|
|
| Current Status and Proposal of a Guideline for Manual Slide Review of Automated Complete Blood Cell Count and White Blood Cell Dfferential
|
Hee-Yeon Woo, M.D.,1
Sang-Yong Shin, M.D.,1
Hyosoon Park, M.D., 1
Young Jae Kim, M.D.,2
Hee-Jin Kim, M.D.,3
Young Kyung Lee, M.D.,4
Seok-Lae Chae, M.D.,5
Yoon Hwan Chang, M.D.,6
Jong Rak Choi, M.D.,7
Kyungja Han, M.D.,8
Sung Ran Cho, M.D.,9
and Kye Chul Kwon, M.D.10 1
Young Jae Kim, M.D.,2
Hee-Jin Kim, M.D.,3
Young Kyung Lee, M.D.,4
Seok-Lae Chae, M.D.,5
Yoon Hwan Chang, M.D.,6
Jong Rak Choi, M.D.,7
Kyungja Han, M.D.,8
Sung Ran Cho, M.D.,9
and Kye Chul Kwon, M.D.10
|
1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
|
2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
|
3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
|
4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
|
5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University, Goyang, Korea.
|
6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
|
7Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
|
8Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
|
9Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
|
10Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
|
 Corresponding author: Hyosoon Park, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 108 Pyeong-dong, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-746, Korea. Tel: +82-2-2001-2368, Fax: +82-2-2001-2364, Email: hspcp@naver.com Corresponding author: Hyosoon Park, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 108 Pyeong-dong, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-746, Korea. Tel: +82-2-2001-2368, Fax: +82-2-2001-2364, Email: hspcp@naver.com
|
|
Received April 30, 2010; Revised July 01, 2010; Accepted September 15, 2010.
|
|
|
Abstract
|
Background
Manual slide review (MSR) is usually triggered by the results of automated hematolgy analyzers, but each laboaratory has different ciriteria for MSR. This study was carried out to investigate the current status of MSR criteria of automated complete blood cell count (CBC) and white blood cell (WBC) differential results and to propose a basic guideline for MSR.
Methods
Total 111 laboratories were surveyed regarding MSR using questionnaires. The questionnaire asked: kinds of automated hematology analyzers used and the presence of criteria triggering MSR in seven categories: 1) CBC results, 2) 5 differential WBC counts, 3) 3 differential WBC counts, 4) automated reticulocyte counts, 5) delta check, 6) instrument flags (or messages), 7) clinical information (wards or diseases). Based on the survey results, we determined basic and extended criteria for MSR. With these criteria, we consulted nine hematology experts to get a consensus.
Results
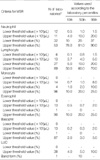
All 111 laboratories had their own MSR criteria. Among 111 laboratories, 98 (88.3%) used more than three criteria for MSR including CBC results and 5-part WBC differential count results and 95 (85.6%) had criteria of flags triggering MSR. For MSR criteria with numeric values, the 10th, 50th, and 90th percentiles of upper and lower threshold values were obtained. The basic guideline for MSR was made.
Conclusions
We proposed a basic guideline for MSR. This guideline would be helpful to hematology laboratories for their daily operation and providing more rapid and accurate CBC and WBC differential results.
|




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print