Abstract
We report a familial case of visceral larva migrans of Toxocara canis after eating raw chicken liver. A 9-year-old female ate raw chicken liver with her father and older brother and was admitted to the hospital with periumbilical pain, a mild fever, and headache. The total peripheral eosinophil count was 9,884/mm3 and the total lgE concentration was 2,317 IU/dL. Chest and abdominal computed tomography (CT) scans demonstrated multiple, poorly-defined, small, nodular lesions scattered in the liver and lung parenchyma. Toxocara ELISA and Western blot tests were positive in the patient, and her father and brother. A liver biopsy revealed extensive eosinophilic infiltrations in the portal and lobular areas. She took albendazole for 5 days and was discharged in good condition. These results suggest that clinicians should consider foodborne toxocariasis in patients with multiple, small nodules in the liver and lung parenchyma with eosinophilia and a history of raw meat ingestion.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
IgG immunoblot to Toxocara canis TES-Ag. Patients 1 and 2, and positive control revealed the same banding pattern.
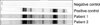
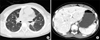
Fig. 2
Chest and abdominal CT images of patient 1. (A) Chest CT scan shows multiple, small nodules with poorly-defined margins and a ground-glass opacity. (B) Abdominal CT scan shows multiple, low-attenuated small nodules.
References
1. Snyder CH. Visceral larva migrans. ten years' experience. Pediatrics. 1961. 28:85–91.
3. Magnaval JF, Glickman LT, Dorchies P, Morassin B. Highlights of human toxocariasis. Korean J Parasitol. 2001. 39:1–11.

4. Glickman LT, Schantz PM. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of zoonotic toxocariasis. Epidemiol Rev. 1981. 3:230–250.

6. Nagakura K, Tachibana H, Kaneda Y, Keto Y. Toxocariasis possibly caused by ingesting raw chicken. J infect Dis. 1989. 160:735–736.

7. Obweller A, Jensen-Jarolim E, Auer H, Huber A, Kraft D, Aspock H. Toxocara infections in humans: symptomatic course of toxocarosis correlates significantly with levels of IgE/anti-IgE immune complexes. Parasite Immunol. 1998. 20:311–317.
8. Park HY, Lee SU, Huh S, Kong Y, Magnaval JF. A seroepidemiological survey for toxocariasis in apparently healthy residents in Gwangwon-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2002. 40:113–117.

9. Kwon NH, Oh MJ, Lee SP, Lee BJ, Choi DC. The Clinical impact of toxocariasis in patients with unknown eosinophilia. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 25:299–304.
10. Magnaval JF, Fabre R, Maurieres P, Charlet JP, de Larrard B. Application of the western blotting procedure for the immunodiagnosis of human toxocariasis. Parasitol Res. 1991. 77:697–702.

11. Magnaval JF, Fabre R, Maurieres P, Charlet JP, de Larrard B. Evaluation of an immunoenzymatic assay detecting specific anti-Toxocara immunoglobulin E for diagnosis and posttreatment follow-up of human toxocariasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992. 30:2269–2274.

12. Yoshikawa M, Nishiofuku M, Moriya K, Ouji Y, Ishizaka S, Kasahara K, et al. A familial case of visceral toxocariasis due to consumption of raw bovine liver. Parasitol Int. 2008. 57:525–529.

13. Magnaval JF. Comparative efficacy of diethylcarbamazine and mebendazole for the treatment of human toxicariasis. Parasitolotgy. 1995. 110:529–533.

14. Lim YH, Lee BJ, Lee SP, Jang SI, Kang SY, Choi DC. Comparison between steroid alone and steroid/albendazole combination therapy in human toxocariasis with eosinophilia. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 21:427. (abstract).
15. Despommier D. Toxacariasis: clinical aspects, epidemiology, medical ecology, and molecular aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003. 16:265–272.

16. Sturchler D, Schubarth P, Gualzata M, Gottstein B, Oettli A. Thiabendazole vs albndazole in treatment of toxocariasis; a clinical trial. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1989. 83:473–478.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download