Abstract
Purpose
HER-2/neu overexpression is documented in some bladder cancers. To our knowledge, there are no current studies evaluating urine HER-2/neu levels. Therefore, we examined the clinical significance of serum and urine HER-2/neu protein in bladder cancer.
Materials and Methods
Urothelial bladder carcinoma patients (n=38, including 31 men and 7 women) and healthy controls (n=25, including 20 men and 5 women) were included in the study. Urine cytology and serum and urine HER-2/neu levels were measured before the transurethral resection of bladder tumor procedure. Prognostic factors including tumor stage, histologic grade, tumor size, multiplicity, and preoperative urine cytology and their association with urinary HER-2/neu were analyzed by simple and multiple regression analyses.
Results
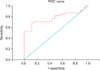
There was no significant difference in serum HER-2/neu between the two groups (p=0.489). The mean urinary HER-2/neu was 7,586.82 relative luminescence unit (RLU) in bladder cancer patients and 4,245.84 RLU in healthy controls. The mean RLU values of urinary HER-2/neu in the bladder cancer patient group were significantly higher than in healthy controls (p=0.012). An receiver operating characteristic curve was generated, and using the cutoff value of ≥4,800 RLU of urinary HER-2/neu, 71.1% sensitivity and 84.0% specificity were obtained. Among the clinical factors, only positive preoperative urine cytology samples were associated with urinary HER-2/neu levels by both simple and multiple regression analyses.
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common malignant bladder neoplasm. Molecular therapy targets and molecular markers are not consistently identified for urinary tract cancers, except for renal cell carcinoma. The human proto-oncogene HER-2/neu (c-erbB2, ErbB-2) is a 185-kilodalton transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase located at chromosome 17q [1]. HER-2/neu protein overexpression and HER-2/neu gene amplification were correlated with higher histologic tumor grade and primary bladder cancer invasiveness in several studies; however, these reports used immunohistochemistry, fluorescent in situ hybridization, or polymerase chain reaction [2-7]. Such methods are required for tumor tissue processing. The extracellular ligand-binding domain of HER-2/neu is shed into the bloodstream and can be measured quantitatively. The clinical significance of serum HER-2/neu levels has been demonstrated in breast, lung, colorectal, and gastric cancers [8-11]. To our knowledge, however, there are no studies of urine HER-2/neu in bladder cancer patients. We therefore examined the clinical utility of serum and urine HER-2/neu and their association with several clinical prognostic factors.
Patients (n=38, 31 men and 7 women) with histologically confirmed bladder urothelial carcinoma were identified from January 2009 to March 2011 and were included in the patient group. Controls included 25 healthy volunteers (20 men and 5 women). No other malignancies were present in either group. This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of our institute. Preoperative urine cytology was performed on bladder cancer patients before the transurethral resection of bladder tumor procedure. Blood and urine (first voided morning sample) were collected for serum and urine HER-2/neu measurements. Samples were centrifuged at 1,500xg for 10 minutes at 4℃ and were stored in a deep freezer at -80℃ until analyzed. Serum and urine HER-2/neu were measured at least twice with the Siemens serum Her-2/neu test on the ADVIA Centaur immunoassay system (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc., Deerfield, IL, USA), and each mean value was taken to be a representative value.
The differences in HER-2/neu levels between both groups were analyzed by using Student's t-test. The influence of HER-2/neu on prognostic factors including tumor stage (by the UICC 2002 TNM staging system, for muscle invasiveness), high histologic grade (2004 World Health Organization grading system, for low or high grade), tumor size (greater or less than 3 cm), multiplicity, and preoperative urine cytology results was also analyzed by using simple and multiple regression analysis. Statistical analysis was performed by using SPSS ver. 14.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Statistical significance was defined at p-values less than 0.05.
The mean age of the bladder patients was 69.4 years (range, 45 to 82 years), and the mean age of the control population was 62.3 years (range, 43 to 83 years). The mean serum HER-2/neu in bladder cancer patients was 8.41 ng/ml (range, 4.0 to 14.0; standard deviation [SD], ±2.33; 95% confidence interval [CI], 7.58-9.24) and that in healthy controls was 8.56 ng/ml (range, 5.1 to 12.5; SD, ±1.93; 95% CI, 7.61-9.27). There were no significant differences identified between the two groups (p=0.489). The mean urinary HER-2/neu was 7586.82 relative luminescence unit (RLU; range, 2,900 to 38,504; SD, ±7,711.20; 95% CI, 5,052.20-10,121.42) in bladder cancer patients and 4,245.84 RLU (range, 2,747 to 5,455; SD, ±719.85; 95% CI, 3,948.70-4,542.00) in healthy controls. The mean RLU values of urinary HER-2/neu were significantly higher in bladder cancer patients than in healthy controls (p=0.012). The brief characteristics of patients and comparisons of the groups are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
To evaluate the diagnostic value, an receiver operating characteristic curve was generated by using urinary HER-2/neu values obtained from 38 bladder cancer patients and 25 healthy volunteers (Fig. 1). Using the cutoff value of ≥4,800 RLU of urinary HER-2/ neu, 71.1% sensitivity and 84.0% specificity were obtained. We examined the association of urinary HER-2/neu with muscle invasiveness (vs. non-muscle invasiveness), histologic grade (high vs. low grade), tumor size (greater or less than 3 cm), multiplicity (vs. solitary mass), and preoperative urine cytology (positive vs. negative). Only positive preoperative urine cytology samples were associated with urinary HER-2/neu levels by both simple and multiple regression analyses (Table 3).
The clinical significance of serum HER-2/neu has already been evaluated in prostate, colorectal, and stomach cancers; patients with elevated serum HER-2/neu demonstrate poor survival compared with patients with lower HER-2/neu [10,12,13]. Several studies have reported an association between prognosis and HER-2/neu oncogene overexpression from bladder cancer specimens [5-7,14]. Unlike previous studies using bladder cancer tissue, blood or urine samples can be collected for measurement of HER-2/neu without surgery or biopsy. Proteolytic cleavage of the extracellular domain of the HER-2/neu molecule results in HER-2/neu protein excretion into the blood circulation [15,16]. Preoperative serum and urinary HER-2/neu have been measured in gastric and colorectal cancer patients, and serum HER-2/neu was significantly higher in the patient groups [10-12]. Urinary HER-2/neu was significantly elevated in gastric cancer patients, although the process of urinary HER-2/neu protein excretion is still unclear [12]. Ecke et al reported that serum HER-2/neu can differ between bladder cancer patients and controls with high sensitivity [17]; however, in the present study, we did not find a difference between the two groups. Although serum HER-2/neu was not significantly different between the bladder cancer and control groups in the present study, urinary HER-2/neu was significantly elevated in the bladder cancer group. Bladder cancer patient urine typically contains tumor cells, red blood cells, and secreted protein, which suggests the potential for elevated urinary HER-2/neu in cancer patients compared with healthy controls. We analyzed the characteristics of patients with urinary HER-2/neu, and positive preoperative urine cytology samples were associated with high urinary HER-2/neu by both simple and multiple regression analyses (Table 3). Other clinical data, including muscle invasiveness, high histologic grade, tumor size (greater or less than 3 cm), and multiplicity were not significantly associated with high urinary HER-2/neu levels. The general sensitivity and specificity of bladder tumor antigen tests, nuclear matrix protein 22 tests, immunoCyt, and UroVysion are relatively high; such tests have been used for bladder cancer screening and monitoring but are still unsatisfactory compared with cytology. The other urinary markers, such as AURKA, BLCA-1, BLCA-4, CEACAM1, survivin, and urinary UBC test are now investigational, and these urinary markers have a relatively high false-positive rate [18]. As another urinary marker, urinary HER-2/neu protein showed 71.1% sensitivity and 84.0% specificity using the cutoff value of ≥4,800 RLU. Our study was limited by a small sample size, and therefore larger-scale studies are necessary to establish the usefulness of urinary HER-2/neu measurement. Additional studies might reveal associations between serum or urine HER-2/neu in bladder cancer and HER-2/neu immunohistochemical staining study, bladder cancer recurrence, progression, and survival. Further, targeted therapy with monoclonal antibodies to the HER-2/neu oncoprotein, such as trastuzumab in breast cancer patients, might be clinically applicable in bladder cancer patients.
Bladder cancer patients demonstrated significantly higher urinary HER-2/neu levels than did healthy controls. Urinary HER-2/neu was associated with positive urine cytology samples. These findings suggest that urinary HER-2/neu may be valuable as a new urinary marker. Additional studies should examine the prognostic significance of serum and urinary HER-2/neu.
Figures and Tables
FIG. 1
ROC curve for urinary HER-2/neu. Using the cutoff value of ≥4,800 RLU of urinary HER-2/neu, 71.1% sensitivity and 84.0% specificity were obtained. ROC: receiver operating characteristic, RLU: relative luminescence unit.
References
1. Yamamoto T, Ikawa S, Akiyama T, Semba K, Nomura N, Miyajima N, et al. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986. 319:230–234.
2. Coombs LM, Pigott DA, Sweeney E, Proctor AJ, Eydmann ME, Parkinson C, et al. Amplification and over-expression of c-erbB-2 in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Br J Cancer. 1991. 63:601–608.
3. Moriyama M, Akiyama T, Yamamoto T, Kawamoto T, Kato T, Sato K, et al. Expression of c-erbB-2 gene product in urinary bladder cancer. J Urol. 1991. 145:423–427.
4. Sato K, Moriyama M, Mori S, Saito M, Watanuki T, Terada K, et al. An immunohistological evaluation of C-erbB-2 gene product in patients with urinary bladder carcinoma. Cancer. 1992. 70:2493–2498.
5. Coogan CL, Estrada CR, Kapur S, Bloom KJ. HER-2/neu protein overexpression and gene amplification in human transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. 2004. 63:786–790.
6. Kim SW, Chung HS, Lee SJ, Lee JY, Cho YH, Yoon MS, et al. Amplification and overexpression of c-erbB2/neu in bladder tumor using real-time quantitative PCR with TaqMan detection system. Korean J Urol. 2001. 42:924–933.
7. Shim HY, Woo YN. Immunohistochemical expression of ras p21 and HER-2/neu oncoprotein in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Korean J Urol. 1995. 36:1315–1322.
8. Andersen TI, Paus E, Nesland JM, McKenzie SJ, Børresen AL. Detection of c-erbB-2 related protein in sera from breast cancer patients. Relationship to ERBB2 gene amplification and c-erbB-2 protein overexpression in tumour. Acta Oncol. 1995. 34:499–504.
9. Osaki T, Mitsudomi T, Oyama T, Nakanishi R, Yasumoto K. Serum level and tissue expression of c-erbB-2 protein in lung adenocarcinoma. Chest. 1995. 108:157–162.
10. Tsigris C, Karayiannakis AJ, Zbar A, Syrigos KN, Baibas N, Diamantis T, et al. Clinical significance of serum and urinary c-erbB-2 levels in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2002. 184:215–222.
11. Kono K, Naganuma H, Sekikawa T, Amemiya H, Takahashi A, Iizuka H, et al. Serum level of HER-2/neu in patients with gastric cancer: correlation with HER-2/neu overexpression in gastric carcinoma tissue. Tumour Biol. 2000. 21:139–144.
12. Tsigris C, Karayiannakis AJ, Syrigos KN, Zbar A, Diamantis T, Kalahanis N, et al. Clinical significance of soluble c-erbB-2 levels in the serum and urine of patients with gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2002. 22:3061–3065.
13. Tambo M, Higashihara E, Terado Y, Nutahara K, Okegawa T. Comparison of serum HER2/neu with immunohistochemical HER2/neu expression for the prediction of biochemical progression in metastatic prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 2009. 16:369–374.
14. Jalali Nadoushan MR, Taheri T, Jouian N, Zaeri F. Overexpression of HER-2/neu oncogene and transitional cell carcinoma of bladder. Urol J. 2007. 4:151–154.
15. Mori S, Mori Y, Mukaiyama T, Yamada Y, Sonobe Y, Matsushita H, et al. In vitro and in vivo release of soluble erbB-2 protein from human carcinoma cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990. 81:489–494.
16. Pupa SM, Ménard S, Morelli D, Pozzi B, De Palo G, Colnaghi MI. The extracellular domain of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein is released from tumor cells by proteolytic cleavage. Oncogene. 1993. 8:2917–2923.
17. Ecke TH, Schlechte HH, Schulze G, Lenk SV, Loening SA. Four tumour markers for urinary bladder cancer--tissue polypeptide antigen (TPA), HER-2/neu (ERB B2), urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and TP53 mutation. Anticancer Res. 2005. 25:635–641.
18. Tilki D, Burger M, Dalbagni G, Grossman HB, Hakenberg OW, Palou J, et al. Urine markers for detection and surveillance of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2011. 60:484–492.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download