturbances of bladder and urethral function in Parkinson's disease. International Urology and Nephrology. 1985. 17:35–41.
2. Andersen JT, Bradley WE. Cystometric, sphincter and electromyelographic abnormalities in Parkinson's disease. The Journal of Urology. 1976. 116:75–78.
3. Araki I, Kuno S. Assessment of voiding dysfunction in Parkinson's disease by the international prostate symptom score. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiat. y. 2000. 68:429–433.
4. Berger Y, Blaivas JG, DeLaRocha ER, Salinas JM. Urodynamic findings in Parkinson's disease. The Journal of Urology. 1987. 138:836–838.
5. Choi HR, Chung WS, Shim BS, Kwon SW, Hong SJ, Chung BH, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of prostatism in Korea: Application of I-PSS. Korean Journal of Urology. 1997. 38:1067–1074.
6. Defreitas GA, Lemack GE, Zimmern PE, Dewey RB, Roehrborn CG, O'Suilleabhain PE. Distinguishing neurogenic from non-neurogenic detrusor overactivity: A urodynamic assessment of lower urinary tract symptoms in patients with and without Parkinson's disease. Urology. 2003. 62:651–655.
7. Grimby A, Milsom I, Molander U, Wiklund I, Ekelund P. The influence of urinary incontinence on the quality of life of elderly women. Age and Ageing. 1993. 22:82–89.
8. Hely MA, Morris JG, Reid WG, Trafficante R. Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson's disease: Non-L-dopa-responsive problems dominate at 15 years. Movement Disorders. 2005. 20:190–199.
9. Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism: Onset, progression, and mortality. Neurology. 1967. 17:427–442.
10. Jirovec MM. The impact of daily exercise on the mobility, balance, and urine control of cognitively impaired nursing home residents. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 1991. 28:145–151.
11. Johanson JF. Gastrointestinal diseases: Risk factors and prevention. 1997. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven.
12. Jolleys JV, Donovan JL, Nanchahal K, Peters TJ, Abrahams P. Urinary symptoms in the community: How bothersome are they? British Journal of Urology. 1994. 74:551–555.
13. Kakizaki H, Matsuura S, Mitsui T, Ameda K, Tanaka H, Koyanagi T. Questionnaire analysis on sex difference in lower urinary tract symptoms. Urology. 2002. 59:58–62.
14. Kanazawa M, Yoshiike N, Osaka T, Numba Y, Zimmet P, Inoue S. Criteria and classification of obesity in Japan and Asia-Oceania. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2002. 11:S732–S737.
15. Kegel AH. Progressive resistance exercise in the functional restoration of the perineal muscles. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1948. 56:238–248.
16. Korean Continence Society. Textbook of voiding dysfunction and female urology. 2004. Seoul: Ilchokak.
17. Lemack GE, Dewey RB Jr, Roehrborn CG, O'Suilleabhain PE, Zimmern PE. Questionnaire-based assessment of bladder dysfunction in patients with mild to moderate Parkinson's disease. Urology. 2000. 56:250–254.
18. Lim KC, Park KO, Kim BJ. A study on the correlations between social support, dependence of activities of daily living and depression in patients with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Korean Academy of Adult Nursing. 1997. 9:366–377.
19. Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE. Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003. 348:1356–1364.
20. Okamura K, Usami T, Nagahama K, Maruyama S, Mizuta E. "Quality of life" assessment of urination in elderly Japanese men and women with some medical problems using international prostate symptom score and King's health questionnaire. European Urology. 2002. 41:411–419.
21. Park YR. Process of seeking positive life of patients with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006. 36:710–720.
22. Pavlakis AJ, Siroky MB, Goldstein I, Krane RJ. Neurourologic findings in Parkinson's disease. The Journal of Urology. 1983. 129:80–83.
23. Scarpero HM, Fiske J, Xue X, Nitti VW. American Urological Association Symptom Index for lower urinary tract symptoms in women: Correlation with degree of bother and impact on quality of life. Urology. 2003. 61:1118–1122.
24. Smeltzer SC, Bare BG, Hinkle JL, Cheever KH. Brunner & Suddarth's textbook of medical-surgical nursing. 2007. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
25. Snyder CH, Adler CH. The patient with Parkinson's disease: Part I-treating the motor symptoms; Part II-treating the nonmotor symptoms. Journal of American Academy of Nurse Practitioners. 2007. 19:179–197.
26. Sohng KY, Moon JS, Lee KS. Prevalence and associated factors of falls among people with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004. 34:1081–1091.
27. Sohng KY, Moon JS, Lee KS, Choi DW. The development and effects of a self-management program for patients with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007. 37:891–901.
28. Subak LL, Whitcomb E, Shen H, Saxton J, Vittinghoff E, Brown JS. Weight loss: A novel and effective treatment for urinary incontinence. The Journal of Urology. 2005. 174:190–195.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download