Abstract
Ossification of the ligamentum flavum (OLF) is a definite clinical entity and is thought to be a form of ectopic ossification which develops predominantly in the lower thoracic spine. OLF causes progressive compressive myelopathy, radiculopathy, or combination of both. We experienced 3 cases of OLF with neurological symptoms, which were treated by posterior decompressive laminectomy and removal of the ossified ligamentum flavum with or without fusion with symptomatic improvement.
REFERENCES
1). Casino CM, Blando AV. Calcification of ligamentum flavum causing spinal cord compressing in a stroke patient. Arch. Phys Med Rehabil. 75:226–228. 1994.
2). Kim NH, Han DY, Kang SS. Ossification of ligamentum flavum. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 24:977–981. 1989.
3). Ko JH, Lee SC, Lee DH. Paraplegia caused by the ossified ligamentum flavum. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1:356–360. 1994.
5). Miyamoto S, Takaoka K, Yonenobu K, Ono K. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum induced by bone mor -phogenic protein. J Bone Joint Surg. 74B:279–283. 1992.
6). Miyasaka K, Kaneda K, Ito T. Ossification of spinal ligaments causing thoracic radiculomyelopathy. Radiology. 143:463–468. 1982.

7). Okada K, Oka S, Tohge K. Thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligementum flavum, clinicopathologic study and surgical treatment. Spine. 280-287:1991.
8). Otani K, Aihara T, Tanaka A. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. Int Orthop. 10:135–139. 1986.
9). Park SR, Kim HS, Kang JS, Lee YH, Lee JH, Park JS. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum and the posterior longitudinal ligament of the lumbar spine. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 4:356–360. 1997.
10). Polgar F. Uber interarkuelle wibelverkalkung. fortschr. Geb. Rontgen. 40:292–298. 1929; (Quoted in Kudo S. Ossification of thoracic ligamenta flava. AJR,. 141(1):1181983).
Fig 1.
Preoperative anteroposterior & lateral radiographs shows a compression fracture of the body of T12 and triangular shaped mass are protruded into the spinal canal at T10-11, T11-12 level (case 1).
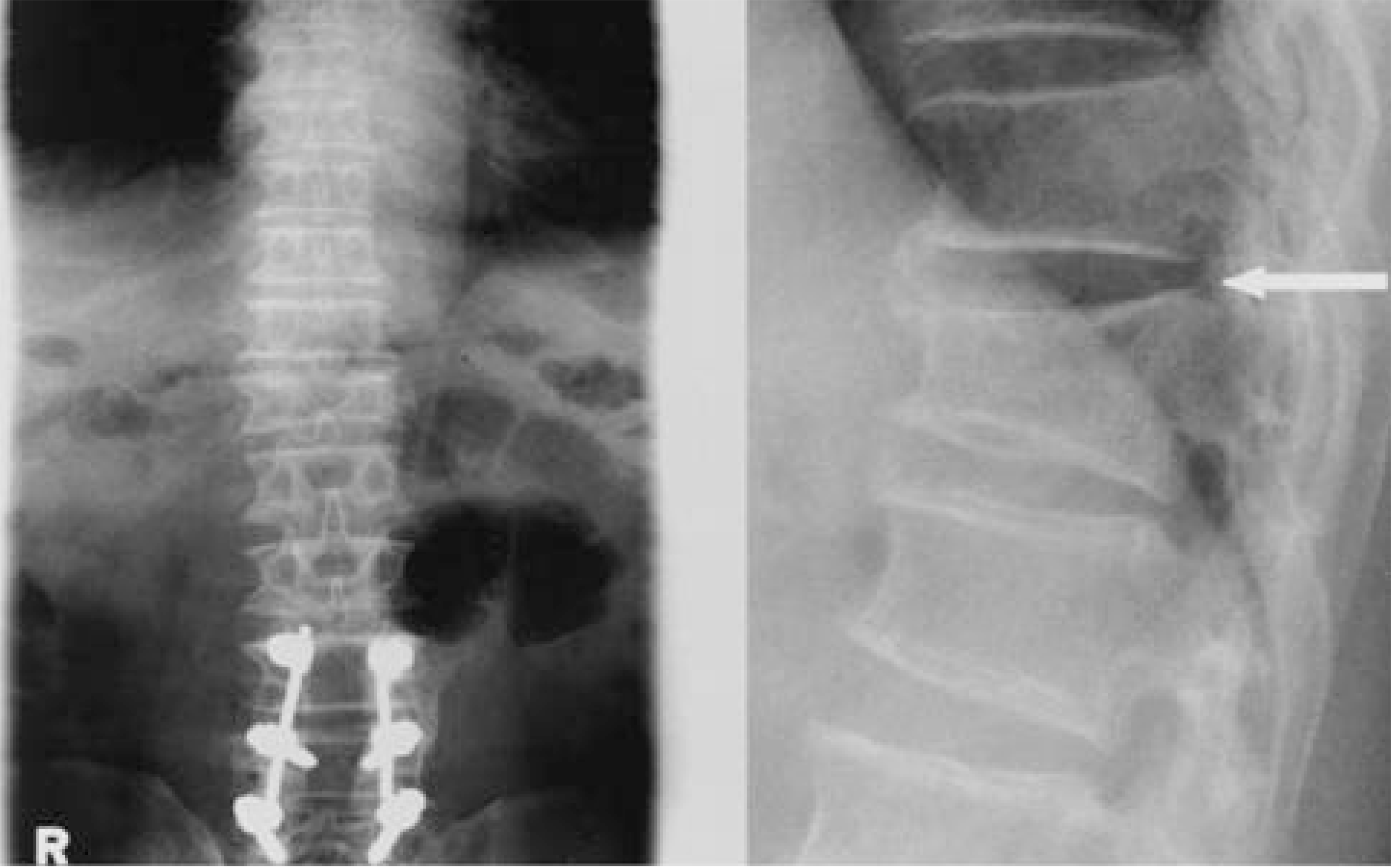
Fig 2.
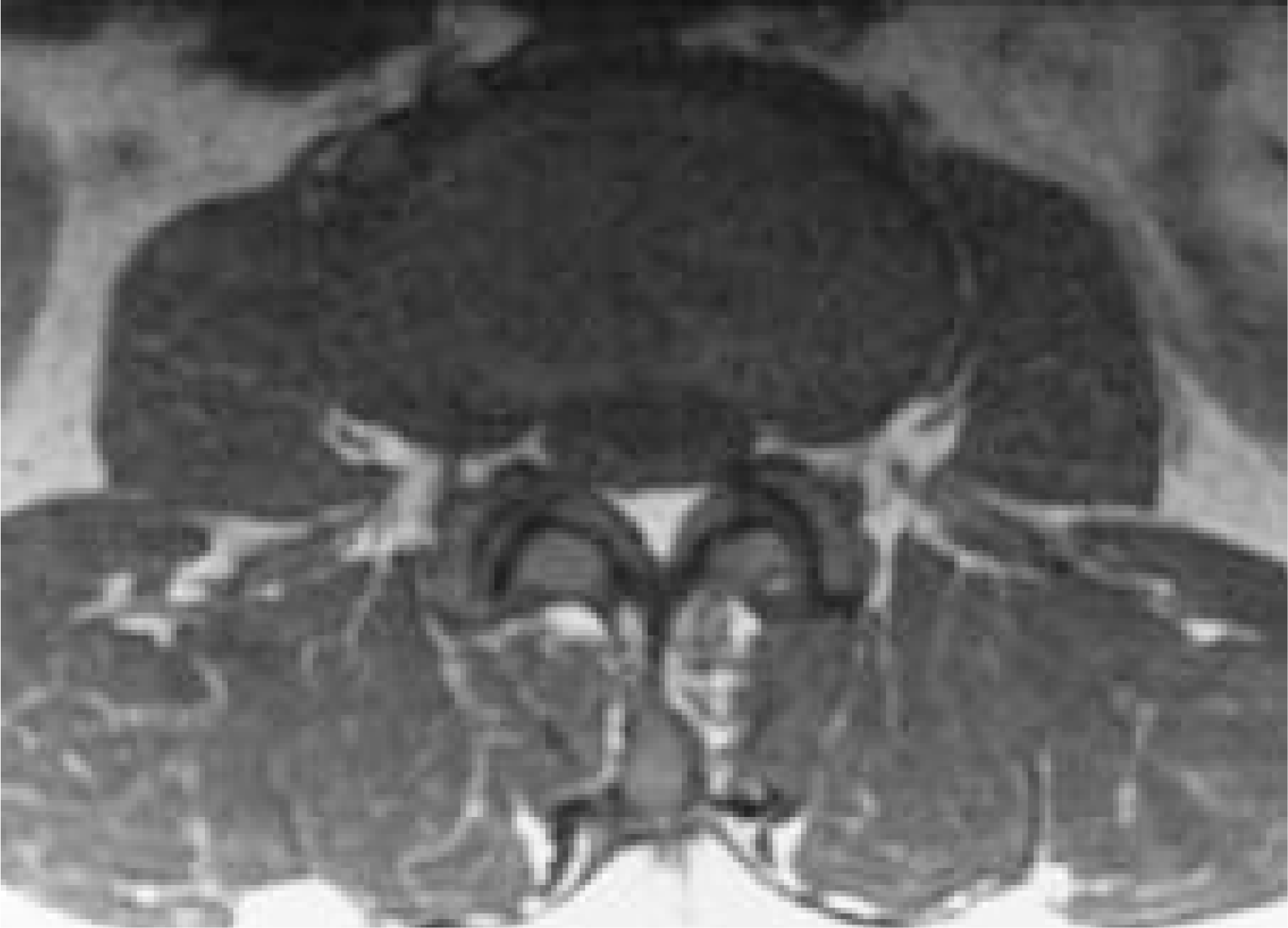
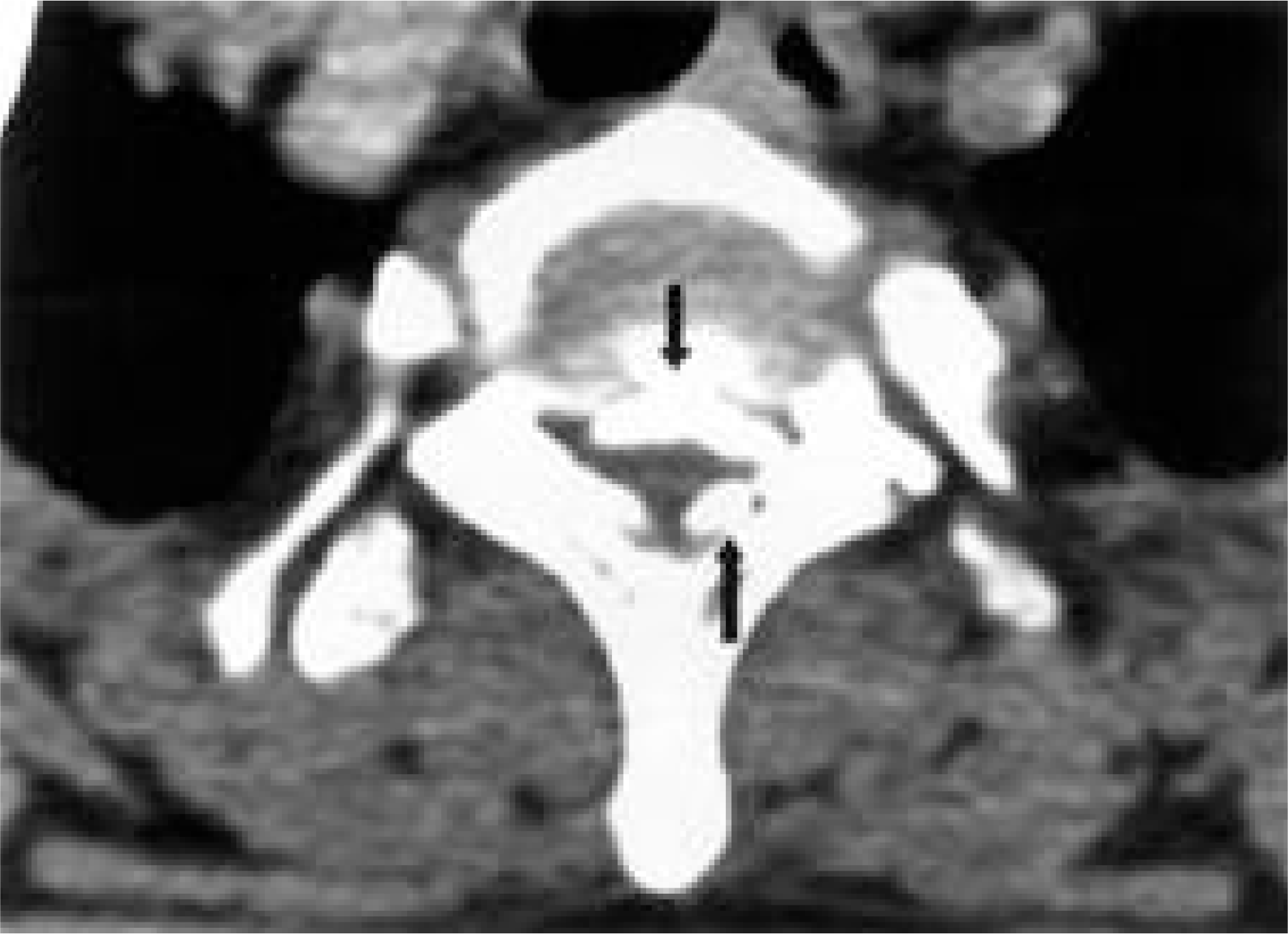
On CT scan, the spinal canal is compressed by ossified mass and intervertebral disc at T11-12 level.
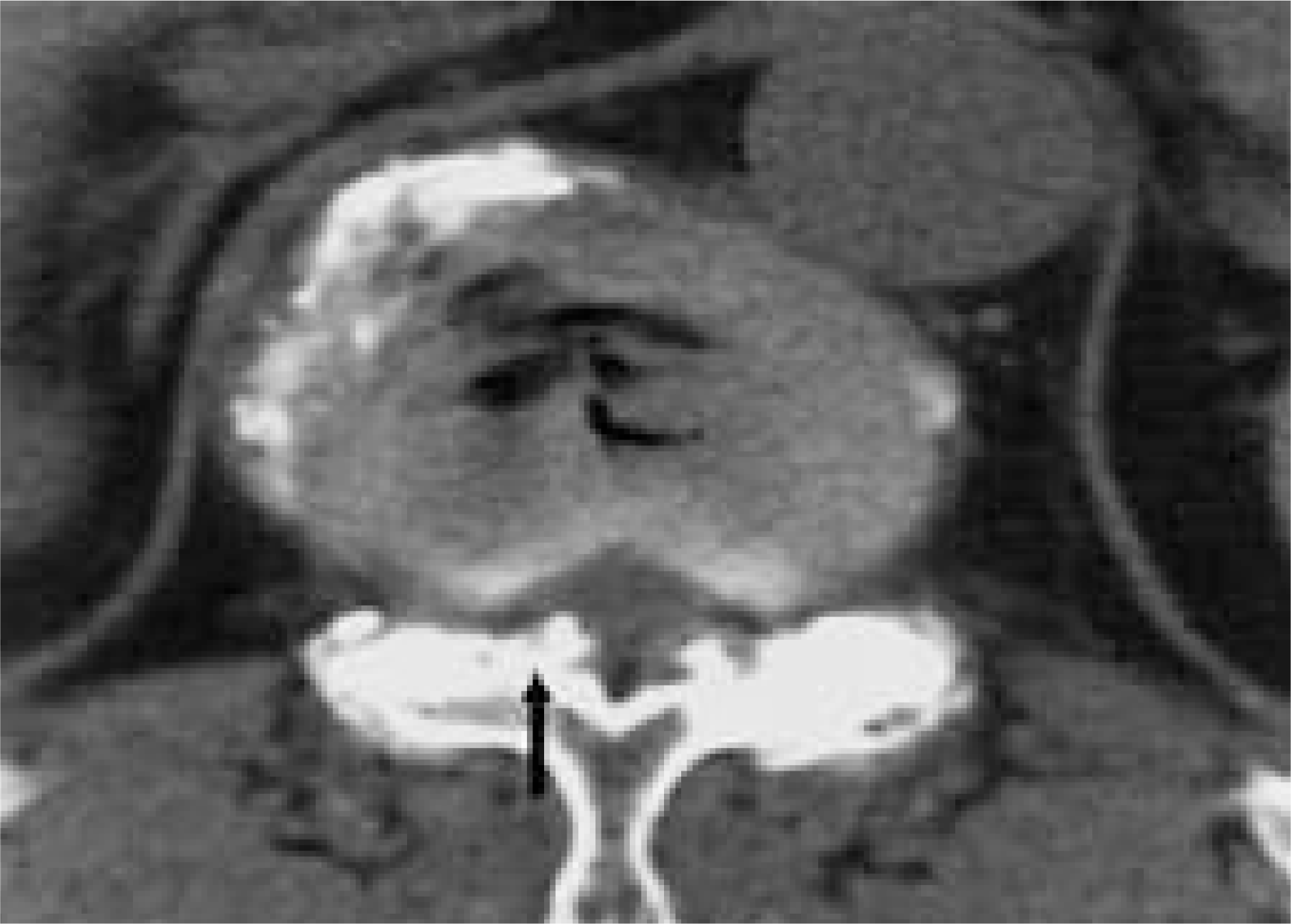
Fig 4.
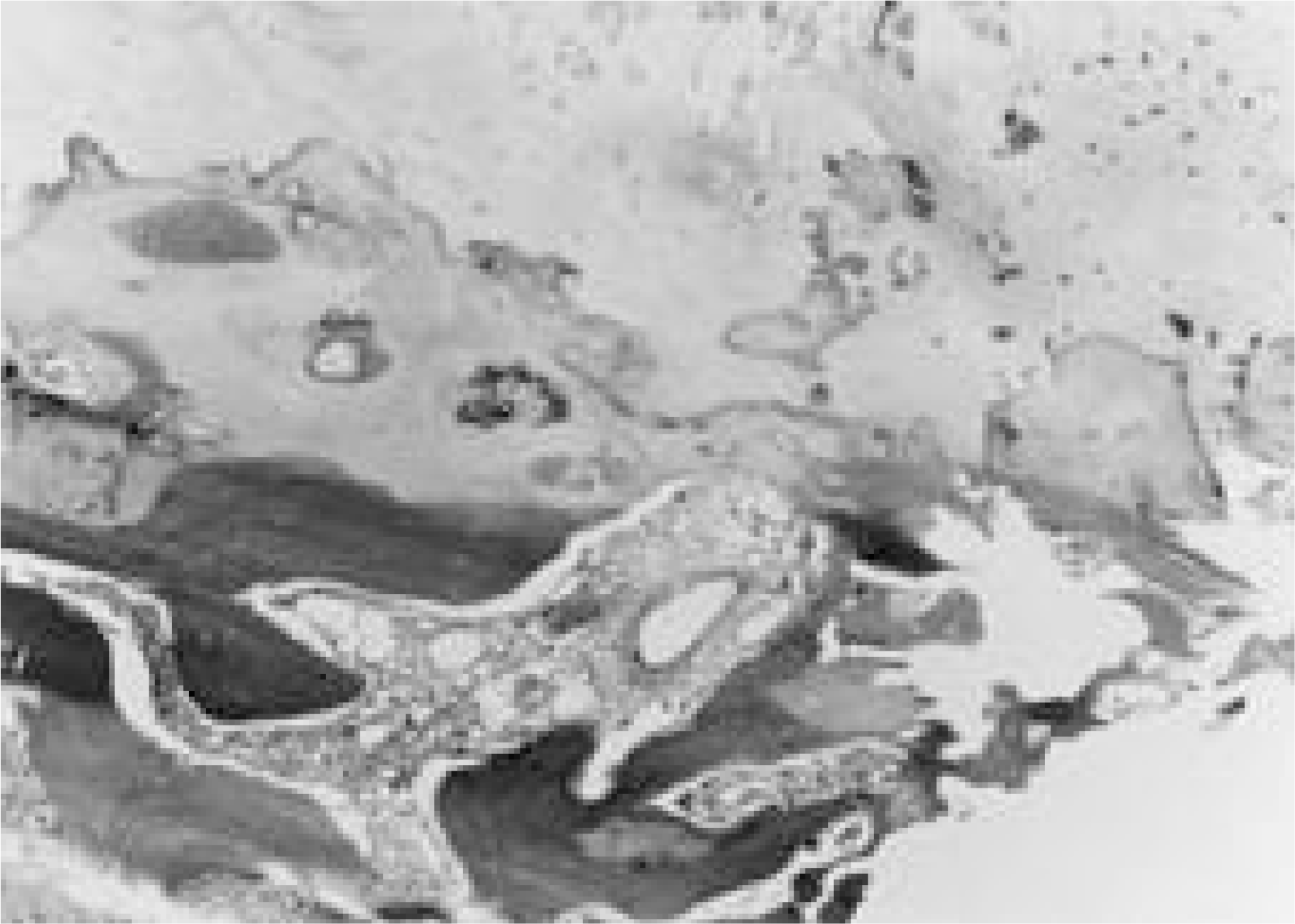
Microscopically, section of the mass shows an area of ossification in the ligamentum flavum (H&E × 400).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download