Abstract
Objectives
Breast conserving surgery (BCS) for early breast cancer is now an accepted treatment, but there are controversies about its comparability with mastectomy. Thus, we investigated the survival outcomes who underwent BCS and modified radical mastectomy (MRM).
Methods
In this retrospective review, we analyzed the survival outcomes of 618 patients with early breast cancer who underwent two different surgery from January 2002 to December 2009. Postoperative pathologic difference, disease free survival period, overall survival period, recurrence pattern, recurrent rate and site were compared. In addition, preoperative patients data are also collected.
Results
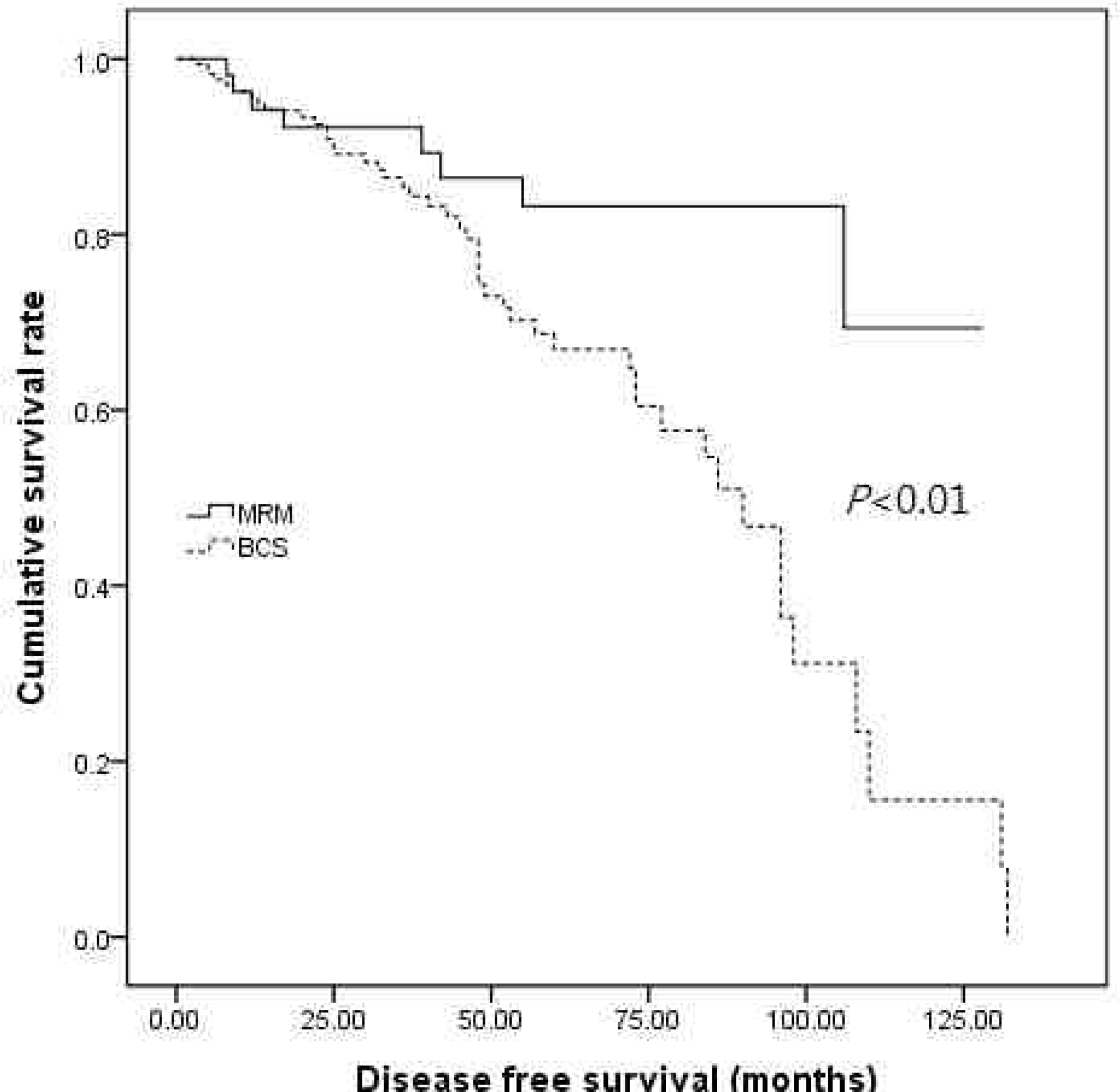
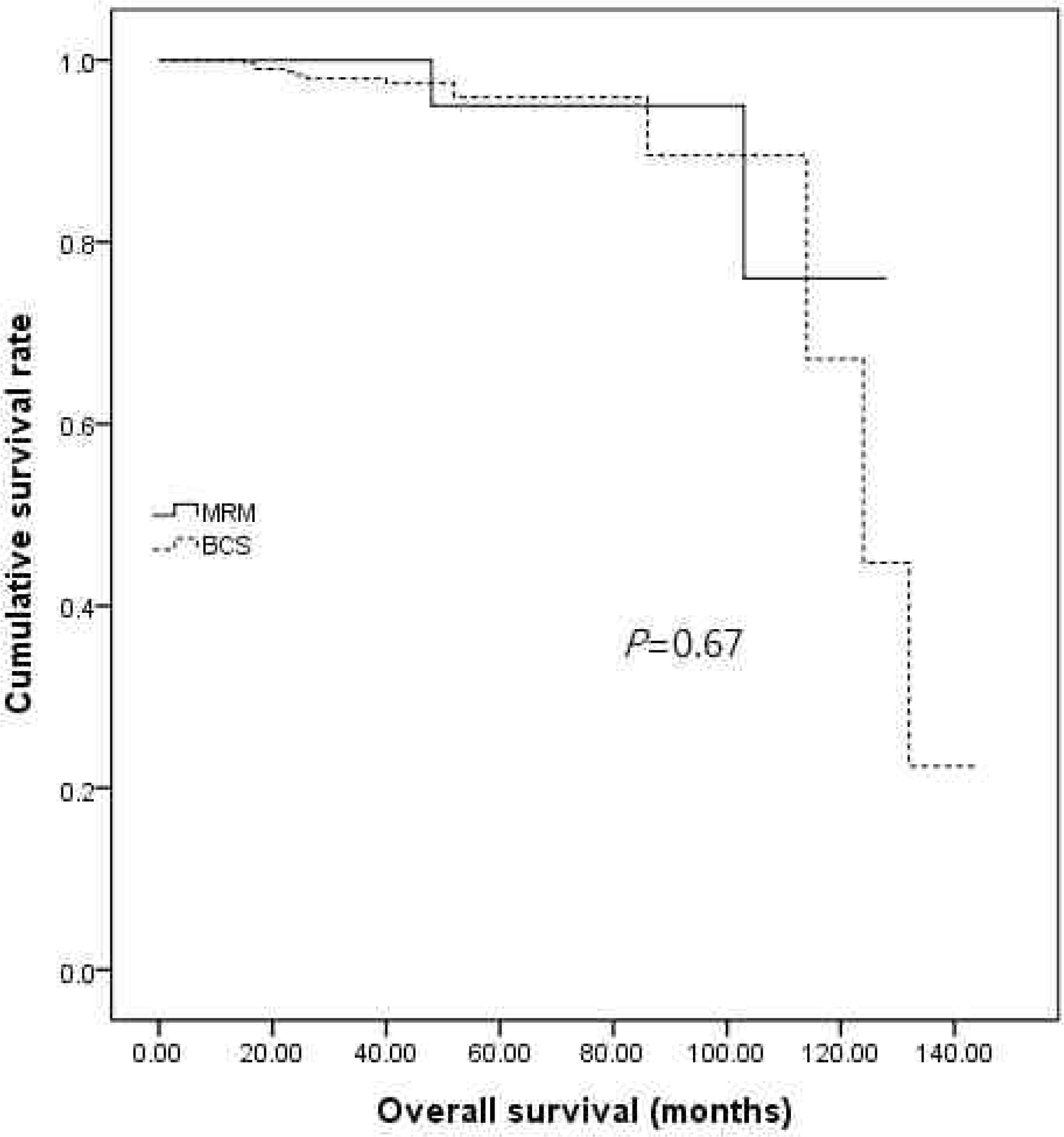
Disease free survival period of MRM and BCS was 108.46 months and 80.82 months, respectively (P< 0.01). However, there was no significant correlation between overall survival period and operative methods (P= 0.67). In addition, recurrence pattern (P= 0.21), recurrent rate (P= 0.36) and site (P= 0.45, P= 0.09) were not associated with operative method.
Conclusions
In this study, we can suggest that early breast cancer patients could improve their disease free survival if they underwent MRM. So, when we operate high risk breast cancer patients, MRM could be considered for their disease free life. Further studies may be required to establish appropriate strategy of surgery for early breast cancer.
References
1. Lee JS, Bae YT. Clinical Analysis of breast cancer patients treated with surgery. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2004; 7:174–9.

2. Natarajan L, Pu M, Parker BA, Thomson CA, Caan BJ, Flatt SW, et al. Time-varying effects of prognostic factors associated with dis-ease-free survival in breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 2009; 169:1463–70.

3. Lee JB, Kim DH, Min BW, Ryu KW, Um JW, Kim AR, et al. Factors influencing the recurrence of breast cancer following modified radical mastectomy. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2001; 4:128–35.

4. van Dongen JA, Voogd AC, Fentiman IS, Legrand C, Sylvester RJ, Tong D, et al. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing breast-conserving therapy with mastectomy: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer 10801 Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:1143–50.

5. McCready D, Holloway C, Shelly W, Down N, Robinson P, Sinclair S, et al. Surgical management of early stage invasive breast cancer: a practice guideline. Can J Surg. 2005; 48:185–94.
6. Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1233–41.

7. Arriagada R, Lê MG, Guinebretiè re JM, Dunant A, Rochard F, Tursz T. Late local recurrences in a randomised trial comparing conservative treatment with total mastectomy in early breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:1617–22.

8. Poggi MM, Danforth DN, Sciuto LC, Smith SL, Steinberg SM, Liewehr DJ, et al. Eighteen-year results in the treatment of early breast carcinoma with mastectomy versus breast conservation therapy:: the National Cancer Institute Randomized Trial. Cancer. 2003; 98:697–702.
9. Van der Sangen MJ, Van de Wiel FM, Poortmans PM, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Roumen RM, et al. Are breast conservation and mastectomy equally effective in the treatment of young women with early breast cancer? Long-term results of a population-based cohort of 1,451 patients aged ≤40 years. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 127:207–15.
10. Chan A, Pintilie M, Vallis K, Girourd C, Goss P. Breast cancer in women < or = 35years: Review of 1002 cases from a single institution. Ann Oncol. 2000; 11:1255–62.
11. Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Luini A, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-con-serving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1227–32.

12. Brooks JP, Danforth DN, Albert P, Sciuto LC, Smith SL, Camphausen KA, et al. Early ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences after breast conservation affect survival: an analysis of the national cancer institute randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 62:785–9.

13. Fodor J, Toth J, Major T, Polgar C. Incidence and time of occurrence of regional recurrence in stage I-II breast cancer: value of adjuvant irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 44:281–7.

14. Bland KI, Copeland III EM. Breast. In Schwartz SI, Shires GT, Spencer FC. Principles of surgery. 6th ed.New York: McGraw-Hill Inc.;1994. p. 554–7.
15. Valagussa P, Bonadonna G, Veronesi U. Patterns of relapse and survival following radical mastectomy. Analysis of 716 consecutive patients. Cancer. 1978; 41:1170–8.
16. Lee SJ, Hwang SO, Jung JH, Park HY, Lee JH, Eun YA. Prognosis of isolated local recurrence after modified radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009; 76:293–300.

17. Son BH, Lee PC, Yoon HS, Kwak HS, Lee KC, Kim CS, et al. Patterns of locoregional and systemic failure after a mastectomy in breast cancer and risk factors predicting failure. J Korean Surg Soc 2000;59:305–12.
Table 1.
Clinicopathologic characteristics
Table 2.
Disease free survival period and overall survival period between MRM and BCS group
| Mean time (month) | 95% CI | HR | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease free survival | 0.36 | <0.01 | ||
| MRM | 108.46 | 96.32-120.61 | ||
| BCS | 80.82 | 71.75-89.89 | ||
| Overall survival | 0.71 | 0.67 | ||
| MRM | 119.25 | 108.27–130.24 | ||
| BCS | 121.96 | 110.76–133.15 |
Table 3.
Postoperative recurrence pattern, recurrent rate site between MRM and BCS group




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download