Abstract
The coexistence of an epithelial lesion and a subepithelial lesion is uncommon. In almost all such cases, the coexistence of these lesions appears to be incidental. It is also extremely rare to encounter a neoplasm in the surface epithelium that overlies a benign mesenchymal tumor in the esophagus. Several cases of a coexisting esophageal neoplasm overlying a leiomyoma that is treated endoscopically or surgically have been reported previously. Here, three cases of a superficial esophageal neoplasm that developed over an esophageal leiomyoma and was then successfully removed by endoscopic submucosal dissection are described.
Esophageal leiomyoma, although rare, is the most common benign mesenchymal tumor of the esophagus: it accounts for 60% to 70% of all benign esophageal tumors.12 The incidence of esophageal leiomyoma in autopsy cases ranges from 0.005% to 5%.3 It usually appears as a solitary tumor (97%), and multiple leiomyomas of the esophagus have been documented only extremely rarely.4
The coexistence of an epithelial lesion and a subepithelial lesion is uncommon: in almost all such cases, the coexistence of the lesions appears to be incidental. It is also extremely rare to encounter a neoplasm in the surface epithelium overlying a benign mesenchymal tumor in the esophagus. Several cases of coexisting squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and leiomyoma in the esophagus have been reported, and most were treated surgically.567 In the present report, three cases of superficial esophageal neoplasms (SENs) that overlaid leiomyoma and were successfully removed by endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) are reported. The literature is also reviewed.
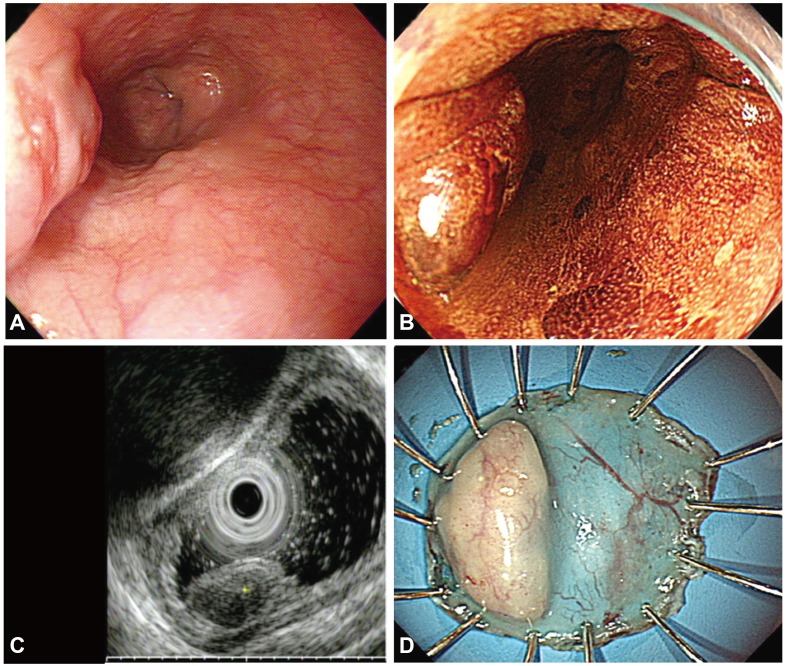
A 66-year-old man was referred to our hospital for the treatment of an epithelial lesion with severe dysplasia, which was histologically confirmed at a local primary care clinic. Five years previously, he had undergone esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) during a health checkup, and an esophageal subepithelial tumor (SET) was diagnosed during the examination. However, the patient did not return for follow-up of the lesion. The EGD showed a protruding mass that measured 1×1 cm in diameter and was located 25 cm from the upper incisors. The surface mucosa of the lesion was slightly irregular and did not stain with Lugol's solution. Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) demonstrated a hypoechoic and homogeneous lesion that originated from the muscularis mucosa (MM) below the epithelial layer. Endoscopic biopsy confirmed that the esophageal lesion was an SCC. EUS and chest computed tomography showed no evidence of lymph node metastasis in the mediastinum. The patient was diagnosed with SCC overlying a leiomyoma from the MM. En bloc resection using ESD was chosen as a curative treatment (Fig. 1). Histopathological examination of the resected lesion revealed an esophageal leiomyoma that underlay the SCC in situ and was 20×11 mm in size, and the leiomyoma consisted of bland spindle cells with cigar-shaped nuclei. The atypical squamous cells were confined to the mucosa, and both the lateral and vertical resection margins were tumor-free. Immunohistochemical staining showed Ki-67-positive atypical squamous cells in the entire layer. The leiomyoma demonstrated diffuse positive staining for smooth muscle actin (Fig. 2). The patient was followed up with annual EGD after the ESD. There was no local recurrence over the following 46 months.
A 74-year-old man was admitted for treatment of a histologically proven esophageal SCC. EGD revealed a 1 cm-sized elevated lesion with a smooth surface that was located in the proximal third of the esophagus. After the lesion was sprayed with Lugol's solution, ill-demarcated and unstained areas could be observed overlying the lesion. EUS demonstrated a hypoechoic tumor that was 5.6×2.9 mm in size and that originated from the MM. The patient was diagnosed with SCC overlying a leiomyoma from the MM. ESD was performed under general anesthesia. En bloc resection of the lesion was performed. There was no lymphovascular invasion or involvement of the deep resection margin, but there was involvement of the lateral resection margin in one block section. Histopathological examination of the resected lesion revealed high-grade dysplasia that overlay a leiomyoma (Fig. 3). The leiomyoma was positive for smooth muscle actin and desmin and its greatest dimension was 1.3 cm (Fig. 4). Follow-up endoscopy was selected rather than additional surgical resection because the apparent involvement of the lateral resection margin could have been a false positive due to a cautery effect. The patient underwent endoscopic examination after 8 months. Local recurrence was not observed; therefore, no biopsy was performed. The patient was also followed up with annual EGD and to date, the patient has remained disease-free for 28 months.
A 78-year-old man underwent EGD for screening because of anemia. EGD revealed an SET in the lower esophagus. Endoscopic biopsy showed high-grade dysplasia. EUS demonstrated a homogeneous and hypoechoic tumor that was 7.4×4.4 mm in size and located in the MM. It was concluded that the lesion had high-grade dysplasia and was a leiomyoma. Therefore, ESD was performed and the resected specimen was 30×23 mm in size (Fig. 5). Histopathological examination of the resected lesion revealed an esophageal leiomyoma that was 14×7×3 mm in size and covered with high-grade dysplasia. The resection margins were clear. After the treatment, the patient was followed up for 38 months with annual endoscopic examination. Local recurrence was not observed.
Three cases of SENs overlying a leiomyoma that were successfully treated with ESD are reported. The three patients have remained disease-free for 46, 28, and 38 months, respectively.
Leiomyoma is the most common SET of the esophagus: it accounts for two-thirds of all benign tumors and has an incidence at autopsy of 0.005% to 5%.123 Leiomyomas occur most commonly in patients between 20 and 60 years of age and are found more often in men than in women by a ratio of 2 to 1. Leiomyoma usually appears as a solitary tumor (97%). Esophageal carcinoma is approximately 50 times more common than leiomyoma.4 However, it is extremely rare to observe coexisting esophageal carcinoma and leiomyoma; most cases of such coexisting lesions that have been reported previously were detected incidentally following surgery. Their incidence ranges from 1.2% to 9.1%.68 Similarly, in our hospital, of the 1,142 patients who underwent surgical resection due to esophageal cancer between 1995 and 2013, 38 patients (3.3%) also had leiomyoma in the esophagus. The advances in EUS technology and prolonged lifespans mean that it is now possible to diagnose SENs that coexist with leiomyoma before surgery. Nevertheless, the frequency with which esophageal carcinoma and leiomyoma coexist is very low.
A review of the literature revealed that it contains only eight cases of coexisting leiomyomas and SENs, which were treated by endoscopic resection (ER).9101112131415
Table 1 summarizes the clinicopathological features of these eight cases as well as those of the present cases. In all cases, the patients were middle-aged to elderly and there was a male predominance (the male:female ratio was 10:1). The leiomyoma arose from the MM in 10 cases and from the muscularis propria (MP) in the remaining case. The SEN was removed by endoscopic mucosal resection and ESD in six and five cases, respectively. En bloc resection of the overlying SEN and the leiomyoma was performed in all cases except in case 4:12 in this case, only the overlying SEN was subjected to ER because the leiomyoma originated from the MP, which meant that it could not be removed en bloc.
The relationship between SEN and leiomyoma is unclear, especially in terms of causality. Several possibilities have been proposed. First, the chronic stimulation of the epithelium over the pre-existing leiomyoma may induce the epithelial carcinogenesis.616 However, if this is the case, one would expect to see more reports on esophageal carcinoma overlying a leiomyoma. As a result, some authors have argued that it is unlikely that the carcinogenesis of the esophagus relates to the leiomyoma.6 Second, it has been suggested that the coexisting SEN and leiomyoma are an example of collision tumors, in which synchronously growing, morphologically different neighboring neoplasms expand into each other.17
EUS is essential for determining the strategy for treating coexisting esophageal leiomyoma and SEN. Misdiagnosis of the leiomyoma as an invasion of an SEN could lead to unnecessary surgery due to overestimation of the depth of the invasion. In contrast, if a leiomyoma originating from the MM is located very close to the SEN, or if a leiomyoma originating from proper muscle lifts up the SEN, this could lead to underestimation of the degree of SEN invasion and the inappropriate decision to perform ER rather than surgery.
According to the guidelines of the Japanese Esophageal Society for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal SCC, ER is recommended in patients with SEN, which is limited to high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, including neoplasia in the epithelium and lamina propria without vascular invasion or lymph node metastasis.18 Tumors that have invaded the MM or submucosa are associated with a higher risk of lymph node metastasis, and ER can be considered if there are no additional risk factors, such as a poorly differentiated component or lymphovascular invasion.19 A review of the literature revealed that there was no evidence of recurrence following ER of coexisting esophageal leiomyoma and SEN.9101112131415 Moreover, analysis of the surgically resected specimens showed that the SCCs were all SENs that overlaid a leiomyoma.620 Based on these findings, ER may be considered a curative treatment for SCC overlying a leiomyoma. We recommend ER of the overlying SEN and leiomyoma if the leiomyoma originates from the MM, and ER of the SEN alone if the leiomyoma originates from the MP, as this would avoid potential complications such as esophageal perforation.
In conclusion, to avoid unnecessary surgery, it is recommended that cases of coexisting esophageal leiomyoma and SEN be diagnosed appropriately through the use of multiple diagnostic modalities.
References
1. Punpale A, Rangole A, Bhambhani N, et al. Leiomyoma of esophagus. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007; 13:78–81. PMID: 17505413.
2. Fountain SW. Leiomyoma of the esophagus. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1986; 34:194–195. PMID: 2426836.

3. Postlethwait RW, Musser AW. Changes in the esophagus in 1,000 autopsy specimens. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1974; 68:953–956. PMID: 4420581.

4. Mutrie CJ, Donahue DM, Wain JC, et al. Esophageal leiomyoma: a 40-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005; 79:1122–1125. PMID: 15797036.

5. Iwaya T, Maesawa C, Uesugi N, et al. Coexistence of esophageal superficial carcinoma and multiple leiomyomas: a case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:4588–4592. PMID: 16874880.

6. Iizuka T, Kato H, Watanabe H, Itabashi M, Hirota T. Superficial carcinoma of the esophagus coexisting with esophageal leiomyoma: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1984; 14:115–122. PMID: 6708309.
7. Mizobuchi S, Kuge K, Matsumoto Y, et al. Co-existence of early esophageal carcinoma and leiomyoma: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2004; 34:751–754. PMID: 15640507.

8. Suzuki H, Nagayo T. Primary tumors of the esophagus other than squamous cell carcinoma: histologic classification and statistics in the surgical and autopsied materials in Japan. Int Adv Surg Oncol. 1980; 3:73–109. PMID: 6926744.
9. Ahn SY, Jeon SW. Endoscopic resection of co-existing severe dysplasia and a small esophageal leiomyoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:137–140. PMID: 23326177.

10. Ishida M, Mochizuki Y, Iwai M, Yoshida K, Kagotani A, Okabe H. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in situ overlying leiomyoma: a case report with review of the literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 6:3026–3028. PMID: 24294396.
11. Niimi K, Kodashima S, Ono S, Goto O, Yamamichi N, Fujishiro M. Curative ESD for intraepithelial esophageal carcinoma with leiomyoma mimicking submucosal invasive carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 1:68–71. PMID: 21160655.

12. Ishihara R, Yamamoto S, Yamamoto S, et al. Endoscopic resection of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma overlying leiomyoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:745–747. PMID: 18206883.

13. Joo SY, Lee WS, Park SY, et al. A case of esophageal carcinoma coexisting with leiomyoma removed by endoscopic resection. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 34:324–328.
14. Fu KI, Muto M, Mera K, et al. Carcinoma coexisting with esophageal leiomyoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:272–273. PMID: 12145610.

15. Nagashima R, Takeda H, Motoyama T, Tsukamoto O, Takahashi T. Coexistence of superficial esophageal carcinoma and leiomyoma: case report of an endoscopic resection. Endoscopy. 1997; 29:683–684. PMID: 9360884.

16. Kuwano H, Sadanaga N, Watanabe M, Yasuda M, Nozoe T, Sugimachi K. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma occurring in the surface epithelium over a benign tumor. J Surg Oncol. 1995; 59:268–272. PMID: 7630176.

17. Sarbia M, Katoh E, Borchard F. Collision tumor of squamous cell carcinoma and leiomyoma in the esophagus. Pathol Res Pract. 1993; 189:360–362. PMID: 8332578.

18. Ono S, Fujishiro M, Koike K. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal neoplasms. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 4:162–166. PMID: 22624067.

19. Ezoe Y, Muto M, Horimatsu T, et al. Efficacy of preventive endoscopic balloon dilation for esophageal stricture after endoscopic resection. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011; 45:222–227. PMID: 20861798.

20. Yoshikane H, Tsukamoto Y, Niwa Y, et al. The coexistence of esophageal submucosal tumor and carcinoma. Endoscopy. 1995; 27:119–123. PMID: 7601022.

Fig. 1
(A) An endoscopic image shows a subepithelial tumor with an eroded surface in the middle third of the esophagus. (B) Lugol chromoendoscopy shows the iodine-unstained lesion. (C) Endoscopic ultrasonography demonstrates a hypoechoic, homogeneous lesion that originates from the muscularis mucosa and is covered by a squamous cell carcinoma in situ. (D) The specimen with the lesion after its en bloc resection.
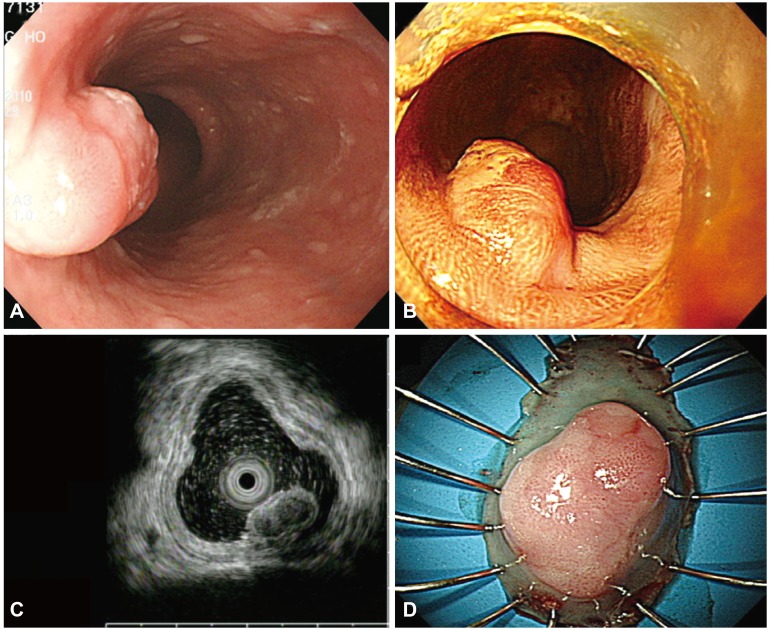
Fig. 2
(A) Histopathologically, the resected lesion is a squamous cell carcinoma that overlies a leiomyoma in situ. The red arrows correspond to the lateral margins of the squamous cell carcinoma (H&E stain, ×12.5). (B) The esophageal leiomyoma is composed of bland spindle cells with no mitosis or nuclear atypia (H&E stain, ×40). (C) The entire layer of atypical epithelial cells is positive for the Ki-67 stain and demonstrates a Ki-67 labeling index of less than 1% (×40). (D) The esophageal leiomyoma is strongly and diffusely positive for smooth muscle actin (×40).
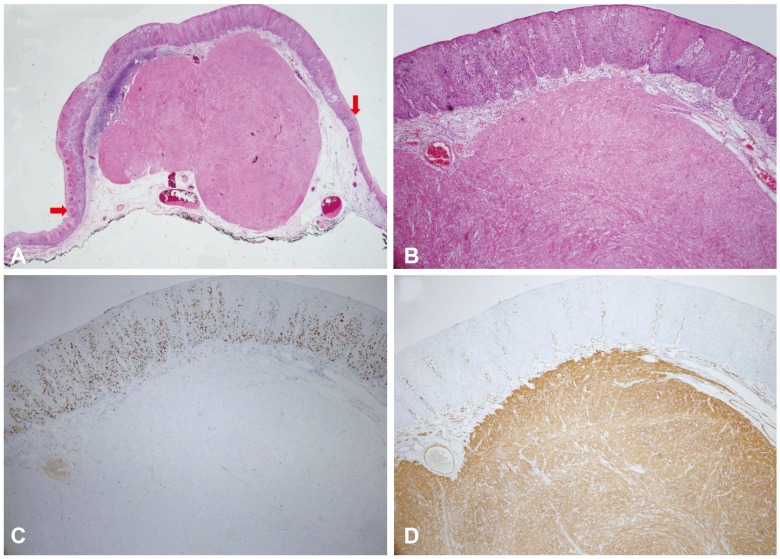
Fig. 3
(A) Endoscopic examination shows a subepithelial tumor with a flat hyperemic lesion in the upper esophagus. (B) Lugol chromoendoscopy shows the iodine-unstained lesion. (C) Endoscopic ultrasonography demonstrates a hypoechoic, homogeneous lesion that originates from the muscularis mucosa and is covered by a superficial squamous cell carcinoma. (D) The specimen with the lesion after en bloc resection.
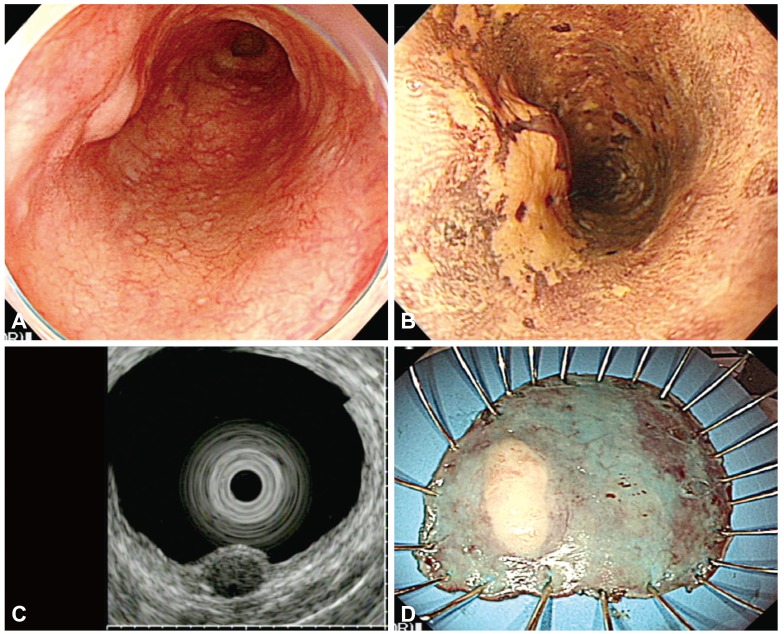
Fig. 4
(A) Histological mapping of the resected specimen shows severe dysplasia with a leiomyoma. The black lines indicate the cutting line of the block sections. The yellow circle corresponds to the leiomyoma and the red squares correspond to atypical squamous cells. The lateral margin is positive in section 2 (arrow). (B) There are two sections: section 1 is composed of leiomyoma and severe squamous cell dysplasia on the lateral portion (red arrow), and section 2 shows the positive lateral margin (H&E stain, ×12.5). (C) The positive margin can be seen when the black circle in Fig. 5B is magnified (H&E stain, ×100). (D) The specimen with the lesion is histologically diagnosed after resection as high-grade intraepithelial squamous neoplasia (H&E stain, ×40). (E) The esophageal leiomyoma is strongly and diffusely positive for smooth muscle actin (×40). (F) The esophageal leiomyoma is positive for desmin (×40).
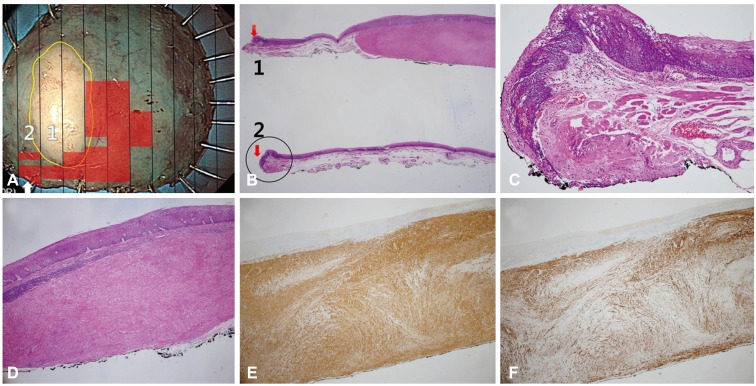
Fig. 5
(A) The endoscopic images show a subepithelial tumor with an eroded hyperemic lesion in the lower esophagus. (B) Lugol chromoendoscopy shows the iodine-unstained lesion. (C) Endoscopic ultrasonography demonstrates a hypoechoic, homogeneous lesion that originates from the muscularis mucosa and is covered by high-grade dysplasia. (D) The specimen with the lesion after en bloc resection.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download