Abstract
A 21-year-old woman with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) was admitted with dyspnea on exertion for a year. A transesophageal echocardiogram showed dilated aortic root with intimal thickening. A positron emission tomography/computed tomography demonstrated increase in glucose hypermetabolic along the walls of the aortic valve, ascending aorta, aortic arch, and aorta, vasculitis was observed. She underwent the Bentall operation due to inflammation at sinus of right coronary cusp. She started high dose glucocorticoid after the operation. Currently she is able to sustain with low dose steroid after gradually tapered. Her symptoms were disappeared, and inflammatory markers decreased to within the normal range. Aortitis and aortic aneurysms are an uncommon manifestation of SLE. Furthermore, almost of lupus patients with medium and large vessel vasculitis are not biopsied or studied histologically. We present first case in Korea that was a 21-year-old woman who diagnosed with lupus aortitis by pathology after aortic valve replacement operation.
REFERENCES
1. Slobodin G, Naschitz JE, Zuckerman E, Zisman D, Rozenbaum M, Boulman N, et al. Aortic involvement in rheumatic diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006; 24(2 Suppl 41):S41–7.
2. Ramos-Casals M, Nardi N, Lagrutta M, Brito-Zerón P, Bové A, Delgado G, et al. Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and clinical characteristics in 670 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2006; 85:95–104.
3. Breynaert C, Cornelis T, Stroobants S, Bogaert J, Vanhoof J, Blockmans D. Systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with aortitis. Lupus. 2008; 17:72–4.
4. Wang J, French SW, Chuang CC, McPhaul L. Pathologic quiz case: an unusual complication of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000; 124:324–6.

5. Silver AS, Shao CY, Ginzler EM. Aortitis and aortic thrombus in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2006; 15:541–3.

6. Dhaon P, Das SK, Saran RK, Parihar A. Is aorto-arteritis a manifestation of primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome? Lupus. 2011; 20:1554–6.

7. Vaideeswar P, Deshpande JR. Pathology of Takayasu arteritis: a brief review. Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2013; 6:52–8.

8. Drenkard C, Villa AR, Reyes E, Abello M, Alarcón-Segovia D. Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1997; 6:235–42.

10. Ménard GE. Establishing the diagnosis of Libman-Sacks endocarditis in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Gen Intern Med. 2008; 23:883–6.

Figure 1.
(A) Parasternal long axis view of transthoracic echo-cardiography showed slightly thickened aortic valve and moderately thickened aortic root. (B) Parasternal long axis view of transthoracic echocardiography (zoomed view) showed thickened aortic valve and aortic root (left). Color Doppler showed jet flow of severe aortic regurgitation in diastole (right). (C) 47o aortic valve short axis view of transesophageal echocardiography showed focally thickened aortic valve and aortic root (left). Color Doppler showed jet flow of aortic regurgitation in diastole (right). BP: blood pressure, LA: left atrium, LVOT: left ventricular outflow tract, LV: left ventricle, RV: Right ventricle.
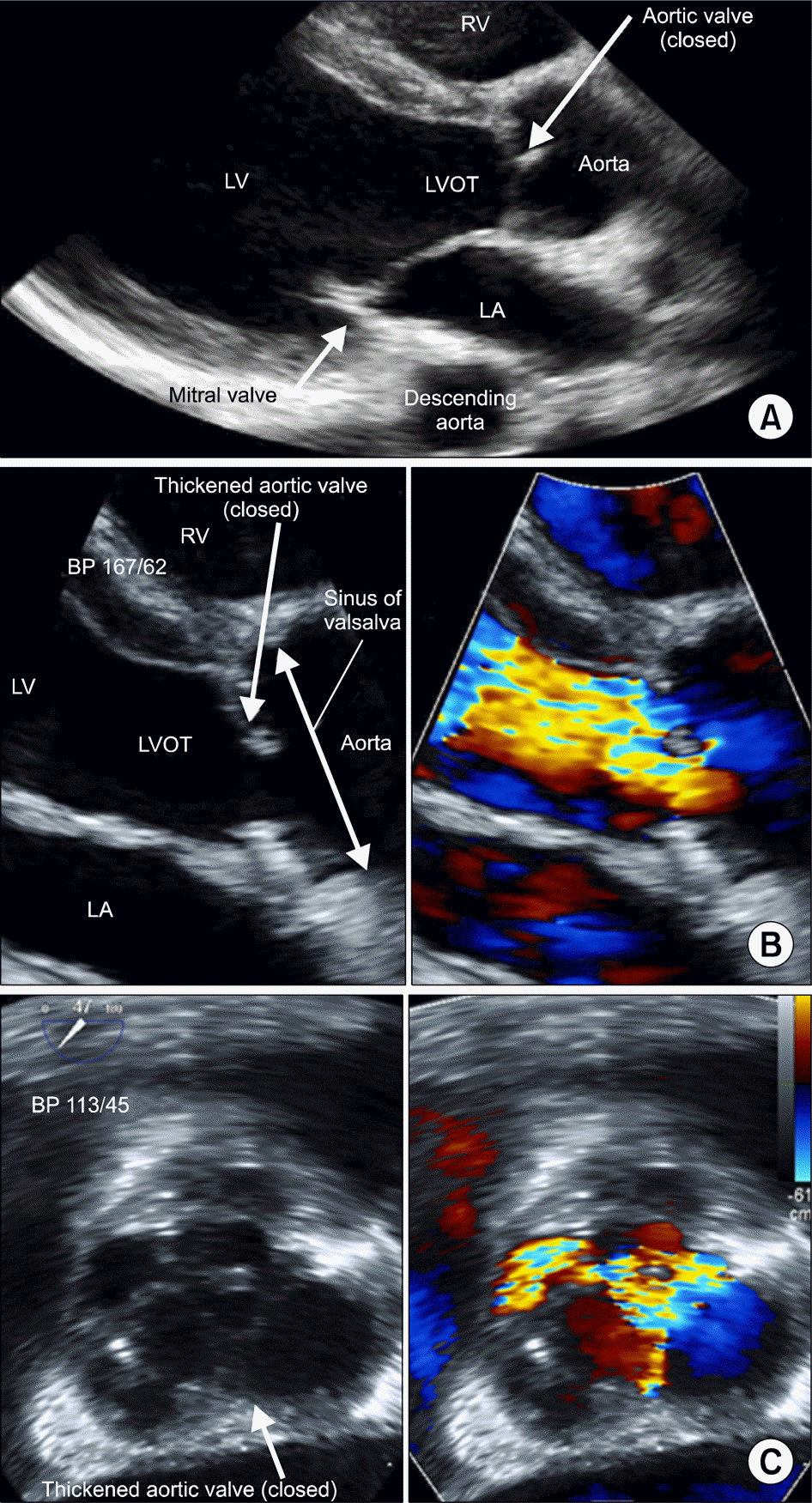
Figure 2.
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography shows significant increased in 18-fluorodeoxyglucose uptakes along the walls of aortic valve, ascending aorta, aortic arch, descending thoracic aorta, and abdominal aorta, that were suggestive of vasculitis. (A) Coronal view, (B) sagittal view.
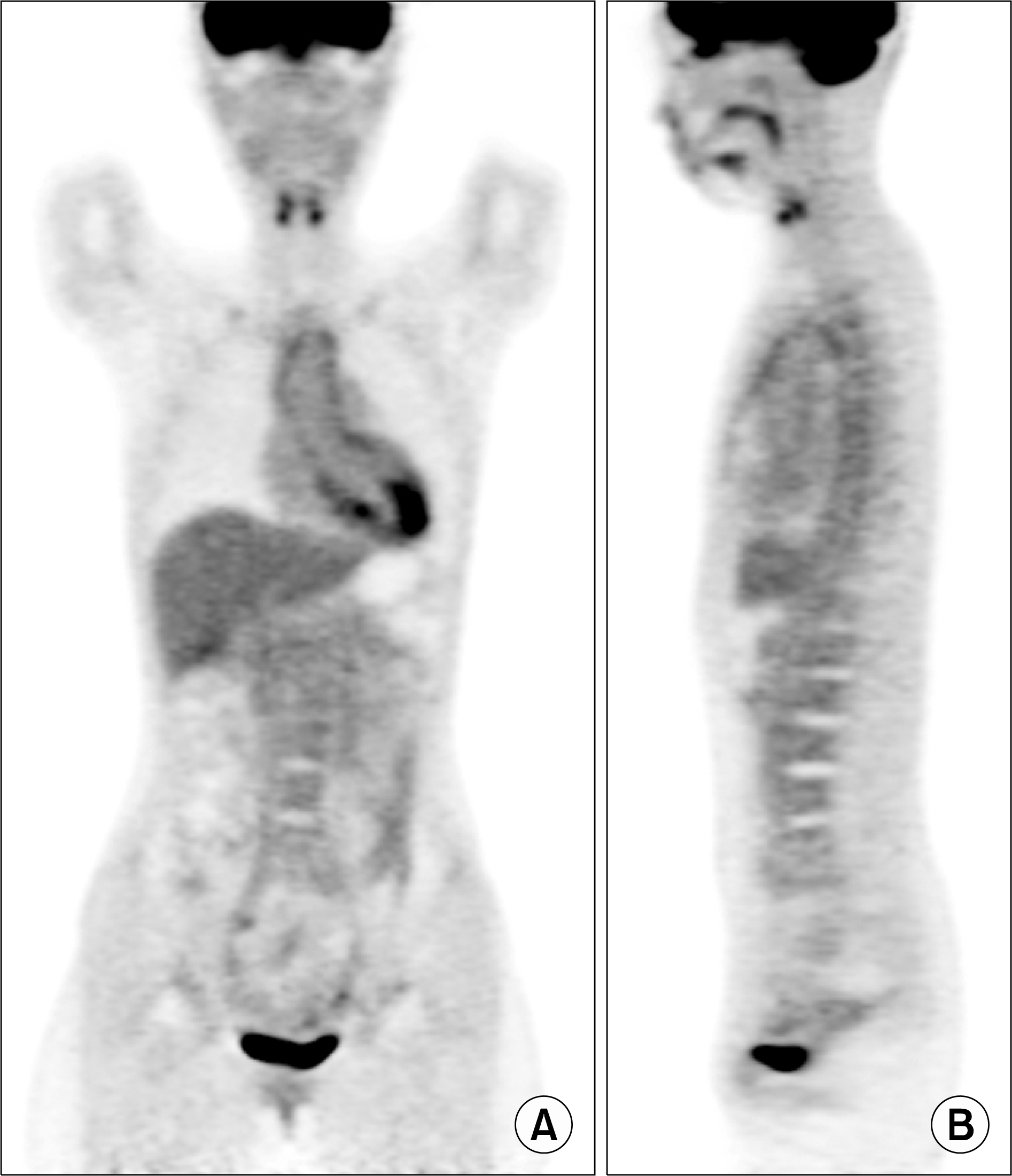
Figure 3.
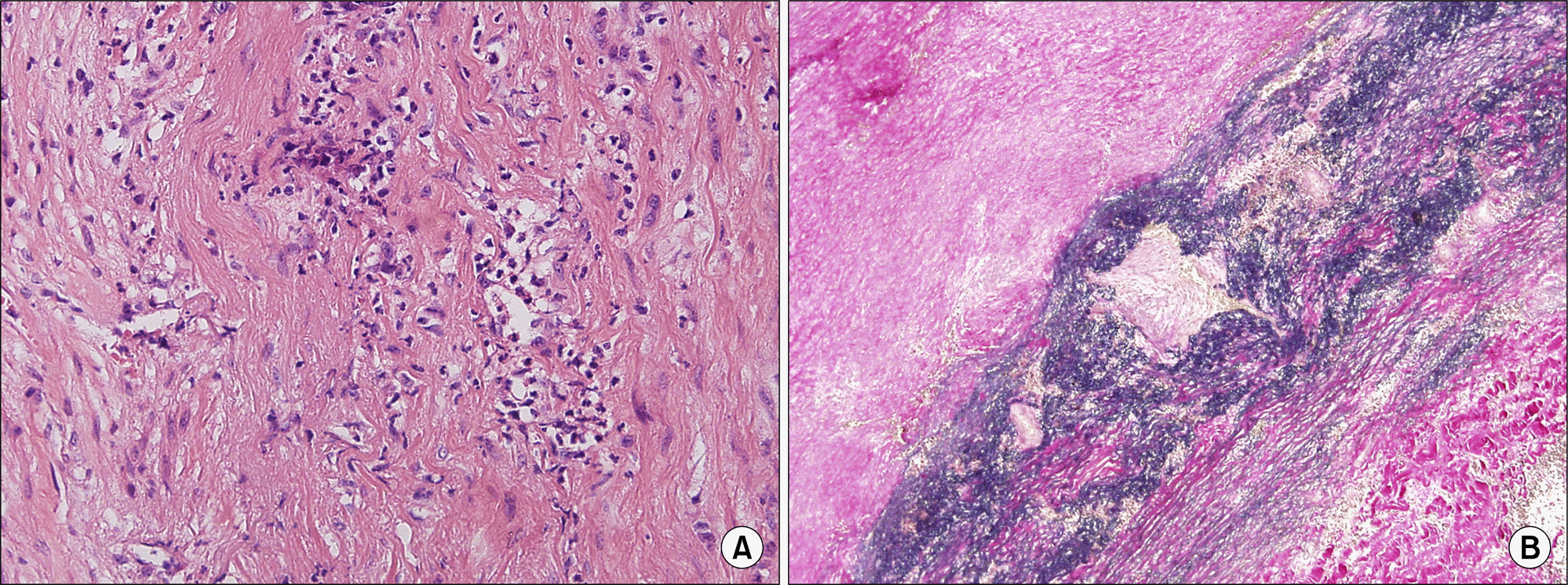
Aortitis was present in ascending aorta biopsy. It showed necrotizing inflammation of media with neovascularization and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration in media and adventitia associated with small vessel vasculitis, consistent with lupus aortitis. (A) Hematoxylin-eosin, Media (×200), (B) Elastic van Gieson stain (×40).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download