Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Colonoscopic findings. (A) Hyperemic ileocecal valve was observed. (B) No visible mass is found in the hepatic flexure of ascending colon.
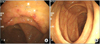
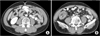
Fig. 2
Abdominal computed tomography findings. (A) Well-defined, 3 cm sized low attenuated submucosal mass is identified on the hepatic flexure of ascending colon. (B) A round target-shaped mass is revealed in the right lower quadrant consisting of different densities.
References
1. Bardaji M, Roset F, Camps R, Sant F, Fernandez-Layos MJ. Symptomatic colonic lipoma: differential diagnosis of large bowel tumors. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1998. 13:1–2.
2. Algin C, Hacioglu A, Aydin T, Ihtiyar E. Esophagectomy in esophageal lipoma: report of a case. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2006. 17:110–112.
3. Deeths TM, Madden PN, Dodds WJ. Multiple lipomas of the stomach and duodenum. Am J Dig Dis. 1975. 20:771–774.
4. Kim BC, Jung SW, Kwon SH, Park JS, Ko BK, Kim YM, et al. A case of jejuno-jejunal intussusception caused by a small intestinal lipoma. Korean J Med. 2008. 75:333–336.
5. Pemberton LB, Manax WG. Complete obstruction of the colon by lipoma. Surgery. 1971. 69:139–141.
6. Ryu KW, Kim DS, Hong BW, Lee JB, Moon HY, Choi SY. Diagnosis and treatment of adult intussusception due to gastrointestinal lipoma. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000. 59:61–66.
7. Heiken JP, Forde KA, Gold RP. Computed tomography as a definitive method for diagnosing gastrointestinal lipomas. Radiology. 1982. 142:409–414.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


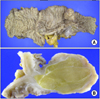
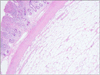
 XML Download
XML Download